Abstract
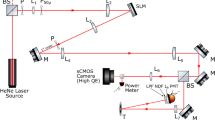
We investigate a single-pixel camera (SPC) that relies on non-mechanical scanning with a terahertz (THz) spatial light modulator (SLM) and Compressed Sensing (CS) for image generation. The camera is based on a 350 GHz multiplier source and a Golay cell detector. The SLM consists of a Germanium disc, which is illuminated by a halogen lamp. The light of the lamp is transmitted through a thin-film transistor (TFT) liquid crystal display (LCD). This enables the generation of light patterns on the Germanium disc, which in turn produce reflecting patterns for THz radiation. Using up to 1000 different patterns the pseudo-inverse reconstruction algorithm and the CS algorithm CoSaMP are evaluated with respect to image quality. It is shown that CS allows a reduction of the necessary measurements by a factor of three without compromising the image quality.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Heinz, T. May, D. Born, G. Zieger, K. Peiselt, A. Brömel, S. Anders, V. Zakosarenko, T. Krause, A. Krüger, M. Schulz, and H.-G. Meyer, “Development of passive submillimeter-wave video imaging systems,” in SPIE Defense, Security, and Sensing: SPIE, 2013, pp. 87150E.
Jinshan Ding, M. Kahl, O. Loffeld, and P. H. Bolivar, “THz 3-D Image Formation Using SAR Techniques: Simulation, Processing and Experimental Results,” IEEE Trans. THz Sci. Technol, vol. 3, no. 5, pp. 606–616, 2013.
A. Luukanen, T. Kiuru, M. M. Leivo, A. Rautiainen, and J. Varis, “Passive three-colour submillimetre-wave video camera,” in SPIE Defense, Security, and Sensing: SPIE, 2013, pp. 87150F.
S. S. Ahmed, A. Schiessl, and L.-P. Schmidt, “A Novel Fully Electronic Active Real-Time Imager Based on a Planar Multistatic Sparse Array,” IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Techn, vol. 59, no. 12, pp. 3567–3576, 2011.
S. Augustin and H.-W. Hübers, “Phase-Sensitive Passive Terahertz Imaging at 5-m Stand-Off Distance,” IEEE Trans. THz Sci. Technol, vol. 4, no. 4, pp. 418–424, 2014.
N. Rothbart, H. Richter, M. Wienold, L. Schrottke, H. T. Grahn, and H.-W. Hübers, “Fast 2-D and 3-D Terahertz Imaging With a Quantum-Cascade Laser and a Scanning Mirror,” IEEE Trans. THz Sci. Technol, vol. 3, no. 5, pp. 617–624, 2013.
I. Amenabar, F. Lopez, and A. Mendikute, “In Introductory Review to THz Non-Destructive Testing of Composite Mater,” J Infrared Milli Terahz Waves, vol. 34, no. 2, pp. 152–169, 2013.
C. S. Joseph, A. N. Yaroslavsky, V. A. Neel, T. M. Goyette, and R. H. Giles, “Continuous wave terahertz transmission imaging of nonmelanoma skin cancers,” Lasers Surg. Med, vol. 43, no. 6, pp. 457–462, 2011.
F. C. De Lucia, “The submillimeter: A spectroscopist’s view,” Journal of Molecular Spectroscopy, vol. 261, no. 1, pp. 1–17, 2010.
I. R. Medvedev, C. F. Neese, G. M. Plummer, and F. C. De Lucia, “Submillimeter spectroscopy for chemical analysis with absolute specificity,” Opt. Lett, vol. 35, no. 10, p. 1533, 2010.
J. C. Pearson, B. J. Drouin, A. Maestrini, I. Mehdi, J. Ward, R. H. Lin, S. Yu, J. J. Gill, B. Thomas, C. Lee, G. Chattopadhyay, E. Schlecht, F. W. Maiwald, P. F. Goldsmith, and P. Siegel, “Demonstration of a room temperature 2.48–2.75 THz coherent spectroscopy source,” Rev. Sci. Instrum, vol. 82, no. 9, p. 93105, 2011.
