Abstract
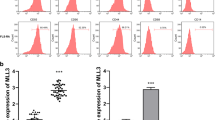
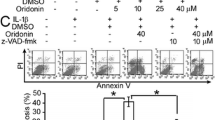
Stimulating fibroblast-like synoviocyte (FLS) apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a promising strategy for clinical treatment. Previous studies have confirmed that geniposide shows a certain anti-arthritic effect in vivo. However, whether geniposide can induce RA FLS apoptosis and the underlying mechanisms has not been elucidated. Herein, adjuvant-induced arthritis (AIA) in rat was induced and FLS was isolated from synovial tissues by tissue explant cultivation method. MTT assay, Hoechst staining, and flow cytometric apoptosis assay were applied to evaluate apoptotic effect of geniposide on AIA FLS. Bcl-2, Bax, and caspase 3 messenger RNA (mRNA) levels, and extracellular-signal-regulated kinases (ERKs) and phosphorylated ERK protein levels were examined by real-time PCR and western blot, respectively. We found that geniposide dose-dependently inhibited AIA FLS proliferation in vitro. AIA FLS treated with geniposide displayed typical apoptotic morphological characteristics including nuclear shrinkage and chromatin condensation. Flow cytometric apoptosis assay indicated that geniposide significantly increased the apoptosis rate of AIA FLS. Additionally, geniposide treatment on AIA FLS decreased Bcl-2 mRNA level and increased Bax and caspase 3 mRNA levels, accompanied by reduced protein levels of phosphorylated-ERK1/2, without affecting total ERK1/2. In conclusion, geniposide effectively induces AIA FLS apoptosis through regulating the apoptosis-related gene expressions and inhibiting ERK signal pathway.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Andreas, K., C. Lubke, T. Haupl, T. Dehne, L. Morawietz, J. Ringe, C. Kaps, and M. Sittinger. 2008. Key regulatory molecules of cartilage destruction in rheumatoid arthritis: an in vitro study. Arthritis Research & Therapy 10: R9.
Huber, L.C., O. Distler, I. Tarner, R.E. Gay, S. Gay, and T. Pap. 2006. Synovial fibroblasts: key players in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 45: 669–675.
Bartok, B., and G.S. Firestein. 2010. Fibroblast-like synoviocytes: key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunological Reviews 233: 233–255.
Thompson, C.B. 1995. Apoptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of disease. Science 267: 1456–1462.
Liu, H., and R.M. Pope. 2003. The role of apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis. Current Opinion in Pharmacology 3: 317–322.
Pope, R.M. 2002. Apoptosis as a therapeutic tool in rheumatoid arthritis. Nature Reviews Immunology 2: 527–535.
Nishioka, K., T. Hasunuma, T. Kato, T. Sumida, and T. Kobata. 1998. Apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis: a novel pathway in the regulation of synovial tissue. Arthritis & Rheumatology 41: 1–9.
Smith, M.D., H. Weedon, V. Papangelis, J. Walker, P.J. Roberts-Thomson, and M.J. Ahern. 2010. Apoptosis in the rheumatoid arthritis synovial membrane: modulation by disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug treatment. Rheumatology (Oxford) 49: 862–875.
Li, R., J. Li, L. Cai, C.M. Hu, and L. Zhang. 2008. Suppression of adjuvant arthritis by hesperidin in rats and its mechanisms. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 60: 221–228.
Zhu, L., J. Wang, T. Wei, J. Gao, H. He, X. Chang, and T. Yan. 2015. Effects of Naringenin on inflammation in complete freund's adjuvant-induced arthritis by regulating Bax/Bcl-2 balance. Inflammation 38: 245–251.
Koo, H.J., K.H. Lim, H.J. Jung, and E.H. Park. 2006. Anti-inflammatory evaluation of gardenia extract, geniposide and genipin. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 103: 496–500.
Kim, J., H.Y. Kim, and S.M. Lee. 2013. Protective effects of geniposide and genipin against hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. Biomolecules & Therapeutics (Seoul) 21: 132–137.
Liu, J.H., F. Yin, L.X. Guo, X.H. Deng, and Y.H. Hu. 2009. Neuroprotection of geniposide against hydrogen peroxide induced PC12 cells injury: involvement of PI3 kinase signal pathway. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica 30: 159–165.
Wang, F., J. Cao, J. Hao, and K. Liu. 2014. Pharmacokinetics, bioavailability and tissue distribution of geniposide following intravenous and peroral administration to rats. Biopharmaceutics & Drug Disposition 35: 97–103.
Chen, J.Y., H. Wu, H. Li, S.L. Hu, M.M. Dai, and J. Chen. 2015. Anti-inflammatory effects and pharmacokinetics study of geniposide on rats with adjuvant arthritis. International Immunopharmacology 24: 102–109.
Dai, M.M., H. Wu, H. Li, J. Chen, J.Y. Chen, S.L. Hu, and C. Shen. 2014. Effects and mechanisms of geniposide on rats with adjuvant arthritis. International Immunopharmacology 20: 46–53.
Zhu, J., X. Gao, W.L. Xie, Y.Z. Jin, and W.J. Sun. 2005. Effect of geniposide on serum IL-1beta and TNF-alpha of rheumatoid arthritis rats. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 30: 708–711.
