Abstract
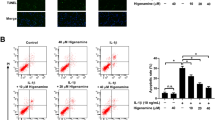
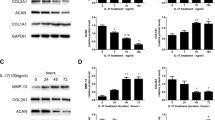
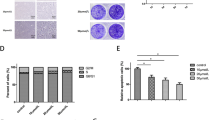
Statins are widely used hypocholesterolemic drugs that block the mevalonate pathway. Some studies have shown that statins may have the potential to inhibit intervertebral disk (IVD) degeneration (IDD). Interleukin (IL)-1β, a catabolic cytokine, is a key regulator of IDD. This study aimed to investigate the mechanism underlying the effect of simvastatin on IDD. The viability of nucleus pulposus (NP) cells was determined by the methyl-thiazolyl-tetrazolium (MTT) assay. The apoptosis of NP cells was measured by flow cytometric analysis, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL), and western blotting of relevant apoptotic proteins. The protein levels of catabolic factors and anabolic factors were determined by western blotting. The cells were stimulated with IL-1β in the absence or presence of simvastatin to investigate the effects on matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-3, MMP-13, a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs (ADAMTS)-4, ADAMTS-5, type II collagen, and aggrecan expression. Our findings indicate that simvastatin considerably inhibited IL-1β-induced apoptosis in NP cells. We also found that simvastatin attenuated IL-1β-induced expression and MMP-3, MMP-13, ADAMTS-4, and ADAMTS-5 activities and also reduced the decrease in type II collagen and aggrecan expression. In addition, simvastatin considerably suppressed the nuclear translocation and activation of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-KB) by inhibiting p65 phosphorylation and translocation and blocking inhibitor kB-α degradation. It also inhibited MAPK pathway activation by blocking c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), p38, and ERK phosphorylation. The results of our study revealed that simvastatin is a potential agent for IDD prevention and treatment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li, D., B. Zhu, L. Ding, W. Lu, G. Xu, and J. Wu. 2014. Role of the mitochondrial pathway in serum deprivation-induced apoptosis of rat endplate cells. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 452: 354–360.
Kellgren, J.H. 1977. The anatomical source of back pain. Rheumatology and Rehabilitation 16: 3–12.
Anderson, J.A., E.O. Otun, and B.J. Sweetman. 1987. Occupational hazards and low back pain. Reviews on Environmental Health 7: 121–160.
Walker, B.F., R. Muller, and W.D. Grant. 2003. Low back pain in Australian adults: the economic burden. Asia-Pacific Journal of Public Health 15: 79–87.
Luoma, K., H. Riihimaki, R. Luukkonen, R. Raininko, E. Viikari-Juntura, and A. Lamminen. 2000. Low back pain in relation to lumbar disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 25: 487–492.
Antoniou, J., T. Steffen, F. Nelson, N. Winterbottom, A.P. Hollander, R.A. Poole, M. Aebi, and M. Alini. 1996. The human lumbar intervertebral disc: evidence for changes in the biosynthesis and denaturation of the extracellular matrix with growth, maturation, ageing, and degeneration. Journal of Clinical Investigation 98: 996–1003.
Tiaden, A.N., M. Klawitter, V. Lux, A. Mirsaidi, G. Bahrenberg, S. Glanz, L. Quero, T. Liebscher, K. Wuertz, M. Ehrmann, and P.J. Richards. 2012. Detrimental role for human high temperature requirement serine protease A1 (HTRA1) in the pathogenesis of intervertebral disc (IVD) degeneration. Journal of Biological Chemistry 287: 21335–21345.
Boos, N., S. Weissbach, H. Rohrbach, C. Weiler, K.F. Spratt, and A.G. Nerlich. 2002. Classification of age-related changes in lumbar intervertebral discs: 2002 Volvo award in basic science. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 27: 2631–2644.
Vo, N.V., R.A. Hartman, T. Yurube, L.J. Jacobs, G.A. Sowa, and J.D. Kang. 2013. Expression and regulation of metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in intervertebral disc aging and degeneration. The Spine Journal: Official Journal of the North American Spine Society 13: 331–341.