R. Eichholz, H. Richter, S. G. Pavlov, M. Wienold, L. Schrottke, R. Hey, H. T. Grahn, and H.-W. Hübers, “Multi-channel terahertz grating spectrometer with quantum-cascade laser and microbolometer array,” Appl. Phys. Lett, vol. 99, no. 14, p. 141112, 2011.
H.-W. Hübers, R. Eichholz, S. G. Pavlov, and H. Richter, “High Resolution Terahertz Spectroscopy with Quantum Cascade Lasers,” J Infrared Milli Terahz Waves, vol. 34, no. 5-6, pp. 325–341, 2013.
F. Ospald, W. Zouaghi, R. Beigang, C. Matheis, J. Jonuscheit, B. Recur, J.-P. Guillet, P. Mounaix, W. Vleugels, P. V. Bosom, L. V. González, I. López, R. M. Edo, Y. Sternberg, and M. Vandewal, “Aeronautics composite material inspection with a terahertz time-domain spectroscopy system,” Opt. Eng, vol. 53, no. 3, p. 31208, 2014.
N. Karpowicz, H. Zhong, C. Zhang, K.-I. Lin, J.-S. Hwang, J. Xu, and X.-C. Zhang, “Compact continuous-wave subterahertz system for inspection applications,” Appl. Phys. Lett, vol. 86, no. 5, p. 54105, 2005.
K. Kawase, Y. Ogawa, Y. Watanabe, and H. Inoue, “Non-destructive terahertz imaging of illicit drugs using spectral fingerprints,” Opt. Express, vol. 11, no. 20, p. 2549, 2003.
Y. C. Shen, L. Gan, M. Stringer, A. Burnett, K. Tych, H. Shen, J. E. Cunningham, Parrott, E. P. J, J. A. Zeitler, L. F. Gladden, E. H. Linfield, and A. G. Davies, “Terahertz pulsed spectroscopic imaging using optimized binary masks,” Appl. Phys. Lett, vol. 95, no. 23, p. 231112, 2009.
D. J. Benford, S. H. Moseley, G. J. Stacey, R. A. Shafer, J. G. Staguhn, R. K. Melugin, and H.-P. Roeser, “Far-infrared imaging spectroscopy with SAFIRE on SOFIA,” in SPIE Astronomical Telescopes and Instrumentation: SPIE, 2003, pp. 105–114.
TeraSense. Available: http://terasense.com/.
F. Schuster, D. Coquillat, H. Videlier, M. Sakowicz, F. Teppe, L. Dussopt, B. Giffard, T. Skotnicki, and W. Knap, “Broadband terahertz imaging with highly sensitive silicon CMOS detectors,” Opt. Express, vol. 19, no. 8, p. 7827, 2011.
N. Oda, T. Ishi, T. Morimoto, T. Sudou, H. Tabata, S. Kawabe, K. Fukuda, A. W. M. Lee, and Q. Hu, “Real-time transmission-type terahertz microscope with palm size terahertz camera and compact quantum cascade laser,” in SPIE Terahertz Emitters, Receivers, and Applications III: SPIE, 2012, pp. 84960Q.
Infrared Laboratories. Available: http://www.infraredlaboratories.com/Bolometers.shtml.
A. L. Woodcraft, M. I. Hollister, D. Bintley, M. A. Ellis, X. Gao, W. S. Holland, M. J. MacIntosh, P. A. R. Ade, J. S. House, C. L. Hunt, R. V. Sudiwala, W. D. Duncan, G. C. Hilton, K. D. Irwin, C. D. Reintsema, C. C. Dunare, W. Parkes, A. J. Walton, J. B. Kycia, M. Amiri, B. Burger, M. Halpern, J. Zmuidzinas, and S. Withington, “Characterization of a prototype SCUBA-2 1280-pixel submillimetre superconducting bolometer array,” in SPIE Astronomical Telescopes and Instrumentation: SPIE, 2006, pp. 62751F.
M. F. Duarte, M. A. Davenport, D. Takhar, J. N. Laska, Ting Sun, K. F. Kelly, and R. G. Baraniuk, “Single-Pixel Imaging via Compressive Sampling,” IEEE Signal Process. Mag, vol. 25, no. 2, pp. 83–91, 2008.
