Abstract
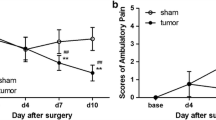
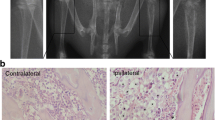
Cannabinoid receptor type 2 (CB2) agonists display potential analgesic effects in acute and neuropathic pain. However, its complex cellular and molecular mechanisms in bone cancer pain remain unclear. And less relevant reports concerned its time-dependent effects on the long-lasting modifications of behavior, spinal inflammatory cytokines levels, astrocytes activity induced by bone cancer pain. A rat model of bone cancer pain induced by intra-tibia inoculation of Walker 256 mammary gland carcinoma cells was utilized. Pain behaviors at different time points were assessed by ambulatory pain scores and paw withdrawal mechanical threshold (PWMT). Pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, IL-18, and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), were quantitated by Western blots. Glial activity was assessed by immunohistochemistry. Intra-tibia inoculation of Walker 256 mammary gland carcinoma cells induced progressive bone cancer pain; a long-term up-regulation of IL-1β, IL-6, IL-18, and TNF-α; and the activation of glia in spinal cord. Activation of microglia was first evident on day 4 after surgery and reached to a peak on day 7 while activation of astrocytes was on day 10. A single intrathecal injection of JWH-015 attenuated bone cancer induced spontaneous pain and mechanical allodynia, reduced the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and inhibited the activity of astrocytes. All the modifications were transient and peaked at 24 h after JWH-015 administration. Furthermore, the protective effects of JWH-015 were reversed in the presence of CB2-selective antagonist AM630. Overall, our results provided evidences for the persistent participation of inflammation reaction in the progression of bone cancer pain, and demonstrated that JWH-015 reduced the expression of IL-1β, IL-6, IL-18, and TNF-α and inhibited astrocytes activation in a time-dependent manner, thereby displaying an analgesic effect.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CB1 :
-
Cannabinoid receptor type 1
- CB2 :
-
Cannabinoid receptor type 2
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor alpha
- PWMT:
-
Paw withdrawal mechanical threshold
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl sulfoxide
- PBS:
-
Phosphate buffered saline
- GFAP:
-
Glial fibrillary acidic protein
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- CCR:
-
Chemokine receptor
- COX:
-
Cyclo-oxygen-ase
- NMDA:
-
N-methyl-d-aspartic acid receptor
References
Hernandez, B.Y., M.D. Green, K.D. Cassel, A.M. Pobutsky, V. Vu, and L.R. Wilkens. 2010. Preview of Hawaii cancer facts and Figures 2010. Hawaii Medical Journal 69: 223–224.
Coleman, R.E. 2006. Clinical features of metastatic bone disease and risk of skeletal morbidity. Clinical Cancer Research: an Official Journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 12: 6243s–6249s.
DeNardo, D.G., M. Johansson, and L.M. Coussens. 2008. Immune cells as mediators of solid tumor metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Reviews 27: 11–18.
Luger, N.M., D.B. Mach, M.A. Sevcik, and P.W. Mantyh. 2005. Bone cancer pain: from model to mechanism to therapy. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management 29: S32–S46.
O’Connor, J.P., and T. Lysz. 2008. Celecoxib, NSAIDs and the skeleton. Drugs of Today 44: 693–709.
Davis, M.P. 2014. Cannabinoids in pain management: CB1, CB2 and non-classic receptor ligands. Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs 23: 1123–1140.
Gilron, I., and A.H. Dickenson. 2014. Emerging drugs for neuropathic pain. Expert Opinion on Emerging Drugs 19: 329–341.
Devane, W.A., F.A. Dysarz 3rd, M.R. Johnson, L.S. Melvin, and A.C. Howlett. 1988. Determination and characterization of a cannabinoid receptor in rat brain. Molecular Pharmacology 34: 605–613.
Tsou, K., S. Brown, M.C. Sanudo-Pena, K. Mackie, and J.M. Walker. 1998. Immunohistochemical distribution of cannabinoid CB1 receptors in the rat central nervous system. Neuroscience 83: 393–411.
Gaffuri, A.L., D. Ladarre, and Z. Lenkei. 2012. Type-1 cannabinoid receptor signaling in neuronal development. Pharmacology 90: 19–39.
Harvey-Girard, E., A.C. Giassi, W. Ellis, and L. Maler. 2013. Expression of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor in the gymnotiform fish brain and its implications for the organization of the teleost pallium. The Journal of Comparative Neurology 521: 949–975.
Klein, T.W., C. Newton, K. Larsen, L. Lu, I. Perkins, L. Nong, and H. Friedman. 2003. The cannabinoid system and immune modulation. Journal of Leukocyte Biology 74: 486–496.
