Abstract
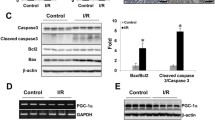
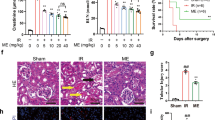
We examine whether BML-111, a lipoxin receptor agonist, inhibits renal ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury, and whether peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α (PPARα) or heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) is involved in protective effects of BML-111 on kidney against I/R injury. Rats subjected to renal I/R injury were treated with or without BML-111. Renal histological and immunohistochemical studies were performed. Expressions of phosphorylated p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (pp38 MAPK), phosphorylated PPARα (pPPARα), and HO-1 were assessed in NRK-52E cells exposed to BML-111. The binding activity of PPARα to peroxisome proliferator-responsive element (PPRE) on HO-1 promoter in the cells was determined. BML-111 treatment resulted in a marked reduction in the severity of histological features of renal I/R injury, and attenuated the rise in renal myeloperoxidase and malondialdehyde, blood urea nitrogen and creatinine, urinary N-acetyl-β-glucosaminidase, and leucine aminopeptidase levels caused by I/R injury. BML-111 stimulated the renal expressions of pPPARα and HO-1, and cellular messenger RNA (mRNA) and protein expressions of pPPARα and HO-1 which were both blocked by GW6471, a selective PPARα antagonist, and ZnPP-IX, a specific inhibitor of HO-1 pretreatment. The pp38 MAPK inhibitor SB203580 blocked the BML-111-induced expressions of pp38 MAPK, pPPARα, and HO-1 in NRK-52E cells. The binding activity of PPARα to PPRE in nuclear extracts of NRK-52E cells was enhanced by treatment of the cells with BML-111, and was suppressed by GW6471 and SB203580. BML-111 protects the kidney against I/R injury via activation of p38 MAPK/PPARα/HO-1 pathway.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wen, X., R. Murugan, Z. Peng, and J.A. Kellum. 2010. Pathophysiology of acute kidney injury: a new perspective. Contributions to Nephrology 165: 39–45.
Eltzschig, H.K., and T. Eckle. 2011. Ischemia and reperfusion-from mechanism to translation. Nature Medicine 17: 1391–1401.
Chok, M.K., S. Ferlicot, M. Conti, A. Almolki, A. Dürrbach, S. Loric, et al. 2009. Renoprotective potency of heme oxygenase-1 induction in rat renal ischemia-reperfusion. Inflammation & Allergy Drug Targets 8: 252–259.
Nath, K.A. 2006. Heme oxygenase-1: a provenance for cytoprotective pathways in the kidney and other tissues. Kidney International 70: 432–443.
Li Volti, G., V. Sorrenti, P. Murabito, F. Galvano, M. Veroux, A. Gullo, et al. 2007. Pharmacological induction of heme oxygenase-1 inhibits iNOS and oxidative stress in renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Transplantation Proceedings 39: 2986–2991.
Patel, N.S.A., R. di Paola, E. Mazzon, D. Britti, C. Thiemermann, and S. Cuzzocrea. 2008. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α contributes to the resolution of inflammation after renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 328: 635–643.
Miglio, G., A.C. Rosa, L. Rattazzi, C. Grange, M. Collino, G. Camussi, et al. 2011. The subtypes of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors expressed by human podocytes and their role in decreasing podocyte injury. British Journal of Pharmacology 162: 111–125.
Cheng, C.F., W.S. Lian, S.H. Chen, P.F. Lai, H.F. Li, Y.F. Lan, et al. 2012. Protective effects of adiponectin against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury via prostacyclin-PPARα-heme oxygenase-1 signaling pathway. Journal of Cellular Physiology 227: 239–249.
Li, S., K.K. Nagothu, V. Desai, T. Lee, W. Branham, C. Molan, et al. 2009. Transgenic expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α in mice confers protection during acute kidney injury. Kidney International 76: 1049–1062.
Chen, H.H., T.W. Chen, and H. Lin. 2009. Prostacycin-induced peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α translocation attenuates NF-κB and TNF-α activation after renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. American Journal of Physiology. Renal Physiology 297: F1109–F1118.
Chen, H.H., T.W. Chen, and H. Lin. 2010. Pravastatin attenuates carboplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rodents via peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α-regulated heme oxygenase-1. Molecular Pharmacology 78: 36–45.