Roberts, S., B. Caterson, J. Menage, E.H. Evans, D.C. Jaffray, and S.M. Eisenstein. 2000. Matrix metalloproteinases and aggrecanase: their role in disorders of the human intervertebral disc. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 25: 3005–3013.
Bachmeier, B.E., A. Nerlich, N. Mittermaier, C. Weiler, C. Lumenta, K. Wuertz, and N. Boos. 2009. Matrix metalloproteinase expression levels suggest distinct enzyme roles during lumbar disc herniation and degeneration. European Spine Journal 18: 1573–1586.
Lee, S., C.S. Moon, D. Sul, J. Lee, M. Bae, Y. Hong, M. Lee, S. Choi, R. Derby, B.J. Kim, J. Kim, J.S. Yoon, L. Wolfer, J. Kim, J. Wang, S.W. Hwang, and S.H. Lee. 2009. Comparison of growth factor and cytokine expression in patients with degenerated disc disease and herniated nucleus pulposus. Clinical Biochemistry 42: 1504–1511.
Le Maitre, C.L., A.J. Freemont, and J.A. Hoyland. 2005. The role of interleukin-1 in the pathogenesis of human intervertebral disc degeneration. Arthritis Research and Therapy 7: R732–745.
Millward-Sadler, S.J., P.W. Costello, A.J. Freemont, and J.A. Hoyland. 2009. Regulation of catabolic gene expression in normal and degenerate human intervertebral disc cells: implications for the pathogenesis of intervertebral disc degeneration. Arthritis Research and Therapy 11: R65.
Endo, A. 1992. The discovery and development of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Journal of Lipid Research 33: 1569–1582.
Thanusubramanian, H., M.K. Kishore, R. Shetty, and M.B. Amberkar. 2016. A Retrospective study of the treatment outcome of drug therapies used in heart failure patients with associated co-morbidities in a tertiary care hospital. Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research 10: Fc06–09.
Bellosta, S., D. Via, M. Canavesi, P. Pfister, R. Fumagalli, R. Paoletti, and F. Bernini. 1998. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors reduce MMP-9 secretion by macrophages. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 18: 1671–1678.
Luan, Z., A.J. Chase, and A.C. Newby. 2003. Statins inhibit secretion of metalloproteinases-1, -2, -3, and -9 from vascular smooth muscle cells and macrophages. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 23: 769–775.
Thunyakitpisal, P.D., and R. Chaisuparat. 2004. Simvastatin, an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, reduced the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (Gelatinase B) in osteoblastic cells and HT1080 fibrosarcoma cells. Journal of Pharmacological Sciences 94: 403–409.
Hatano, H., A. Maruo, M.E. Bolander, and G. Sarkar. 2003. Statin stimulates bone morphogenetic protein-2, aggrecan, and type 2 collagen gene expression and proteoglycan synthesis in rat chondrocytes. Journal of Orthopaedic Science 8: 842–848.
Yudoh, K., and R. Karasawa. 2010. Statin prevents chondrocyte aging and degeneration of articular cartilage in osteoarthritis (OA). Aging (Albany NY) 2: 990–998.
Zhang, H., and C.Y. Lin. 2008. Simvastatin stimulates chondrogenic phenotype of intervertebral disc cells partially through BMP-2 pathway. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 33: E525–531.
Than, K.D., S.U. Rahman, L. Wang, A. Khan, K.A. Kyere, T.T. Than, Y. Miyata, Y.S. Park, F. La Marca, H.M. Kim, H. Zhang, P. Park, and C.Y. Lin. 2014. Intradiscal injection of simvastatin results in radiologic, histologic, and genetic evidence of disc regeneration in a rat model of degenerative disc disease. The Spine Journal 14: 1017–1028.