Solas, M., P.T. Francis, R. Franco, and M.J. Ramirez. 2013. CB2 receptor and amyloid pathology in frontal cortex of Alzheimer’s disease patients. Neurobiology of Aging 34: 805–808.
Moreno-Martet, M., F. Espejo-Porras, J. Fernandez-Ruiz, and E. de Lago. 2014. Changes in endocannabinoid receptors and enzymes in the spinal cord of SOD1(G93A) transgenic mice and evaluation of a Sativex((R)) -like combination of phytocannabinoids: interest for future therapies in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics 20: 809–815.
Lanciego, J.L., P. Barroso-Chinea, A.J. Rico, L. Conte-Perales, L. Callen, E. Roda, V. Gomez-Bautista, I.P. Lopez, C. Lluis, J.L. Labandeira-Garcia, and R. Franco. 2011. Expression of the mRNA coding the cannabinoid receptor 2 in the pallidal complex of Macaca fascicularis. Journal of Psychopharmacology 25: 97–104.
Gong, J.P., E.S. Onaivi, H. Ishiguro, Q.R. Liu, P.A. Tagliaferro, A. Brusco, and G.R. Uhl. 2006. Cannabinoid CB2 receptors: immunohistochemical localization in rat brain. Brain Research 1071: 10–23.
Onaivi, E.S., H. Ishiguro, J.P. Gong, S. Patel, A. Perchuk, P.A. Meozzi, L. Myers, Z. Mora, P. Tagliaferro, E. Gardner, A. Brusco, B.E. Akinshola, Q.R. Liu, B. Hope, S. Iwasaki, T. Arinami, L. Teasenfitz, and G.R. Uhl. 2006. Discovery of the presence and functional expression of cannabinoid CB2 receptors in brain. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1074: 514–536.
Rahn, E.J., and A.G. Hohmann. 2009. Cannabinoids as pharmacotherapies for neuropathic pain: from the bench to the bedside. Neurotherapeutics: the Journal of the American Society for Experimental NeuroTherapeutics 6: 713–737.
Fernandez-Ruiz, J. 2009. The endocannabinoid system as a target for the treatment of motor dysfunction. British Journal of Pharmacology 156: 1029–1040.
Marrs, W.R., J.L. Blankman, E.A. Horne, A. Thomazeau, Y.H. Lin, J. Coy, A.L. Bodor, G.G. Muccioli, S.S. Hu, G. Woodruff, S. Fung, M. Lafourcade, J.P. Alexander, J.Z. Long, W. Li, C. Xu, T. Moller, K. Mackie, O.J. Manzoni, B.F. Cravatt, and N. Stella. 2010. The serine hydrolase ABHD6 controls the accumulation and efficacy of 2-AG at cannabinoid receptors. Nature Neuroscience 13: 951–957.
Pertwee, R.G., A.C. Howlett, M.E. Abood, S.P. Alexander, V. Di Marzo, M.R. Elphick, P.J. Greasley, H.S. Hansen, G. Kunos, K. Mackie, R. Mechoulam, and R.A. Ross. 2010. International union of basic and clinical pharmacology. LXXIX. Cannabinoid receptors and their ligands: Beyond CB(1) and CB(2). Pharmacological Reviews 62: 588–631.
Atwood, B.K., and K. Mackie. 2010. CB2: a cannabinoid receptor with an identity crisis. British Journal of Pharmacology 160: 467–479.
Watkins, L.R., E.D. Milligan, and S.F. Maier. 2001. Glial activation: a driving force for pathological pain. Trends in Neurosciences 24: 450–455.
Guo, W., H. Wang, M. Watanabe, K. Shimizu, S. Zou, S.C. LaGraize, F. Wei, R. Dubner, and K. Ren. 2007. Glial-cytokine-neuronal interactions underlying the mechanisms of persistent pain. Journal of Neuroscience : the Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience 27: 6006–6018.
Sun, Y.E., L. Peng, X. Sun, J. Bo, D. Yang, Y. Zheng, C. Liu, B. Zhu, Z. Ma, and X. Gu. 2012. Intrathecal injection of spironolactone attenuates radicular pain by inhibition of spinal microglia activation in a rat model. PLoS One 7: e39897.
Sun, Y., W. Zhang, Y. Liu, X. Liu, Z. Ma, and X. Gu. 2014. Intrathecal injection of JWH015 attenuates remifentanil-induced postoperative hyperalgesia by inhibiting activation of spinal glia in a rat model. Anesthesia and Analgesia 118: 841–853.
Bossu, P., A. Ciaramella, F. Salani, D. Vanni, I. Palladino, C. Caltagirone, and G. Scapigliati. 2010. Interleukin-18, from neuroinflammation to Alzheimer’s disease. Current Pharmaceutical Design 16: 4213–4224.
