Abstract
Objective
This study was performed to evaluate the effect of pregabalin co-administration with vitamin E in Partial Sciatic Nerve Ligation (PSNL)-induced neuropathic pain in rats.
Methods
Male Wistar rats were randomly allocated as control, sham, and PSNL groups (n = 8). PSNL was induced by tight ligation of the sciatic nerve with a copper wire. On day 14th, the PSNL and sham operated rats received either pregabalin (1, 3, and 30 mg/kg), vitamin E (100 and 200 mg/kg), or their combination intraperitoneally. An antinociceptive effect was evaluated as latency times and Maximum possible Effect Percent (%MPE) using tail-flick test. Locomotor activity was evaluated by open-field test before PSNL surgery and then twice at the 14th days (before and after drug injection). Ligated nerves were removed on the 28th days after surgery for histological examinations.
Results
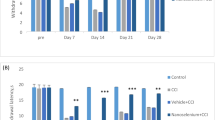
The time course of latency times and %MPE showed significant decrease in PSNL but not in sham and control groups. Pregabalin (3 and 30 mg/kg) and vitamin E (100 and 200 mg/kg) caused significant increases in latency time in PSNL (but not sham) group compared to control group. Vitamin E 200 mg/kg increased significantly %MPE in PSNL group compared to sham group. In addition, the %MPE following combination treatment of pregabalin (30 mg/kg) and vitamin E (100 mg/kg) was significantly higher than both vitamin E and control group. Also combination of pregabalin with 100 mg/kg of vitamin E reversed Wallerian degeneration of sciatic nerve and the inflammatory responses to almost similar to sham group. Pregabalin and vitamin E did not affect locomotor activity.
Conclusion
Our results showed antinociceptive effects of both vitamin E and pregabalin alone or in combination in PSNL rats and also neuroprotective properties without affecting locomotor activity.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afonseca SO et al (2013) Vitamin E for prevention of oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy: a pilot randomized clinical trial. Sao Paulo Med J 131:35–38
Atreya S (2016) Pregabalin in Chemotherapy Induced Neuropathic Pain. Indian J Palliat Care 22:101–103. doi:10.4103/0973-1075.173941
Attal N, Bouhassira D (2015) Pharmacotherapy of neuropathic pain: which drugs, which treatment algorithms? Pain 156(Suppl 1):S104–114. doi:10.1097/01.j.pain.0000460358.01998.15
Attal N, Cruccu G, Baron R, Haanpaa M, Hansson P, Jensen TS, Nurmikko T (2010) EFNS guidelines on the pharmacological treatment of neuropathic pain: 2010 revision. Eur J Neurol 17:1113–1188. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2010.02999.x
Bohlega S et al (2010) Guidelines for the pharmacological treatment of peripheral neuropathic pain: expert panel recommendations for the middle East region. J Int Med Res 38:295–317
Canos A, Cort L, Fernandez Y, Rovira V, Pallares J, Barbera M, Morales-Suarez-Varela M (2015) Preventive analgesia with pregabalin in neuropathic pain from “Failed Back Surgery Syndrome”: assessment of sleep quality and disability. Pain Med. doi:10.1111/pme.12895
Cardenas DD, Emir B, Parsons B (2015) Examining the time to therapeutic effect of pregabalin in spinal cord injury patients with neuropathic pain. Clin Ther 37:1081–1090. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2015.02.028
Carozzi V, Canta A, Chiorazzi A (2015) Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: what do we know about mechanisms? Neurosci Lett 596:90–107
Chaparro LE, Wiffen PJ, Moore RA, Gilron I (2012) Combination pharmacotherapy for the treatment of neuropathic pain in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 7:CD008943. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008943.pub2
Chudinova VV, Alekseev SM, Zakharova EI, Evstigneeva RP (1994) Lipid peroxidation and mechanism of antioxidant effect of vitamin E. Bioorg Khim 20:1029–1046
Dworkin RH et al (2010) Recommendations for the pharmacological management of neuropathic pain: an overview and literature update. Mayo Clin Proc 85:S3–14. doi:10.4065/mcp.2009.0649
Freynhagen R, Serpell M, Emir B, Whalen E, Parsons B, Clair A, Latymer M (2015) A comprehensive drug safety evaluation of pregabalin in peripheral neuropathic pain. Pain Pract 15:47–57. doi:10.1111/papr.12146
Gajraj NM (2005) Pregabalin for pain management. Pain Pract 5:95–102. doi:10.1111/j.1533-2500.2005.05205.x
Gajraj NM (2007) Pregabalin: its pharmacology and use in pain management. Anesth Analg 105:1805–1815
Guedes RP, Araujo AS, Janner D, Bello-Klein A, Ribeiro MF, Partata WA (2008) Increase in reactive oxygen species and activation of Akt signaling pathway in neuropathic pain. Cell Mol Neurobiol 28:1049–1056. doi:10.1007/s10571-008-9279-9
