Abstract
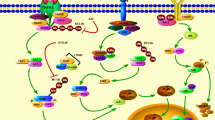
Matrix metalloproteinase 13 (MMP-13) plays an important role in the process of pro-inflammatory cytokine-induced intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD). This study examined the effect of IL-17 on the regulation of MMP-13 and the extracellular matrix (ECM) in the intervertebral disc (IVD). We then examined whether salubrinal, a known inhibitor of eIF2α dephosphorylation, inhibited the IL-17-induced changes mentioned above. Furthermore, we demonstrated a potential therapeutic role for salubrinal in alleviating the chronic inflammatory-dependent degenerative state commonly observed in IDD. After inflammatory distress with IL-17, RT-PCR and western blot were employed to investigate the expression of MMP-13, collagen type II (COL2A1), collagen type I (COL1A1), and aggrecan (ACAN) in nucleus pulpous (NP) tissue. Activation of the NF-kB pathway was measured by western blot and immunocytochemistry following IL-17 treatment. We also examine the level of eIF2α phosphorylation after IL-17 treatment with or without salubrinal. Then, we investigated interactions of the NF-kB pathway to eIF2α phosphorylation. Moreover, we employed salubrinal and a specific inhibitor of NF-kB (BAY11-7082) to evaluate their effects on IL-17-driven regulation of MMP-13 and the ECM, as well as on the activation of NF-kB. The results showed that IL-17 increased the production of MMP-13 and decreased expression of COL2A1 and ACAN via the NF-kB pathway. Either IL-17 or salubrinal increased the level of eIF2α phosphorylation, but the effects of BAY11-7082 on the level of p-eIF2α were not detectable. BAY11-7082 and salubrinal significantly suppressed IL-17-driven intervertebral disc degeneration. Furthermore, salubrinal produced stronger effects than BAY11-7082. These results imply the potential involvement of IL-17 in IDD through activation of NF-kB signaling, which successively upregulated the expression of MMP-13 and led to the degradation of the ECM. Furthermore, salubrinal can inhibit this process through inhibition of NF-kB activation that is not directly linked to eIF2α phosphorylation, suggesting a potential therapeutic role in IDD.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aigner, Thomas, Pia Margarethe Gebhard, Erik Schmid, Brigitte Bau, Vincent Harley, and Ernst Pöschl. 2003. SOX9 expression does not correlate with type II collagen expression in adult articular chondrocytes. Matrix Biology 22(4): 363–372. doi:10.1016/s0945-053x(03)00049-0.
Boos, Norbert, Sabine Weissbach, Helmut Rohrbach, Christoph Weiler, Kevin F. Spratt, and Andreas G. Nerlich. 2002. Classification of age-related changes in lumbar intervertebral discs: 2002 Volvo Award in basic science. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 27(23): 2631–2644.
Cnop, M., L. Ladriere, P. Hekerman, F. Ortis, A.K. Cardozo, Z. Dogusan, D. Flamez, M. Boyce, J. Yuan, and D.L. Eizirik. 2007. Selective inhibition of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 alpha dephosphorylation potentiates fatty acid-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and causes pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction and apoptosis. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 282(6): 3989–3997. doi:10.1074/jbc.M607627200.
Fujita, N., S.S. Gogate, K. Chiba, Y. Toyama, I.M. Shapiro, and M.V. Risbud. 2012. Prolyl hydroxylase 3 (PHD3) modulates catabolic effects of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) on cells of the nucleus pulposus through co-activation of nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB)/p65 signaling. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 287(47): 39942–39953. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.375964.
Gong, N., J.H. Wu, Z.S. Liang, W.H. Jiang, and X.W. Wang. 2015. Role of salubrinal in protecting cardiomyocytes from doxorubicin-induced apoptosis. Genetics and Molecular Research 14(4): 12377–12385. doi:10.4238/2015.October.16.4.
Hamamura, K., A. Nishimura, T. Iino, S. Takigawa, A. Sudo, and H. Yokota. 2015. Chondroprotective effects of salubrinal in a mouse model of osteoarthritis. Bone and Joint Research 4(5): 84–92.
