Abstract
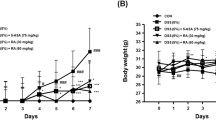
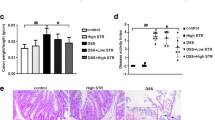
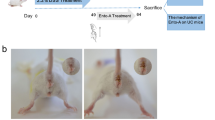
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) has received much attention due to its increasing worldwide incidence and potential increased risk of colorectal cancer. The protective function of a Rho-associated protein kinase inhibitor (Y-27632) against 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS) induced mouse colitis has been proven in previous studies, but the concrete therapeutic mechanism of Y-27632 is still not completely illuminated. This current research is intended for further investigation of the effect and mechanism of Y-27632 in a mouse model of acute experimental ulcerative colitis induced by dextran sulfate sodium (DSS). A total of 24 male BALB/c mice were randomly separated into the following three groups (n = 8 per group) and injected intraperitoneally with the corresponding reagents for 7 days: control group (PBS), DSS group (PBS), and Y-27632 group (PBS and Y-27632; 10 mg/kg). Our data indicated that Y-27632 could significantly improve the severity of colitis, as evidenced by the disease activity index (DAI) scores, histological damage, and colon length. Additionally, Y-27632 treatment significantly decreased CD68 and proinflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-17F (IL-17F), and interleukin-6 (IL-6). Furthermore, Y-27632 potently and pleiotropically suppressed nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and signal transduction and transcriptional activator 3 (STAT3) activation as well as the activity of prosurvival genes that are dependent on these transcription factors. In summary, the study demonstrates that Y-27632 exerts ameliorative effects on colonic inflammation mediated through dual inhibition of the NF-κB and IL-6/STAT3 pathways and thus is likely to function as a prospective novel treatment for human ulcerative colitis (UC).







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ma, X., Y. Hu, X. Li, X. Zheng, Y. Wang, J. Zhang, C. Fu, and F. Geng. 2018. Periplaneta americana ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in rats by Keap1/Nrf-2 activation, intestinal barrier function, and gut microbiota regulation. Frontiers in Pharmacology 9: 944. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00944.
Ananthakrishnan, A.N., H. Khalili, G.G. Konijeti, L.M. Higuchi, P. de Silva, C.S. Fuchs, W.C. Willett, J.M. Richter, and A.T. Chan. 2014. Long-term intake of dietary fat and risk of ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Gut 63 (5): 776–784. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2013-305304.
Targan, S.R., and L.C. Karp. 2005. Defects in mucosal immunity leading to ulcerative colitis. Immunological Reviews 206: 296–305. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0105-2896.2005.00286.x.
Moura, F.A., K.Q. de Andrade, J.C.F. Dos Santos, O.R.P. Araújo, and M.O.F. Goulart. 2015. Antioxidant therapy for treatment of inflammatory bowel disease: does it work? Redox Biology 6: 617–639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2015.10.006.
Damião, Aomc, M.F.C. de Azevedo, A.S. Carlos, M.Y. Wada, T.V.M. Silva, and F.C. Feitosa. 2019. Conventional therapy for moderate to severe inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic literature review. World Journal of Gastroenterology 25 (9): 1142–1157. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i9.1142.
Zhang, M., Y. Zhao, N. Wu, Y. Yao, M. Xu, H. Du, and Y. Tu. 2018. The anti-inflammatory activity of peptides from simulated gastrointestinal digestion of preserved egg white in DSS-induced mouse colitis. Food & Function 9 (12): 6444–6454. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8fo01939h.
Funakoshi, T., K. Yamashita, N. Ichikawa, M. Fukai, T. Suzuki, R. Goto, T. Oura, N. Kobayashi, T. Katsurada, S. Ichihara, M. Ozaki, K. Umezawa, and S. Todo. 2012. A novel NF-kappaB inhibitor, dehydroxymethylepoxyquinomicin, ameliorates inflammatory colonic injury in mice. Journal of Crohn's & Colitis 6 (2): 215–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crohns.2011.08.011.