Ha KY, Carragee E, Cheng I, Kwon SE, Kim YH (2011) Pregabalin as a neuroprotector after spinal cord injury in rats: biochemical analysis and effect on glial cells. J Korean Med Sci 26:404–411. doi:10.3346/jkms.2011.26.3.404
Herrera E, Barbas C (2001) Vitamin E: action, metabolism and perspectives. J Physiol Biochem 57:43–56
Hoshida S, Hatano M, Furukawa M, Ito M (2009) Neuroprotective effects of vitamin E on adult rat motor neurones following facial nerve avulsion. Acta Otolaryngol 129:330–336. doi:10.1080/00016480802210431
Igarashi A et al (2015) Cost-effectiveness analysis of pregabalin for treatment of chronic low back pain in patients with accompanying lower limb pain (neuropathic component) in Japan. Clin Outcomes Res 7:505–520. doi:10.2147/CEOR.S89833
Jang Y, Song HK, Yeom MY, Jeong DC (2012) The immunomodulatory effect of pregabalin on spleen cells in neuropathic mice. Anesth Analg 115:830–836. doi:10.1213/ANE.0b013e31825d2ad1
Jiang Q, Yin X, Lill MA, Danielson ML, Freiser H, Huang J (2008) Long-chain carboxychromanols, metabolites of vitamin E, are potent inhibitors of cyclooxygenases. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105:20464–20469
Kalso E, Aldington DJ, Moore RA (2013) Drugs for neuropathic pain. BMJ 347:f7339
Kim HK, Park SK, Zhou JL, Taglialatela G, Chung K, Coggeshall RE, Chung JM (2004) Reactive oxygen species (ROS) play an important role in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Pain 111:116–124. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2004.06.008
Kim HK, Kim JH, Gao X, Zhou JL, Lee I, Chung K, Chung JM (2006) Analgesic effect of vitamin E is mediated by reducing central sensitization in neuropathic pain. Pain 122:53–62. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2006.01.013
Kim MJ, Hong BH, Zhang EJ, Ko YK, Lee WH (2012) Antinociceptive effects of intraperitoneal and intrathecal vitamin e in the rat formalin test Korean. J Pain 25:238–244. doi:10.3344/kjp.2012.25.4.238
Kottschade LA et al (2011) The use of vitamin E for the prevention of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: results of a randomized phase III clinical trial. Support Care Cancer 19:1769–1777
Kuhad A, Chopra K (2009) Tocotrienol attenuates oxidative-nitrosative stress and inflammatory cascade in experimental model of diabetic neuropathy. Neuropharmacology 57:456–462. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2009.06.013
La Porta C, Lara-Mayorga IM, Negrete R, Maldonado R (2016) Effects of pregabalin on the nociceptive, emotional and cognitive manifestations of neuropathic pain in mice. Eur J Pain. doi:10.1002/ejp.868
Li R, Shen L, Yu X, Ma C, Huang Y (2016) Vitamin C enhances the analgesic effect of gabapentin on rats with neuropathic pain. Life Sci 157:25–31. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2016.05.035
Mangaiarkkarasi A, Rameshkannan S, Ali RM (2015) Effect of gabapentin and pregabalin in rat model of taxol induced neuropathic pain. J Clin Diagn Res 9:FF11–14. doi:10.7860/JCDR/2015/13373.5955
Mao YF, Yan N, Xu H, Sun JH, Xiong YC, Deng XM (2009) Edaravone, a free radical scavenger, is effective on neuropathic pain in rats. Brain Res 1248:68–75. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2008.10.073
Mixcoatl-Zecuatl T et al (2008) Synergistic antiallodynic interaction between gabapentin or carbamazepine and either benfotiamine or cyanocobalamin in neuropathic rats. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 30:431–441. doi:10.1358/mf.2008.30.6.1232963
Morani AS, Bodhankar SL (2010a) Early co-administration of vitamin E acetate and methylcobalamin improves thermal hyperalgesia and motor nerve conduction velocity following sciatic nerve crush injury in rats. Pharmacol Rep 62:405–409
Morani AS, Bodhankar SL (2010b) Early co-administration of vitamin E acetate and methylcobalamin improves thermal hyperalgesia and motor nerve conduction velocity following sciatic nerve crush injury in rats. Pharmacol Rep 62:405–409
Nagkirshna L, Tamma N, Tadvi N, MabuShareef S (2013) Evaluation of protective of Vitamin-E on vincristine induced peripheral neuropathy in Albino Rats. J Eval Med Dent Sci 2:2538
O’Leary KA, Pascual-Tereasa Sd, Needs PW, Bao Y-P, O’Brien NM, Williamson G (2004) Effect of flavonoids and vitamin E on cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) transcription. Mutat Res Fundam Mol Mech Mutagen 551:245–254
O’Connor AB, Dworkin RH (2009) Treatment of neuropathic pain: an overview of recent guidelines. Am J Med 122:S22–32. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2009.04.007
Park ES, Gao X, Chung JM, Chung K (2006) Levels of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species increase in rat neuropathic spinal dorsal horn neurons. Neurosci Lett 391:108–111. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2005.08.055