Hamamura, K., C.C. Lin, and H. Yokota. 2013. Salubrinal reduces expression and activity of MMP13 in chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 21(5): 764–772. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2013.02.657.
Hamamura, K., A. Nishimura, A. Chen, S. Takigawa, A. Sudo, and H. Yokota. 2015. Salubrinal acts as a Dusp2 inhibitor and suppresses inflammation in anti-collagen antibody-induced arthritis. Cellular Signalling 27(4): 828–835. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2015.01.010.
Hamamura, K., N. Tanjung, and H. Yokota. 2013. Suppression of osteoclastogenesis through phosphorylation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 alpha. Journal of Bone and Mineral Metabolism 31(6): 618–628. doi:10.1007/s00774-013-0450-0.
He, L., J. Lee, J.H. Jang, K. Sakchaisri, J. Hwang, H.J. Cha-Molstad, K.A. Kim, et al. 2013. Osteoporosis regulation by salubrinal through eIF2alpha mediated differentiation of osteoclast and osteoblast. Cellular Signalling 25(2): 552–560. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2012.11.015.
Hotamisligil, G.S. 2010. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the inflammatory basis of metabolic disease. Cell 140(6): 900–917. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.02.034.
Krupkova, O., M. Sekiguchi, J. Klasen, O. Hausmann, S. Konno, S.J. Ferguson, and K. Wuertz-Kozak. 2014. Epigallocatechin 3-gallate suppresses interleukin-1β-induced inflammatory responses in intervertebral disc cells in vitro and reduces radiculopathic pain in rats. European Cells and Materials 28(2): 31.
Le Maitre, C.L., A.J. Freemont, and J.A. Hoyland. 2005. The role of interleukin-1 in the pathogenesis of human intervertebral disc degeneration. Arthritis Research & Therapy 7(4): R732–745. doi:10.1186/ar1732.
Lee, S.I., K.L. Kang, S.I. Shin, Y. Herr, Y.M. Lee, and E.C. Kim. 2012. Endoplasmic reticulum stress modulates nicotine-induced extracellular matrix degradation in human periodontal ligament cells. Journal of Periodontal Research 47(3): 299–308. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0765.2011.01432.x.
Matsuoka, M., and Y. Komoike. 2015. Experimental evidence shows salubrinal, an eIF2alpha dephosphorylation inhibitor, reduces xenotoxicant-induced cellular damage. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16(7): 16275–16287. doi:10.3390/ijms160716275.
Mitchell, P.G., H.A. Magna, L.M. Reeves, L.L. Lopresti-Morrow, S.A. Yocum, P.J. Rosner, K.F. Geoghegan, and J.E. Hambor. 1996. Cloning, expression, and type II collagenolytic activity of matrix metalloproteinase-13 from human osteoarthritic cartilage. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 97(3): 761–768. doi:10.1172/JCI118475.
Moran, E.M., R. Mullan, J. McCormick, M. Connolly, O. Sullivan, O. Fitzgerald, B. Bresnihan, D.J. Veale, and U. Fearon. 2009. Human rheumatoid arthritis tissue production of IL-17A drives matrix and cartilage degradation: synergy with tumour necrosis factor-alpha, Oncostatin M and response to biologic therapies. Arthritis Research & Therapy 11(4): R113. doi:10.1186/ar2772.
Mwale, F., P. Roughley, and J. Antoniou. 2004. Distinction between the extracellular matrix of the nucleus pulposus and hyaline cartilage: a requisite for tissue engineering of intervertebral disc. European Cells & Materials 8(58): 63–64.
Nakajima, S., Y. Chi, K. Gao, K. Kono, and J. Yao. 2015. eIF2alpha-Independent inhibition of TNF-alpha-triggered NF-kappaB activation by salubrinal. Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin 38(9): 1368–1374. doi:10.1248/bpb.b15-00312.
Pfirrmann, Christian W.A., Alexander Metzdorf, Marco Zanetti, Juerg Hodler, and Norbert Boos. 2001. Magnetic resonance classification of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 26(17): 1873–1878.
Roberts, Sally, Bruce Caterson, Menage Janis, E. Helena Evans, David C. Jaffray, and Stephen M. Eisenstein. 2000. Matrix metalloproteinases and aggrecanase: their role in disorders of the human intervertebral disc. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 25(23): 3005–3013.