Zhang, H., Y. Dai, Y. Liu, T. Wu, J. Li, X. Wang, and W. Wang. 2018. Helicobacter pylori colonization protects against chronic experimental colitis by regulating Th17/Treg balance. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases 24 (7): 1481–1492. https://doi.org/10.1093/ibd/izy107.
Guan, Q., and J. Zhang. 2017. Recent advances: the imbalance of cytokines in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Mediators of Inflammation 2017: 4810258. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4810258.
Neurath, M.F. 2014. Cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease. Nature Reviews. Immunology 14 (5): 329–342. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3661.
Xi, M., X. Wang, J. Ge, and D. Yin. 2016. N′-[3-[benzyloxy]benzylidene]-3,4,5-trihydroxybenzohydrazide (1) protects mice against colitis induced by dextran sulfate sodium through inhibiting NF-κB/IL-6/STAT3 pathway. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 477 (2): 290–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.06.059.
Medicherla, K., B.D. Sahu, M. Kuncha, J.M. Kumar, G. Sudhakar, and R. Sistla. 2015. Oral administration of geraniol ameliorates acute experimental murine colitis by inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokines and NF-κB signaling. Food & Function 6 (9): 2984–2995. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5fo00405e.
Khan, H., A. Sureda, T. Belwal, S. Cetinkaya, I. Suntar, S. Tejada, H.P. Devkota, H. Ullah, and M. Aschner. 2019. Polyphenols in the treatment of autoimmune diseases. Autoimmunity Reviews 18 (7): 647–657. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2019.05.001.
Park, M.H., and J.T. Hong. 2016. Roles of NF-kappaB in cancer and inflammatory diseases and their therapeutic approaches. Cells 5 (2). https://doi.org/10.3390/cells5020015.
Wu, H., H. Fan, Z. Shou, M. Xu, Q. Chen, C. Ai, Y. Dong, Y. Liu, Z. Nan, Y. Wang, T. Yu, and X. Liu. 2019. Extracellular vesicles containing miR-146a attenuate experimental colitis by targeting TRAF6 and IRAK1. International Immunopharmacology 68: 204–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2018.12.043.
Wang, H., J. Gu, X. Hou, J. Chen, N. Yang, Y. Liu, G. Wang, M. du, H. Qiu, Y. Luo, Z. Jiang, and L. Feng. 2017. Anti-inflammatory effect of miltirone on inflammatory bowel disease via TLR4/NF-κB/IQGAP2 signaling pathway. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 85: 531–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2016.11.061.
Pandurangan, A.K., S. Ismail, Z. Saadatdoust, and N.M. Esa. 2015. Allicin alleviates dextran sodium sulfate- (DSS-) induced ulcerative colitis in BALB/c mice. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity 2015: 605208. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/605208.
Akanda, M.R., H.H. Nam, W. Tian, A. Islam, B.K. Choo, and B.Y. Park. 2018. Regulation of JAK2/STAT3 and NF-kappaB signal transduction pathways; Veronica polita alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced murine colitis. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 100: 296–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.01.168.
Atreya, R., and M.F. Neurath. 2008. Signaling molecules: the pathogenic role of the IL-6/STAT-3 trans signaling pathway in intestinal inflammation and in colonic cancer. Current Drug Targets 9 (5): 369–374. https://doi.org/10.2174/138945008784221116.
Li, Z.W., B. Sun, T. Gong, S. Guo, J. Zhang, J. Wang, A. Sugawara, et al. 2019. GNAI1 and GNAI3 reduce colitis-associated tumorigenesis in mice by blocking IL6 signaling and down-regulating expression of GNAI2. Gastroenterology 156 (8): 2297–2312. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2019.02.040.
Liu, Y., J. Zhao, Y. Zhao, S. Zong, Y. Tian, S. Chen, M. Li, H. Liu, Q. Zhang, X. Jing, B. Sun, H. Wang, T. Sun, and C. Yang. 2019. Therapeutic effects of lentinan on inflammatory bowel disease and colitis-associated cancer. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine 23 (2): 750–760. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.13897.
Domokos, D., E. Ducza, and R. Gaspar. 2019. RhoA and rho-kinase inhibitors modulate cervical resistance: the possible role of RhoA/rho-kinase signalling pathway in cervical ripening and contractility. European Journal of Pharmacology 843: 27–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.11.017.