Serhan, C.N. 2014. Novel pro-resolving lipid mediators in inflammation are leads for resolution physiologyas. Nature 510: 92–101.
Serhan, C.N., and N. Chiang. 2008. Endogenous pro-resolving and anti-inflammatory lipid mediators: a new pharmacologic genus. British Journal of Pharmacology 153: S200–S215.
Nascimento-Silva, V., M.A. Arruda, C. Barja-Fidalgo, and I.M. Fierro. 2007. Aspirin-triggered lipoxin A4 blocks reactive oxygen species generation in endothelial cells: a novel antioxidative mechanism. Thrombosis and Haemostasis 97: 88–98.
Leonard, M.O., K. Nannan, M.J. Burne, D.W.P. Lappin, P. Doran, P. Coleman, et al. 2002. 15-epi-15-(para-fluorophenoxy)- lipoxin A4-methyl ester, a synthetic analogue of 15-epi-lipoxin A4, is protective in experimental ischemic acute renal failure. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 13: 1657–1662.
Kieran, N.E., P.P. Doran, S.B. Connolly, M.C. Greenan, D.F. Higgins, M. Leonard, et al. 2003. Modification of the transcriptomic response to renal ischemia/reperfusion injury by lipoxin analog. Kidney International 64: 480–492.
Nascimento-Silva, V., M.A. Arruda, C. Barja-Fidalgo, C.G. Villela, and I.M. Fierro. 2005. Novel lipid mediator aspirin-triggered lipoxin A4 induces heme oxygenase-1 in endothelial cells. American Journal of Physiology. Cell Physiology 289: C557–C563.
Biteman, B., I.R. Hassan, E. Walker, A.J. Leedom, M. Dunn, F. Seta, et al. 2007. Interdependence of lipoxin A4 and heme-oxygenase in counter-regulating inflammation during corneal wound healing. FASEB Journal 21: 2257–2266.
Jin, S.W., L. Zhang, Q.Q. Lian, D. Liu, P. Wu, S.L. Yao, et al. 2007. Posttreatment with aspirin-triggered lipoxin A4 analog attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice: the role of heme oxygenase-1. Anesthesia and Analgesia 104: 369–377.
Chen, X.Q., S.H. Wu, Y. Zhou, and Y.R. Tang. 2013. Lipoxin A4-induced heme oxygenase-1 protects cardiomyocytes against hypoxia/reoxygenation injury via p38 MAPK activation and Nrf2/ARE complex. PLoS One 8, e67120.
Chen, X.Q., S.H. Wu, Y. Zhou, and Y.R. Tang. 2013. Involvement of K+ channel-dependent pathways in lipoxin A4-induced protective effects on hypoxia/reoxygenation injury of cardiomyocytes. Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes, and Essential Fatty Acids 88: 391–397.
Sobrado, M., M.P. Pereira, I. Ballesteros, O. Hurtado, D. Fernandez-Lopez, J.M. Pradillo, et al. 2009. Synthesis of lipoxin A4 by 5-lipoxygenase mediates PPARγ-dependent, neuroprotective effects of rosiglitazone in experimental stroke. Journal of Neuroscience 29: 3875–3884.
Weinberger, B., C. Quizon, A.M. Vetrano, F. Archer, J.D. Laskin, and D.L. Laskin. 2008. Mechanisms mediating reduced responsiveness of neonatal neutrophils to lipoxin A4. Pediatric Research 64: 393–398.
McMahon, B., C. Stenson, F. McPhillips, A. Fanning, H.R. Brady, and C. Godson. 2000. Lipoxin A4 antagonizes the mitogenic effects of leukotriene D4 in human renal mesangial cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry 275: 27566–27575.
Lin, H., C.H. Yu, C.Y. Jen, C.F. Cheng, Y. Chou, C.C. Chang, et al. 2010. Adiponection-mediated heme oxygenase-1 induction protects against iron-induced liver injury via a PPARα-dependent mechanism. American Journal of Pathology 177: 1697–1709.
Wu, S.H., Y.M. Zhang, H.X. Tao, and L. Dong. 2010. Lipoxin A4 inhibits transition of epithelial to mesenchymal cells in proximal tubules. American Journal of Nephrology 32: 122–136.
Wu, S.H., X.H. Wu, C. Lu, L. Dong, G.P. Zhou, and Z.Q. Chen. 2006. Lipoxin A4 inhibits connective tissue growth factor-induced production of chemokines in rat mesangial cells. Kidney International 69: 248–256.