Séguin, Cheryle A., Robert M. Pilliar, Peter J. Roughley, and Rita A. Kandel. 2005. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha modulates matrix production and catabolism in nucleus pulposus tissue. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 30(17): 1940–1948.
Sato, A.Y., X. Tu, K.A. McAndrews, L.I. Plotkin, and T. Bellido. 2015. Prevention of glucocorticoid induced-apoptosis of osteoblasts and osteocytes by protecting against endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress in vitro and in vivo in female mice. Bone 73: 60–68. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2014.12.012.
Shiomi, T., V. Lemaitre, J. D’Armiento, and Y. Okada. 2010. Matrix metalloproteinases, a disintegrin and metalloproteinases, and a disintegrin and metalloproteinases with thrombospondin motifs in non-neoplastic diseases. Pathology International 60(7): 477–496. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1827.2010.02547.x.
Tanigawa, S., Y. Aida, T. Kawato, K. Honda, G. Nakayama, M. Motohashi, N. Suzuki, K. Ochiai, H. Matsumura, and M. Maeno. 2011. Interleukin-17F affects cartilage matrix turnover by increasing the expression of collagenases and stromelysin-1 and by decreasing the expression of their inhibitors and extracellular matrix components in chondrocytes. Cytokine 56(2): 376–386. doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2011.08.015.
Wang, S.S., W. Zhang, Y.Q. Zhang, Y. Zhao, Y. Liu, J.K. Li, H.X. Zhang, L. Cheng, and L. Nie. 2015. IL-17A enhances ADAMTS-7 expression through regulation of TNF-alpha in human nucleus pulposus cells. Journal of Molecular Histology 46(6): 475–483. doi:10.1007/s10735-015-9640-5.
Wang, Z., W.C. Hutton, and S.T. Yoon. 2014. Bone morphogenetic protein-7 antagonizes tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced activation of nuclear factor kappaB and up-regulation of the ADAMTS, leading to decreased degradation of disc matrix macromolecules aggrecan and collagen II. The Spine Journal 14(3): 505–512. doi:10.1016/j.spinee.2013.08.016.
Xu, W., Q. Wan, S. Na, H. Yokota, J.L. Yan, and K. Hamamura. 2015. Suppressed invasive and migratory behaviors of SW1353 chondrosarcoma cells through the regulation of Src, Rac1 GTPase, and MMP13. Cellular Signalling 27(12): 2332–2342. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2015.08.014.
Yang, Xiangli, Koichi Matsuda, Peter Bialek, Sylvie Jacquot, Howard C. Masuoka, Schinke Thorsten, Li Lingzhen, Brancorsini Stefano, Sassone-Corsi Paolo, and Tim M. Townes. 2004. ATF4 is a substrate of RSK2 and an essential regulator of osteoblast biology: implication for Coffin-Lowry syndrome. Cell 117(3): 387–398.
Zhang, P., K. Hamamura, C. Jiang, L. Zhao, and H. Yokota. 2012. Salubrinal promotes healing of surgical wounds in rat femurs. Journal of Bone and Mineral Metabolism 30(5): 568–579. doi:10.1007/s00774-012-0359-z.
Zhang, W., L. Nie, Y. Wang, X.P. Wang, H. Zhao, S. Dongol, S. Maharjan, and L. Cheng. 2013. CCL20 secretion from the nucleus pulposus improves the recruitment of CCR6-expressing Th17 cells to degenerated IVD tissues. PloS One 8(6): e66286. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0066286.
Zhongyi, S., Z. Sai, L. Chao, and T. Jiwei. 2015. Effects of nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathway in human intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 40(4): 224–232. doi:10.1097/BRS.0000000000000733.
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by grants from the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2013HM095) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81572191, 81501880).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 618 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, Z., Nie, L., Zhao, Y. et al. Salubrinal Suppresses IL-17-Induced Upregulation of MMP-13 and Extracellular Matrix Degradation Through the NF-kB Pathway in Human Nucleus Pulposus Cells. Inflammation 39, 1997–2007 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-016-0435-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-016-0435-y