Abstract
Objective
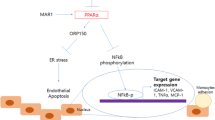
The role of inflammatory and endothelial dysfunction markers in the atherogenic process has been well recognized. The data have made both C-reactive protein (CRP) and von Willebrand factor (vWF) promising targets for the cardiovascular disease research and drug development. Inhibition of CRP and vWF synthesis, therefore, might be a potential therapeutic strategy.
Methods
The effect of sodium salicylate on vWF production by human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) using enzyme-linked immunosorbent Assays (ELISA) and real-time PCR was examined. In addition, small interfering RNA (siRNA) against NF-κB was used to investigate the existence of a role for this signaling pathway.
Results
Our findings demonstrated that sodium salicylate decreased vWF, but not CRP production at both mRNA and protein levels significantly and this might not occur via nuclear transcription factor (NF-κB) inhibition.
Conclusion
Our results indicated a further rationalization of the effects of sodium salicylate on atherothrombotic events by attenuation of vWF production.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bisoendial RJ, Kastelein JJ et al (2005) Activation of inflammation and coagulation after infusion of C-reactive protein in humans. Circ Res 96(7):714–716
Blann AD, Lip GY (2003) Effects of C-reactive protein on the release of von Willebrand factor, E-selectin, thrombomodulin and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 from human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 14(4):335–340
Burke AP, Tracy RP et al (2002) Elevated C-reactive protein values and atherosclerosis in sudden coronary death: association with different pathologies. Circulation 105(17):2019–2023
Dieset I, Hope S et al (2012) Cardiovascular risk factors during second generation antipsychotic treatment are associated with increased C-reactive protein. Schizophr Res 140(1–3):169–174
Jager A, van Hinsbergh VW et al (1999) von Willebrand factor, C-reactive protein, and 5-year mortality in diabetic and nondiabetic subjects: the Hoorn Study. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 19(12):3071–3078
Jankowska EA, von Haehling S et al (2005) Activation of the NF-kappaB system in peripheral blood leukocytes from patients with chronic heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail 7(6):984–990
Joglekar MV, Ware J et al (2013) Platelets, glycoprotein Ib-IX, and von Willebrand factor are required for FeCl(3)-induced occlusive thrombus formation in the inferior vena cava of mice. Platelets 24(3):205–212
Katerinaki E, Haycock JW et al (2006) Sodium salicylate inhibits TNF-alpha-induced NF-kappaB activation, cell migration, invasion and ICAM-1 expression in human melanoma cells. Melanoma Res 16(1):11–22
Kawanami D, Maemura K et al (2006) C-reactive protein induces VCAM-1 gene expression through NF-kappaB activation in vascular endothelial cells. Atheroscler. 185(1):39–46
Kiss K, Kiss J et al (2004) Sodium salicylate inhibits NF-kappaB and induces apoptosis in PC12 cells. J Biochem Biophys Methods 61(1–2):229–240
Kopp E, Ghosh S (1994) Inhibition of NF-kappa B by sodium salicylate and aspirin. Science 265(5174):956–959
Kramer F, Torzewski J et al (2008) Interleukin-1beta stimulates acute phase response and C-reactive protein synthesis by inducing an NFkappaB- and C/EBPbeta-dependent autocrine interleukin-6 loop. Mol Immunol 45(9):2678–2689
Nanchen D, Stott DJ et al (2013) Resting heart rate and incident heart failure and cardiovascular mortality in older adults: role of inflammation and endothelial dysfunction: the PROSPER study. Eur J Heart Fail 15(5):581–588
Palade GE (1953) An electron microscope study of the mitochondrial structure. J Histochem Cytochem 1(4):188–211
Paleolog EM, Crossman DC et al (1990) Differential regulation by cytokines of constitutive and stimulated secretion of von Willebrand factor from endothelial cells. Blood 75(3):688–695
Sanders YV, Eikenboom J et al (2013) Reduced prevalence of arterial thrombosis in von Willebrand disease. J Thromb Haemost 11(5):845–854
Shahani T, Lavend’homme R et al (2010) Activation of human endothelial cells from specific vascular beds induces the release of a FVIII storage pool. Blood 115(23):4902–4909
Sporn LA, Marder VJ et al (1989) Differing polarity of the constitutive and regulated secretory pathways for von Willebrand factor in endothelial cells. J Cell Biol 108(4):1283–1289
Tiong WN, Sim EU et al (2013) Early detection of C-reactive protein and von Willebrand factor levels in Malaysian patients with acute coronary syndrome. J Cardiovasc Dis Res 4(1):3–6
Venugopal SK, Devaraj S et al (2005) Macrophage conditioned medium induces the expression of C-reactive protein in human aortic endothelial cells: potential for paracrine/autocrine effects. Am J Pathol 166(4):1265–1271
Westein E, van der Meer AD et al (2013) Atherosclerotic geometries exacerbate pathological thrombus formation poststenosis in a von Willebrand factor-dependent manner. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110(4):1357–1362
Willeit P, Thompson A et al (2013) Hemostatic factors and risk of coronary heart disease in general populations: new prospective study and updated meta-analyses. PLoS One 8(2):e55175
Wiman B, Andersson T et al (2000) Plasma levels of tissue plasminogen activator/plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 complex and von Willebrand factor are significant risk markers for recurrent myocardial infarction in the Stockholm Heart Epidemiology Program (SHEEP) study. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20(8):2019–2023
Wynants M, Quarck R et al (2012) Effects of C-reactive protein on human pulmonary vascular cells in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Eur Respir J 40(4):886–894
Wynants M, Vengethasamy L et al (2013) NF-kappaB pathway is involved in CRP-induced effects on pulmonary arterial endothelial cells in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 305(12):L934–L942
Xu XM, Sansores-Garcia L et al (1999) Suppression of inducible cyclooxygenase 2 gene transcription by aspirin and sodium salicylate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96(9):5292–5297
Yasojima K, Schwab C et al (2001) Generation of C-reactive protein and complement components in atherosclerotic plaques. Am J Pathol 158(3):1039–1051
Yin MJ, Yamamoto Y et al (1998) The anti-inflammatory agents aspirin and salicylate inhibit the activity of I(kappa)B kinase-beta. Nature 396(6706):77–80
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Research and Enterprise Committee and the Faculty of Allied Health of Iran University of Medical Science and Health Services for ‘seed funding’ for this project.
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interests that could be perceived as influencing the impartiality of the research reported.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shahidi, M., Barati, M., Hayat, P. et al. The in vitro effects of sodium salicylate on von Willebrand factor and C-reactive protein production by endothelial cells. Inflammopharmacol 22, 367–372 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-014-0212-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-014-0212-1