Wu, S.H., P.Y. Liao, L. Dong, and Z.Q. Chen. 2008. Signal pathway involved in inhibition by lipoxin A4 of production of interleukins in endothelial cells by lipopolysaccharide. Inflammation Research 57: 430–437.
Wu, S.H., X.H. Wu, P.Y. Liao, and L. Dong. 2007. Signal transduction involved in protective effects of 15(R/S)-methyl- lipoxin A4 on mesangioproliferative nephritis in rats. Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes, and Essential Fatty Acids 76: 173–180.
Zhang, L., X. Zhang, P. Wu, H. Li, S. Jin, X. Zhou, et al. 2008. BML-111, a lipoxin receptor agonist, modulates the immune response and reduces the severity of collagen-induced arthritis. Inflammation Research 57: 157–162.
Kieran, N.E., P. Maderna, and C. Godson. 2004. Lipoxins: potential anti-inflammatory, proresolution, and antifibrotic mediators in renal disease. Kidney International 65: 1145–1154.
Ohse, T., T. Ota, N. Kieran, C. Godson, K. Yamada, T. Tanaka, et al. 2004. Modulation of interferon-induced genes by lipoxin analogue in anti-glomerular membrane nephritis. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 15: 919–927.
Deng, L.L., L. Zhong, J.R. Lei, L. Tang, L. Liu, S.Q. Xie, et al. 2012. Protective effect of lipoxin A4 against rhabdomyolysis-induced acute kidney injury in rats. Chin J Cell Mol Immunol 28: 907–910 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Brennan, E.P., K.A. Nolan, E. Börgeson, O.S. Gough, C.M. McEvoy, N.G. Docherty, et al. 2013. Lipoxins attenuate renal fibrosis by inducing let-7c and suppressing TGFβR1. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 24: 627–637.
Börgeson, E., N.G. Docherty, M. Murphy, K. Rodgers, A. Ryan, T.P. O'Sullivan, et al. 2011. Lipoxin A4 and benzo-lipoxin A4 attenuate experimental renal fibrosis. FASEB Journal 25: 2967–2979.
Börgeson, E., A.M.F. Johnson, Y.S. Lee, A. Till, G.H. Syed, S.T. Ali-Shah, et al. 2015. Lipoxin A4 attenuates obesity-induced adipose inflammation and associated liver and kidney disease. Cell Metabolism 22: 1–13.
Zhang, L., J. Wan, H. Li, P. Wu, S. Jin, X. Zhou, et al. 2007. Protective effects of BML-111, a lipoxin A4 receptor agonist, on carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury in mice. Hepatology Research 37: 948–956.
Gong, J., S. Guo, H.B. Li, S.Y. Yuan, Y. Shang, and S.L. Yao. 2012. BML-111, a lipoxin receptor agonist, protects haemorrhagic shock-induced acute lung injury in rats. Resuscitation 83: 907–912.
Hawkins, K.E., K.M. DeMars, J. Singh, C. Yang, H.S. Cho, J.C. Frankowski, et al. 2014. Neurovascular protection by post-ischemic intravenous injections of the lipoxin A4 receptor agonist, BML-111, in a rat model of ischemic stroke. Journal of Neurochemistry 129: 130–142.
Wang, Y.Z., Y.C. Zhang, J.S. Cheng, Q. Ni, P.W. Li, W. Han, et al. 2014. Protective effects of BML-111 on cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis-associated lung injury via activation of Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway. Inflammation 37(4): 1120–1133.
Park, S.Y., J.U. Bae, K.W. Hong, and C.D. Kim. 2011. HO-1 induced by cilostazol protects against TNF-α-associated cytotoxicity via a PPAR-γ-dependent pathway in human endothelial cells. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol 15: 83–66.
Krönke, G., A. Kadl, E. Ikonomu, S. Blüml, A. Fürnkranz, I.J. Sarembock, et al. 2007. Expression of heme oxygenase-1 in human vascular cells is regulated by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 27: 1276–1282.
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the National Natural Scientific Grand (No. 81270821 and No. 81300521) from the Government of China, and by the Priority Academic Program Development (PAPD) of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (JX10231801).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
None of the authors has a financial relationship with a commercial entity that has an interest in the subject of this manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, SH., Chen, XQ., Lü, J. et al. BML-111 Attenuates Renal Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Via Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-α-Regulated Heme Oxygenase-1. Inflammation 39, 611–624 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-015-0286-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-015-0286-y