Sutinen, E.M., T. Pirttila, G. Anderson, A. Salminen, and J.O. Ojala. 2012. Pro-inflammatory interleukin-18 increases Alzheimer’s disease-associated amyloid-beta production in human neuron-like cells. Journal of Neuroinflammation 9: 199.
Bossu, P., D. Cutuli, I. Palladino, P. Caporali, F. Angelucci, D. Laricchiuta, F. Gelfo, P. De Bartolo, C. Caltagirone, and L. Petrosini. 2012. A single intraperitoneal injection of endotoxin in rats induces long-lasting modifications in behavior and brain protein levels of TNF-alpha and IL-18. Journal of Neuroinflammation 9: 101.
Karavelioglu, E., Y. Gonul, S. Kokulu, O. Hazman, F. Bozkurt, A. Kocak, and O. Eser. 2014. Anti-inflammatory and antiapoptotic effect of interleukine-18 binding protein on the spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury. Inflammation 37: 917–923.
Miyoshi, K., K. Obata, T. Kondo, H. Okamura, and K. Noguchi. 2008. Interleukin-18-mediated microglia/astrocyte interaction in the spinal cord enhances neuropathic pain processing after nerve injury. Journal of Neuroscience : the Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience 28: 12775–12787.
Zimmermann, M. 1983. Ethical guidelines for investigations of experimental pain in conscious animals. Pain 16: 109–110.
Mao-Ying, Q.L., J. Zhao, Z.Q. Dong, J. Wang, J. Yu, M.F. Yan, Y.Q. Zhang, G.C. Wu, and Y.Q. Wang. 2006. A rat model of bone cancer pain induced by intra-tibia inoculation of Walker 256 mammary gland carcinoma cells. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 345: 1292–1298.
Medhurst, S.J., K. Walker, M. Bowes, B.L. Kidd, M. Glatt, M. Muller, M. Hattenberger, J. Vaxelaire, T. O’Reilly, G. Wotherspoon, J. Winter, J. Green, and L. Urban. 2002. A rat model of bone cancer pain. Pain 96: 129–140.
Mestre, C., T. Pelissier, J. Fialip, G. Wilcox, and A. Eschalier. 1994. A method to perform direct transcutaneous intrathecal injection in rats. Journal of Pharmacological and Toxicological Methods 32: 197–200.
Dixon, W.J. 1980. Efficient analysis of experimental observations. Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology 20: 441–462.
Ji, R.R., Y. Kawasaki, Z.Y. Zhuang, Y.R. Wen, and I. Decosterd. 2006. Possible role of spinal astrocytes in maintaining chronic pain sensitization: review of current evidence with focus on bFGF/JNK pathway. Neuron Glia Biology 2: 259–269.
Rubens, R.D. 1998. Bone metastases—the clinical problem. European Journal of Cancer 34: 210–213.
Solomayer, E.F., I.J. Diel, G.C. Meyberg, C. Gollan, and G. Bastert. 2000. Metastatic breast cancer: clinical course, prognosis and therapy related to the first site of metastasis. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment 59: 271–278.
Romero-Sandoval, A., N. Nutile-McMenemy, and J.A. DeLeo. 2008. Spinal microglial and perivascular cell cannabinoid receptor type 2 activation reduces behavioral hypersensitivity without tolerance after peripheral nerve injury. Anesthesiology 108: 722–734.
Martin Fontelles, M.I., and C. Goicoechea Garcia. 2008. Role of cannabinoids in the management of neuropathic pain. CNS Drugs 22: 645–653.
Elikkottil, J., P. Gupta, and K. Gupta. 2009. The analgesic potential of cannabinoids. Journal of Opioid Management 5: 341–357.
Karst, M., S. Wippermann, and J. Ahrens. 2010. Role of cannabinoids in the treatment of pain and (painful) spasticity. Drugs 70: 2409–2438.
Thaler, A., A. Gupta, and S.P. Cohen. 2011. Cannabinoids for pain management. Advances in Psychosomatic Medicine 30: 125–138.
Lombard, C., M. Nagarkatti, and P. Nagarkatti. 2007. CB2 cannabinoid receptor agonist, JWH-015, triggers apoptosis in immune cells: potential role for CB2-selective ligands as immunosuppressive agents. Clinical Immunology 122: 259–270.
Preet, A., Z. Qamri, M.W. Nasser, A. Prasad, K. Shilo, X. Zou, J.E. Groopman, and R.K. Ganju. 2011. Cannabinoid receptors, CB1 and CB2, as novel targets for inhibition of non-small cell lung cancer growth and metastasis. Cancer Prevention Research 4: 65–75.