Piccolo J, Kolesar JM (2014) Prevention and treatment of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Am J Health Syst Pharm 71:19–25
Rajanandh MG, Kosey S, Prathiksha G (2014) Assessment of antioxidant supplementation on the neuropathic pain score and quality of life in diabetic neuropathy patients—a randomized controlled study. Pharmacol Rep 66:44–48. doi:10.1016/j.pharep.2013.08.003
Rashedy AH, Solimany AA, Ismail AK, Wahdan MH, Saban KA (2013) Histopathological and functional effects of antimony on the renal cortex of growing albino rat Int J. Clin Exp Pathol 6:1467–1480
Reiter E, Jiang Q, Christen S (2007) Anti-inflammatory properties of α-and γ-tocopherol. Mol Asp Med 28:668–691
Reyes-Garcia G, Caram-Salas NL, Medina-Santillan R, Granados-Soto V (2004) Oral administration of B vitamins increases the antiallodynic effect of gabapentin in the rat. Proc West Pharmacol Soc 47:76–79
Riffel AP et al (2016) Systemic administration of vitamins C and E attenuates nociception induced by chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve in rats. Brain Res Bull 121:169–177. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2016.02.004
Romero-Sandoval A, Eisenach JC (2006) Perineural clonidine reduces mechanical hypersensitivity and cytokine production in established nerve injury. Anesthesiology 104:351–355
Siniscalco D et al (2007) Role of reactive oxygen species and spinal cord apoptotic genes in the development of neuropathic pain. Pharmacol Res 55:158–166
Tamaddonfard E et al (2014) Effects of safranal, a constituent of saffron, and vitamin E on nerve functions and histopathology following crush injury of sciatic nerve in rats. Phytomedicine 21:717–723
Taylor CP, Angelotti T, Fauman E (2007) Pharmacology and mechanism of action of pregabalin: the calcium channel alpha2-delta (alpha2-delta) subunit as a target for antiepileptic drug discovery. Epilepsy Res 73:137–150. doi:10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2006.09.008
Torrance N, Smith BH, Bennett MI, Lee AJ (2006) The epidemiology of chronic pain of predominantly neuropathic origin. Results from a general population survey. J Pain 7:281–289. doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2005.11.008
Treede RD et al (2008) Neuropathic pain: redefinition and a grading system for clinical and research purposes. Neurology 70:1630–1635. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000282763.29778.59
van Dam PS, Bravenboer B, van Asbeck BS, Marx JJ, Gispen WH (1999) High rat food vitamin E content improves nerve function in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Eur J Pharmacol 376:217–222. doi:10.1016/S0014-2999(99)00376-3
Verma V, Singh N, Singh Jaggi A (2014) Pregabalin in neuropathic pain: evidences and possible mechanisms. Curr Neuropharmacol 12:44–56. doi:10.2174/1570159X1201140117162802
Vorobeychik Y, Gordin V, Mao J, Chen L (2011) Combination therapy for neuropathic pain: a review of current evidence. CNS Drugs 25:1023–1034. doi:10.2165/11596280-000000000-00000
Wagner R, Heckman HM, Myers RR (1998) Wallerian degeneration and hyperalgesia after peripheral nerve injury are glutathione-dependent. Pain 77:173–179
Wang TX et al (2015) Antinociceptive and hypnotic activities of pregabalin in a neuropathic pain-like model in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 135:31–39. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2015.05.007
Wang RR et al (2016) Oral Administration of pregabalin in rats before or after nerve injury partially prevents spontaneous neuropathic pain and long outlasts the treatment period. Pharmacology 97:251–258. doi:10.1159/000444329
Wefers H, Sies H (1988) The protection by ascorbate and glutathione against microsomal lipid peroxidation is dependent on vitamin E. Eur J Biochem 174:353–357
Yowtak J, Lee KY, Kim HY, Wang J, Kim HK, Chung K, Chung JM (2011) Reactive oxygen species contribute to neuropathic pain by reducing spinal GABA release. Pain 152:844–852. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2010.12.034
Zin CS, Nissen LM, Smith MT, O’Callaghan JP, Moore BJ (2008) An update on the pharmacological management of post-herpetic neuralgia and painful diabetic neuropathy. CNS Drugs 22:417–442. doi:10.2165/00023210-200822050-00005
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meymandi, MS., Sepehri, G., Abdolsamadi, M. et al. The effects of co-administration of pregabalin and vitamin E on neuropathic pain induced by partial sciatic nerve ligation in male rats. Inflammopharmacol 25, 237–246 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-017-0325-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-017-0325-4