W. L. Chan, K. Charan, D. Takhar, K. F. Kelly, R. G. Baraniuk, and D. M. Mittleman, “A single-pixel terahertz imaging system based on compressed sensing,” Appl. Phys. Lett, vol. 93, no. 12, p. 121105, 2008.
S. Busch, B. Scherger, M. Scheller, and M. Koch, “Optically controlled terahertz beam steering and imaging,” Opt. Lett, vol. 37, no. 8, pp. 1391–1393, 2012.
D. Shrekenhamer, C. M. Watts, and W. J. Padilla, “Terahertz single pixel imaging with an optically controlled dynamic spatial light modulator,” Opt. Express, vol. 21, no. 10, pp. 12507–12518, 2013.
L.-J. Cheng and L. Liu, “Optical modulation of continuous terahertz waves towards cost-effective reconfigurable quasi-optical terahertz components,” Opt. Express, vol. 21, no. 23, pp. 28657–28667, 2013.
C. M. Watts, D. Shrekenhamer, J. Montoya, G. Lipworth, J. Hunt, T. Sleasman, S. Krishna, D. R. Smith, and W. J. Padilla, “Terahertz compressive imaging with metamaterial spatial light modulators,” Nature Photon, vol. 8, no. 8, pp. 605–609, 2014.
M. A. Herman and T. Strohmer, “General Deviants: An Analysis of Perturbations in Compressed Sensing,” Selected Topics in Signal Processing, IEEE Journal, vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 342–349, 2010.
Y. Chi, L. L. Scharf, A. Pezeshki, and A. R. Calderbank, “Sensitivity to Basis Mismatch in Compressed Sensing,” IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 59, no. 5, pp. 2182–2195, 2011.
P. Jung and P. Walk, “Sparse Model Uncertainties in Compressed Sensing with Application to Convolutions and Sporadic Communication,” to appear in Compressed Sensing and its Applications, H. Boche, R. Calderbank, G. Kutyniok, and J. Vybiral, Eds.: Springer, 2014, pp. 1–29.
E. J. Candès and T. Tao, “Decoding by Linear Programming,” IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory, vol. 51, no. 12, pp. 4203–4215, 2005.
E. J. Candès, “The restricted isometry property and its implications for compressed sensing,” Compte Rendus de l’Academie des Sciences, vol. 346, no. 9, pp. 589–592, 2008.
T. T. Cai and A. Zhang, “Sharp RIP bound for sparse signal and low-rank matrix recovery,” Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis, vol. 35, no. 1, pp. 74–93, 2013.
E. J. Candès, Y. C. Eldar, D. Needell, and P. Randall, “Compressed sensing with coherent and redundant dictionaries,” Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis, vol. 31, no. 1, pp. 59–73, 2010.
D. Needell and J. A. Tropp, “CoSaMP: Iterative signal recovery from incomplete and inaccurate samples,” Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis, vol. 26, no. 3, pp. 301–321, 2009.
M. Elad, Sparse and redundant representations: From theory to applications in signal and image processing. New York: Springer, 2010.
U. Nakarmi and N. Rahnavard, “BCS: Compressive sensing for binary sparse signals,” in IEEE Military Communications Conference, 2012 - MILCOM 2012, 2012, pp. 1–5.
Z. He, T. Ogawa, and M. Haseyama, “The simplest measurement matrix for compressed sensing of natural images,” in Image Processing (ICIP), 2010 17th IEEE International Conference on, 2010, pp. 4301–4304.
Acknowledgements
The research presented here was partly funded by the European Metrology Research Program (EMRP – Project NEW07 Microwave and terahertz metrology for homeland security). The EMRP is jointly funded by the EMRP participating countries within EURAMET and the European Union.
S. Augustin and J. Hieronymus gratefully acknowledge support by the Helmholtz Research School on Security Technologies (HRSST).
All authors are grateful to Alessandro Maturilli for conducting the spectrometer measurements presented in Fig. 2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Augustin, S., Hieronymus, J., Jung, P. et al. Compressed Sensing in a Fully Non-Mechanical 350 GHz Imaging Setting. J Infrared Milli Terahz Waves 36, 496–512 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10762-014-0141-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10762-014-0141-5