Hu, M.H., K.C. Yang, Y.J. Chen, Y.H. Sun, and S.H. Yang. 2014. Lovastatin prevents discography-associated degeneration and maintains the functional morphology of intervertebral discs. The Spine Journal 14: 2459–2466.
Zhang, H., L. Wang, J.B. Park, P. Park, V.C. Yang, S.J. Hollister, F. La Marca, and C.Y. Lin. 2009. Intradiscal injection of simvastatin retards progression of intervertebral disc degeneration induced by stab injury. Arthritis Research and Therapy 11: R172.
Hu, M.H., L.W. Hung, S.H. Yang, Y.H. Sun, T.T. Shih, and F.H. Lin. 2011. Lovastatin promotes redifferentiation of human nucleus pulposus cells during expansion in monolayer culture. Artificial Organs 35: 411–416.
Zhongyi, S., Z. Sai, L. Chao, and T. Jiwei. 2015. Effects of nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathway in human intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 40: 224–232.
Tian, Y., W. Yuan, N. Fujita, J. Wang, H. Wang, I.M. Shapiro, and M.V. Risbud. 2013. Inflammatory cytokines associated with degenerative disc disease control aggrecanase-1 (ADAMTS-4) expression in nucleus pulposus cells through MAPK and NF-κB. The American Journal of Pathology 182: 2310–2321.
Sun, Z., Z. Yin, C. Liu, H. Liang, M. Jiang, and J. Tian. 2015. IL-1β promotes ADAMTS enzyme-mediated aggrecan degradation through NF-κB in human intervertebral disc. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research 10: 159.
Mengshol, J.A., M.P. Vincenti, C.I. Coon, A. Barchowsky, and C.E. Brinckerhoff. 2000. Interleukin-1 induction of collagenase 3 (matrix metalloproteinase 13) gene expression in chondrocytes requires p38, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and nuclear factor kappaB: differential regulation of collagenase 1 and collagenase 3. Arthritis and Rheumatism 43: 801–811.
Chang, C.H., Y.M. Hsu, Y.C. Chen, F.H. Lin, S. Sadhasivam, S.T. Loo, and S. Savitha. 2014. Anti-inflammatory effects of hydrophilic and lipophilic statins with hyaluronic acid against LPS-induced inflammation in porcine articular chondrocytes. Journal of Orthopaedic Research 32: 557–565.
Wuertz, K., N. Vo, D. Kletsas, and N. Boos. 2012. Inflammatory and catabolic signalling in intervertebral discs: the roles of NF-kappaB and MAP kinases. European Cells & Materials 23: 103–119. discussion 119–120.
Yang, W., X.H. Yu, C. Wang, W.S. He, S.J. Zhang, Y.G. Yan, J. Zhang, Y.X. Xiang, and W.J. Wang. 2015. Interleukin-1beta in intervertebral disk degeneration. Clinica Chimica Acta 450: 262–272.
Le Maitre, C.L., A. Pockert, D.J. Buttle, A.J. Freemont, and J.A. Hoyland. 2007. Matrix synthesis and degradation in human intervertebral disc degeneration. Biochemical Society Transactions 35: 652–655.
Vo, N.V., R.A. Hartman, T. Yurube, L.J. Jacobs, G.A. Sowa, and J.D. Kang. 2013. Expression and regulation of metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in intervertebral disc aging and degeneration. The Spine Journal 13: 331–341.
Wu, X., W. Liu, Z. Duan, Y. Gao, S. Li, K. Wang, Y. Song, Z. Shao, S. Yang, and C. Yang. 2016. The involvement of protease nexin-1 (PN1) in the pathogenesis of intervertebral disc (IVD) degeneration. Science Reports 6: 30563.
Corsini, A., S. Bellosta, R. Baetta, R. Fumagalli, R. Paoletti, and F. Bernini. 1999. New insights into the pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties of statins. Pharmacology & Therapeutics 84: 413–428.
