Abstract
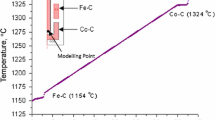
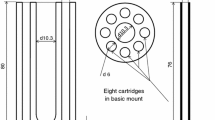
In the framework of the European Metrology Research Project ENG08 “MetroFission,” LNE-Cnam and NPL have undertaken cooperative research into the development of temperature measurement solutions for the next generation of nuclear fission power plants. Currently, in-pile temperature monitoring is usually performed with nickel-based (Type K or N) thermocouples. When these thermocouples are exposed to a neutron flux, the thermoelements transmute, leading to large and unknown drifts in output. In addition, it is impossible to routinely recalibrate the thermocouples after irradiation for obvious reasons of safety. To alleviate this problem, both LNE-Cnam and NPL have developed, via differing approaches, in situ calibration methods for the thermocouples. The self-validating thermocouple methodologies are based on the principle of a miniature fixed-point cell to be co-located with the thermocouple measurement junction in use. The drift of the thermocouple can be monitored and corrected for by regular determination of the output at the phase transition of the fixed-point material: in effect performing regular in situ calibration checks. The two institutes have constructed miniature fixed-point cells for use at three different temperatures; the freezing point of silver \((961.78\,^{\circ }\mathrm{C}\); LNE-Cnam), the freezing point of copper \((1084.62\,^{\circ }\mathrm{C}\); LNE-Cnam and NPL), and the melting point of Fe–C (\({\sim }1154\,^{\circ }\mathrm{C}\); NPL). This paper introduces the construction and validation of the miniature fixed-point cells prior to use, to ensure traceability to the ITS-90. A comparison of the performance of the two cell designs is discussed, where typical industrial Type N thermocouples have been used for measurement of the fixed-point cells. Such initial measurements demonstrate the feasibility of each of these two approaches.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Preston-Thomas, Metrologia 36, 3 (1990)
F. Edler, R. Morice, H. Ogura, J.V. Pearce, Metrologia 48, 90 (2010)
J.V. Pearce, F. Edler, C.J. Elliott, G. Failleau, R. Morice, H. Ogura, Metrologia 48, 375 (2010)
The MetroFission Project, http://projects.npl.co.uk/metrofission/
M. Sadli, D. del Campo, M. de Podesta, T. Deuzé, G. Failleau, C.J. Elliott, S. Fourrez, C. Garcia, J.V. Pearce, in Proceedings of Ninth International Temperature Symposium, Los Angeles, Temperature: Its Measurement and Control in Science and Industry, vol. 8, ed. by C.W. Meyer, A.I.P. Proceedings 1552 (AIP, Melville, NY, 2013), pp. 1003–1008
C.J. Elliott, J.V. Pearce, G. Failleau, T. Deuzé, S. Briaudeau, M. Sadli, G. Machin, Metrologia 49, 88 (2012)
C.J. Elliott, G. Failleau, J.V. Pearce, T. Deuze, M. Sadli, G. Machin, Int. J. Thermophys. (submitted)
Normalisation Française, Métrologie et applications de la statistique, FD X07-021, ISSN 0335-3931 (1999)
O. Ongrai, J.V. Pearce, G. Machin, S.J. Sweeney, Meas. Sci. Technol. 22, 015104 (2011)
D.H. Lowe, G. Machin, Metrologia 49, 189 (2012)
Acknowledgments
This work was completed in the framework of the European Metrology Research Programme (EMRP) ENG08 “MetroFission” project. The EMRP is jointly funded by the EMRP participating countries within EURAMET and the European Union. GF gratefully acknowledges R. Morice for numerous valuable discussions and for sharing ideas about thermocouple self-validation methods developed at LNE-Cnam.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Failleau, G., Elliott, C.J., Deuzé, T. et al. Miniature Fixed-Point Cell Approaches for \({{\varvec{In\,Situ}}}\) Monitoring of Thermocouple Stability. Int J Thermophys 35, 1223–1238 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-014-1667-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-014-1667-4