Cao, H., Q. Feng, W. Xu, X. Li, Z. Kang, Y. Ren, and L. Du. 2010. Genipin induced apoptosis associated with activation of the c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase and p53 protein in HeLa cells. Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin 33: 1343–1348.
Peng, C.H., T.H. Tseng, C.N. Huang, S.P. Hsu, and C.J. Wang. 2005. Apoptosis induced by penta-acetyl geniposide in C6 glioma cells is associated with JNK activation and Fas ligand induction. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 202: 172–179.
Barbosa, C.P., A.M. Ritter, L.G. da Silva, R. Grespan, R.K. Cuman, L. Hernandes, and C.A. Bersani-Amado. 2014. Effects of simvastatin, ezetimibe, and their combination on histopathologic alterations caused by adjuvant-induced arthritis. Inflammation 37: 1035–1043.
Suresh, P., N. Kavitha Ch, S.M. Babu, V.P. Reddy, and A.K. Latha. 2012. Effect of ethanol extract of Trigonella foenum graecum (Fenugreek) seeds on Freund's adjuvant-induced arthritis in albino rats. Inflammation 35: 1314–1321.
Huang, X.Y., X.M. Zhang, F.H. Chen, L.L. Zhou, X.F. Deng, Y.J. Liu, and X.J. Li. 2014. Anti-proliferative effect of recombinant human endostatin on synovial fibroblasts in rats with adjuvant arthritis. European Journal of Pharmacology 723: 7–14.
Livak, K.J., and T.D. Schmittgen. 2001. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25: 402–408.
Bevaart, L., M.J. Vervoordeldonk, and P.P. Tak. 2010. Evaluation of therapeutic targets in animal models of arthritis: how does it relate to rheumatoid arthritis? Arthritis & Rheumatology 62: 2192–2205.
Zhang, L., J. Li, Z. Jiang, L. Sun, X. Mei, B. Yong, and L. Zhang. 2011. Inhibition of aquaporin-1 expression by RNAi protects against aristolochic acid I-induced apoptosis in human proximal tubular epithelial (HK-2) cells. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 405: 68–73.
Perlman, H., L.J. Pagliari, and M.V. Volin. 2001. Regulation of apoptosis and cell cycle activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Current Molecular Medicine 1: 597–608.
Chan, S.L., and V.C. Yu. 2004. Proteins of the bcl-2 family in apoptosis signalling: from mechanistic insights to therapeutic opportunities. Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology 31: 119–128.
Lam, M., G. Dubyak, L. Chen, G. Nunez, R.L. Miesfeld, and C.W. Distelhorst. 1994. Evidence that BCL-2 represses apoptosis by regulating endoplasmic reticulum-associated Ca2+ fluxes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 91: 6569–6573.
Crompton, M. 2000. Bax, Bid and the permeabilization of the mitochondrial outer membrane in apoptosis. Current Opinion in Cell Biology 12: 414–419.
Porter, A.G., and R.U. Janicke. 1999. Emerging roles of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death & Differentiation 6: 99–104.
Schett, G., M. Tohidast-Akrad, J.S. Smolen, B.J. Schmid, C.W. Steiner, P. Bitzan, P. Zenz, K. Redlich, Q. Xu, and G. Steiner. 2000. Activation, differential localization, and regulation of the stress-activated protein kinases, extracellular signal-regulated kinase, c-JUN N-terminal kinase, and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, in synovial tissue and cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis & Rheumatology 43: 2501–2512.
Thiel, M.J., C.J. Schaefer, M.E. Lesch, J.L. Mobley, D.T. Dudley, H. Tecle, S.D. Barrett, D.J. Schrier, and C.M. Flory. 2007. Central role of the MEK/ERK MAP kinase pathway in a mouse model of rheumatoid arthritis: potential proinflammatory mechanisms. Arthritis & Rheumatology 56: 3347–3357.
Ohori, M., M. Takeuchi, R. Maruki, H. Nakajima, and H. Miyake. 2007. FR180204, a novel and selective inhibitor of extracellular signal-regulated kinase, ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis in mice. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology 374: 311–316.
Balmanno, K., and S.J. Cook. 2009. Tumour cell survival signalling by the ERK1/2 pathway. Cell Death & Differentiation 16: 368–377.
Zelivianski, S., M. Spellman, M. Kellerman, V. Kakitelashvilli, X.W. Zhou, E. Lugo, M.S. Lee, R. Taylor, T.L. Davis, R. Hauke, and M.F. Lin. 2003. ERK inhibitor PD98059 enhances docetaxel-induced apoptosis of androgen-independent human prostate cancer cells. International Journal of Cancer 107: 478–485.
Yamanishi, Y., and G.S. Firestein. 2001. Pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis: the role of synoviocytes. Rheumatic Disease Clinics of North America 27: 355–371.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (81102273), Training Programs of Innovation and Entrepreneurship for Undergraduates of Anhui Province (AH201410366126), Program for the Young and Middle-aged Academic Technology Leaders of Anhui Medical University (201309), and Program for the Top Young Talents of Anhui Medical University.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, R., Cai, L., Tang, Wj. et al. Apoptotic Effect of Geniposide on Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes in Rats with Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis via Inhibiting ERK Signal Pathway In Vitro . Inflammation 39, 30–38 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-015-0219-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-015-0219-9