Abstract
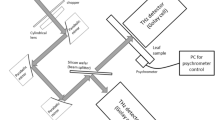
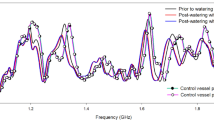
We demonstrate a method for non-destructive and contactless measurements of the water content of plants, e.g. agricultural crops. The measurement is based on the absorption of microwave radiation at 35 GHz inside the plant and additionally takes scattering on the surface of the plant into account.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. T. Furbank, M. Tester, “Phenomics – technologies to relieve the phenotyping bottleneck”, Trends in Plant Science, 16, p. 635-544 (2011)
K. Y. Chuah and T. W. Lau, “Dielectric constants of rubber and palm leaf samples at X-band”, IEEE Trans. on Geoscience Remote Sensing, 33(1), p.221-223 (1995).
C. Mätzler, „Microwave (1-100 GHz) dielectric model of leaves“, IEEE Trans. Geoscience Remote Sensing, 32(5), p. 947-949 (1994).
J. C. Calvet, et al., “Plant water content and temperature of the Amazon forest from satellite microwave radiometry”, IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 32(2), p. 397-408 (1994)
P. Ferrazzoli and L. Guerriero, „Passive microwave remote sensing of forests: a model investigation“, IEEE Geoscience Trans. Remote Sensing, 34(2), p. 433-443 (2002)
E. R. Hunt, Jr. et al., “Comparison of vegetation water contents derived from shortwave-infrared and passive-microwave sensors over central Iowa”, Remote Sensing of Environment, 115(9), p. 2376-2383, (2011)
G. Macelloni et al., “Microwave radiometric measurements of soil moisture in Italy”, Hydrology and Earth Syst. Science, 7(6), p. 937-948 (2003).
D. Sancho-Knapik et al., „Microwave l-band (1730 MHz) accurately estimates the relative water content in poplar leaves. A comparison with a near infrared water index (R1300/R1450)“, Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 151(7), p. 827-832 (2011)
D. M. Mittleman, R. H. Jacobsen, M. C. Nuss, “T-ray imaging”,Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, IEEE Journal of, 2, p. 679-692 (1996)
C. Jördens, M. Scheller, B. Breitenstein, D. Selmar, M. Koch, “Evaluation of leaf water status by means of permittivity at terahertz frequencies”, Journal of Biological Physics, Springer Netherlands, 35, p. 255-264 (2009)
E. Castro-Camus, M. Palomar, A. Covarrubias, “Leaf water dynamics of Arabidopsis thaliana monitored in-vivo using terahertz time-domain spectroscopy”, Scientific reports, Nature Publishing Group, 3, p. 1-5 (2013)
N. Born, D. Behringer, S. Liepelt, S. Beyer, M. Schwerdtfeger, B. Ziegenhagen, M. Koch, “Monitoring plant drought stress response using terahertz time-domain spectroscopy”, Plant physiology, 164(4), p. 1571-1577 (2014)
R. Gente, N. Born, N. Voß, W. Sannemann, J. Léon, M. Koch, E. Castro-Camus, “Determination of Leaf Water Content from Terahertz Time-Domain Spectroscopic Data” Journal of Infrared, Millimeter, and Terahertz Waves, 34, p. 316-323 (2013)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gente, R., Rehn, A. & Koch, M. Contactless Water Status Measurements on Plants at 35 GHz. J Infrared Milli Terahz Waves 36, 312–317 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10762-014-0127-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10762-014-0127-3