Abstract
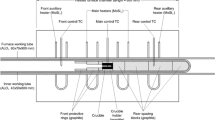
A new laser-based technique to examine heat transfer and energetics of phase transitions in metal–carbon fixed points and potentially to improve the quality of phase transitions in furnaces with poor uniformity is reported. Being reproducible below 0.1 K, metal–carbon fixed points are increasingly used as reference standards for the calibration of thermocouples and radiation thermometers. At NMIA, the Co–C eutectic point is used for the calibration of thermocouples, with the fixed point traceable to the International Temperature Scale (ITS-90) using radiation thermometry. For thermocouple use, these cells are deep inside a high-uniformity furnace, easily obtaining excellent melting plateaus. However, when used with radiation thermometers, the essential large viewing cone to the crucible restricts the furnace depth and introduces large heat losses from the front furnace zone, affecting the quality of the phase transition. Short \(\hbox {CO}_{2}\) laser bursts have been used to illuminate the cavity of a conventional Co–C fixed-point cell during various points in its melting phase transition. The laser is employed to partially melt the metal at the rear of the crucible providing a liquid–solid interface close to the region being observed by the reference pyrometer. As the laser power is known, a quantitative estimate of \((166 \pm 30) \hbox { J}{\cdot }\hbox {g}^{-1}\) can be made for the Co–C latent heat of fusion. Using a single laser pulse during a furnace-induced melt, a plateau up to 8 min is observed before the crucible resumes a characteristic conventional melt curve. Although this plateau is satisfyingly flat, well within 100 mK, it is observed that the plateau is laser energy dependent and elevates from the conventional melt “inflection-point” value.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.J. Ballico, Y. Yamada, in Proceedings of the 3rd Biennial Conference MSA 99 (Metrology Society of Australia, Victoria Australia, 1999), pp. 21–25
F. Jahan, M.J. Ballico, in Proceedings of Ninth International Temperature Symposium (Los Angeles), Temperature: Its Measurement and Control, in Science and Industry, ed. by C.W. Meyer, AIP Conference Proceedings 1552, vol. 8, (AIP, Melville, NY, 2013), pp. 346–351
K. Anhalt, R.D. Taubert, G. Machin, E. Woolliams, M.R. Dury, H. Yoon, M. Sadli, S. Briaudeau, B. Khlevnoy, M.J. Ballico, F. Jahan, A. Todd, D. Woods, Presented at 9th International Temperature Symposium, Temperature: Its Measurement and Control in Science and Industry (Los Angeles, 2012)
M.J. Ballico, F. Jahan, NMIA Measurements of the Thermodynamic Temperature of Metal–Carbon Eutectic Cell, for CCT-WG5 Work-Package 4, NMIA Technical Report TR16, July 2011
Bureau International des Poids et Mesures (BIPM), Supplementary Information for the International Temperature Scale of 1990 (BIPM, Sevres Cedex, France, 1997), pp. 95–96. http://www.bipm.org/utils/common/pdf/ITS-90/ITS-90-Techniques-for-Approximating.pdf. Accessed 16 March 2015
M.J. Ballico, in Proceedings of TEMPMEKO 2004, 9th International Symposium on Temperature and Thermal Measurements, in Industry and Science, ed. by D. Zvizdić, L.G. Bermanec, T. Veliki, T. Stašić (FSB/LPM, Zagreb, Croatia, 2004), pp. 841–846
K. Chahine, M.J. Ballico, J. Reizes, J. Madadnia, in Proceedings of the Metrology Society of Australia MSA 2005 (Metrology Society of Australia, Victoria, Australia, 2005), pp. 163–168
K. Chahine, M.J. Ballico, J. Reizes, J. Madadnia, Int. J. Thermophys. 29, 386 (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van der Ham, E., Ballico, M. & Jahan, F. Laser-Induced Melting of Co-C Eutectic Cells as a New Research Tool. Int J Thermophys 36, 1848–1858 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-015-1894-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-015-1894-3