Yang, W., G. Zhou, T. Yu, L. Chen, L. Yu, Y. Guo, Y. Cong, and Z. Liu. 2018. Critical role of ROCK2 activity in facilitating mucosal CD4(+) T cell activation in inflammatory bowel disease. Journal of Autoimmunity 89: 125–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2017.12.009.
Wang, Y., Y. Lu, J. Chai, M. Sun, X. Hu, W. He, M. Ge, and C. Xie. 2017. Y-27632, a rho-associated protein kinase inhibitor, inhibits systemic lupus erythematosus. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 88: 359–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.01.069.
Rozo, C., Y. Chinenov, R.K. Maharaj, S. Gupta, L. Leuenberger, K.A. Kirou, V.P. Bykerk, S.M. Goodman, J.E. Salmon, and A.B. Pernis. 2017. Targeting the RhoA-ROCK pathway to reverse T-cell dysfunction in SLE. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 76 (4): 740–747. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209850.
Zou, Y., L. Ma, Y. Zhao, S. Zhang, C. Zhou, and Y. Cai. 2018. Inhibition of rho kinase protects against colitis in mice by attenuating intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction via MLC and the NF-κB pathway. International Journal of Molecular Medicine 41 (1): 430–438. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2017.3197.
Wang, Y., Z. Shou, H. Fan, M. Xu, Q. Chen, Q. Tang, X. Liu, H. Wu, M. Zhang, T. Yu, S. Deng, and Y. Liu. 2019. Protective effects of oxymatrine against DSS-induced acute intestinal inflammation in mice via blocking the RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway. Bioscience Reports 39 (7). https://doi.org/10.1042/bsr20182297.
Shi, L., Y. Dai, B. Jia, Y. Han, Y. Guo, T. Xie, J. Liu, X. Tan, P. Ding, and J. Li. 2019. The inhibitory effects of Qingchang Wenzhong granule on the interactive network of inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in rats with dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry 120 (6): 9979–9991. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.28280.
Liu, D., X. Huo, L. Gao, J. Zhang, H. Ni, and L. Cao. 2018. NF-kappaB and Nrf2 pathways contribute to the protective effect of Licochalcone a on dextran sulphate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in mice. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 102: 922–929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.03.130.
Jin, B.R., K.S. Chung, S.Y. Cheon, M. Lee, S. Hwang, S. Noh Hwang, K.J. Rhee, and H.J. An. 2017. Rosmarinic acid suppresses colonic inflammation in dextran sulphate sodium (DSS)-induced mice via dual inhibition of NF-kappaB and STAT3 activation. Scientific Reports 7: 46252. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep46252.
Chen, T., N. Shi, and A. Afzali. 2019. Chemopreventive effects of strawberry and black raspberry on colorectal cancer in inflammatory bowel disease. Nutrients 11 (6). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11061261.
Tao, J.H., J.A. Duan, W. Zhang, S. Jiang, J.M. Guo, and D.D. Wei. 2018. Polysaccharides from Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat ameliorate colitis rats via regulation of the metabolic profiling and NF-kappa B/TLR4 and IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathways. Frontiers in Pharmacology 9: 746. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00746.
Pandurangan, A.K., N. Mohebali, N.M. Esa, C.Y. Looi, S. Ismail, and Z. Saadatdoust. 2015. Gallic acid suppresses inflammation in dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis in mice: possible mechanisms. International Immunopharmacology 28 (2): 1034–1043. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2015.08.019.
Funding
The study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 81774093 and no. 81573784).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study concept and design: Yifan Wang, Meng Xu, and Qianyun Chen; data acquisition: Yifan Wang and Yujin Liu; Yifan Wang and Yujin Liu performed most of the experiments; Yifan Wang, Xueyun Duan, Qing Tang, Xingxing Liu, and Heng Fan wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Duan, X., Liu, X. et al. Rho kinase Blockade Ameliorates DSS-Induced Ulcerative Colitis in Mice Through Dual Inhibition of the NF-κB and IL-6/STAT3 Pathways. Inflammation 43, 857–867 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-019-01171-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-019-01171-2