Zhang, C.C., J.S. Zhou, J.G. Hu, X. Wang, X.S. Zhou, B.A. Sun, C. Shao, and Q. Lin. 2013. Effects of IGF-1 on IL-1beta-induced apoptosis in rabbit nucleus pulposus cells in vitro. Molecular Medicine Reports 7: 441–444.
Nguyen, K.C., W.G. Willmore, and A.F. Tayabali. 2013. Cadmium telluride quantum dots cause oxidative stress leading to extrinsic and intrinsic apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells. Toxicology 306: 114–123.
Gruber, H.E., and E.N. Hanley Jr. 1998. Analysis of aging and degeneration of the human intervertebral disc. Comparison of surgical specimens with normal controls. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 23: 751–757.
Yang, J., X. Liu, K. Bhalla, C.N. Kim, A.M. Ibrado, J. Cai, T.I. Peng, D.P. Jones, and X. Wang. 1997. Prevention of apoptosis by Bcl-2: release of cytochrome c from mitochondria blocked. Science 275: 1129–1132.
Sudo, H., and A. Minami. 2011. Caspase 3 as a therapeutic target for regulation of intervertebral disc degeneration in rabbits. Arthritis and Rheumatism 63: 1648–1657.
Sudo, H., and A. Minami. 2010. Regulation of apoptosis in nucleus pulposus cells by optimized exogenous Bcl-2 overexpression. Journal of Orthopaedic Research 28: 1608–1613.
Studer, R.K., A.M. Aboka, L.G. Gilbertson, H. Georgescu, G. Sowa, N. Vo, and J.D. Kang. 2007. p38 MAPK inhibition in nucleus pulposus cells: a potential target for treating intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 32: 2827–2833.
Chen, Y.J., K.S. Tsai, D.C. Chan, K.C. Lan, C.F. Chen, R.S. Yang, and S.H. Liu. 2014. Honokiol, a low molecular weight natural product, prevents inflammatory response and cartilage matrix degradation in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Journal of Orthopaedic Research 32: 573–580.
Yao, Z., Nie, L., Zhao, Y., Zhang, Y., Liu, Y., Li, J., and L. Cheng. 2016. Salubrinal suppresses IL-17-induced upregulation of MMP-13 and extracellular matrix degradation through the NF-kB pathway in human nucleus pulposus cells, inflammation.
Ghosh, S., and D. Baltimore. 1990. Activation in vitro of NF-kappa B by phosphorylation of its inhibitor I kappa B. Nature 344: 678–682.
Kong, D., T. Zheng, M. Zhang, D. Wang, S. Du, X. Li, J. Fang, and X. Cao. 2013. Static mechanical stress induces apoptosis in rat endplate chondrocytes through MAPK and mitochondria-dependent caspase activation signaling pathways. PLoS One 8: e69403.
Kim, J.H., R.K. Studer, N.V. Vo, G.A. Sowa, and J.D. Kang. 2009. p38 MAPK inhibition selectively mitigates inflammatory mediators and VEGF production in AF cells co-cultured with activated macrophage-like THP-1 cells. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 17: 1662–1669.
Seguin, C.A., M. Bojarski, R.M. Pilliar, P.J. Roughley, and R.A. Kandel. 2006. Differential regulation of matrix degrading enzymes in a TNFalpha-induced model of nucleus pulposus tissue degeneration. Matrix Biology 25: 409–418.
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers, 81072187, 81541056).
Author Contributions
J.T. designed the study and drafted the manuscript. W.L. participated in designing the study and carried the molecular mechanism studies and immunoassays. Y.Z. and X.W. revised the manuscript. Y.S., L.K., W.L., and K.W. participated in collecting clinical samples. S.L. and W.H. did the statistical analysis. C.Y. conceived the study and helped revise the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(GIF 29 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tu, J., Li, W., Zhang, Y. et al. Simvastatin Inhibits IL-1β-Induced Apoptosis and Extracellular Matrix Degradation by Suppressing the NF-kB and MAPK Pathways in Nucleus Pulposus Cells. Inflammation 40, 725–734 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-017-0516-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-017-0516-6