Gu, X., F. Mei, Y. Liu, R. Zhang, J. Zhang, and Z. Ma. 2011. Intrathecal administration of the cannabinoid 2 receptor agonist JWH015 can attenuate cancer pain and decrease mRNA expression of the 2B subunit of N-methyl-D-aspartic acid. Anesthesia and Analgesia 113: 405–411.
Austin, P.J., and G. Moalem-Taylor. 2010. The neuro-immune balance in neuropathic pain: involvement of inflammatory immune cells, immune-like glial cells and cytokines. Journal of Neuroimmunology 229: 26–50.
Kawasaki, Y., L. Zhang, J.K. Cheng, and R.R. Ji. 2008. Cytokine mechanisms of central sensitization: distinct and overlapping role of interleukin-1beta, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in regulating synaptic and neuronal activity in the superficial spinal cord. Journal of Neuroscience : the Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience 28: 5189–5194.
Liou, J.T., F.C. Liu, C.C. Mao, Y.S. Lai, and Y.J. Day. 2011. Inflammation confers dual effects on nociceptive processing in chronic neuropathic pain model. Anesthesiology 114: 660–672.
Raghavendra, V., F. Tanga, and J.A. DeLeo. 2003. Inhibition of microglial activation attenuates the development but not existing hypersensitivity in a rat model of neuropathy. The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 306: 624–630.
Sung, B., G. Lim, and J. Mao. 2003. Altered expression and uptake activity of spinal glutamate transporters after nerve injury contribute to the pathogenesis of neuropathic pain in rats. Journal of Neuroscience : the Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience 23: 2899–2910.
Ji, R.R., and M.R. Suter. 2007. p38 MAPK, microglial signaling, and neuropathic pain. Molecular Pain 3: 33.
Meunier, A., A. Latremoliere, E. Dominguez, A. Mauborgne, S. Philippe, M. Hamon, J. Mallet, J.J. Benoliel, and M. Pohl. 2007. Lentiviral-mediated targeted NF-kappaB blockade in dorsal spinal cord glia attenuates sciatic nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain in the rat. Molecular Therapy : the Journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy 15: 687–697.
Ledeboer, A., M. Gamanos, W. Lai, D. Martin, S.F. Maier, L.R. Watkins, and N. Quan. 2005. Involvement of spinal cord nuclear factor kappaB activation in rat models of proinflammatory cytokine-mediated pain facilitation. The European Journal of Neuroscience 22: 1977–1986.
Vincenzi, F., M. Targa, C. Corciulo, M.A. Tabrizi, S. Merighi, S. Gessi, G. Saponaro, P.G. Baraldi, P.A. Borea, and K. Varani. 2013. Antinociceptive effects of the selective CB2 agonist MT178 in inflammatory and chronic rodent pain models. Pain 154: 864–873.
Abbadie, C., J.A. Lindia, A.M. Cumiskey, L.B. Peterson, J.S. Mudgett, E.K. Bayne, J.A. DeMartino, D.E. MacIntyre, and M.J. Forrest. 2003. Impaired neuropathic pain responses in mice lacking the chemokine receptor CCR2. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 100: 7947–7952.
Guo, W., K. Miyoshi, R. Dubner, M. Gu, M. Li, J. Liu, J. Yang, S. Zou, K. Ren, K. Noguchi, and F. Wei. 2014. Spinal 5-HT3 receptors mediate descending facilitation and contribute to behavioral hypersensitivity via a reciprocal neuron-glial signaling cascade. Molecular Pain 10: 35.
Gu, X., J. Zhang, Z. Ma, J. Wang, X. Zhou, Y. Jin, X. Xia, Q. Gao, and F. Mei. 2010. The role of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit NR2B in spinal cord in cancer pain. European Journal of Pain 14: 496–502.
Cui, J.H., J. Ju, and M.H. Yoon. 2013. Pharmacology of cannabinoid receptor agonists and a cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor in rat bone tumor pain. Pharmacology 92: 150–157.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81070892, 81171047, 81171048, and 81371207) and a grant from the Department of Health of Jiangsu Province of China (XK201140, RC2011006).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Authors’ Contributions
All of the authors read and approved the final manuscript. CEL made substantial contributions to the experiments. YL was mainly involved in the pain behavioral tests and the spinal astrocyte activity assay. BS and YZ performed the surgical procedure, administration of drugs, and Western blotting studies. YES and BLH were responsible for statistical analyses. All of these individuals participated in drafting the manuscript. XPG and ZLM conceived the idea, designed the study, and helped to revise the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Cui’e Lu, Yue Liu, Bei Sun and Yu’e Sun contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, C., Liu, Y., Sun, B. et al. Intrathecal Injection of JWH-015 Attenuates Bone Cancer Pain Via Time-Dependent Modification of Pro-inflammatory Cytokines Expression and Astrocytes Activity in Spinal Cord. Inflammation 38, 1880–1890 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-015-0168-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-015-0168-3