Abstract
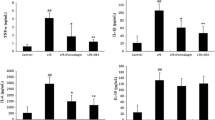
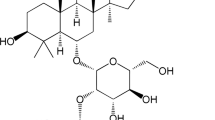
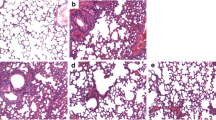
Punicalagin, a bioactive ellagitannin isolated from pomegranate, has been reported to have anti-inflammatory property. In the present study, we analyzed the role of punicalagin against acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in mice. Male BALB/c mice with ARDS, induced by intranasal instillation of LPS, were treated with punicalagin 1 h prior to LPS exposure. The effects of punicalagin on pro-inflammatory cytokines, myeloperoxidase activity, nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) activation, and the histopathological changes were evaluated. The results showed that punicalagin treatment attenuated LPS-induced lung edema, elevating TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β levels in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF). Meanwhile, punicalagin significantly inhibited LPS-induced increases in the macrophage and neutrophil infiltration of lung tissues and myeloperoxidase activity. Furthermore, punicalagin inhibits Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) expression and NF-κB activation induced by LPS. In conclusion, this is the first study to demonstrate that punicalagin protects against LPS-induced ARDS in mice. The underlying mechanisms may include inhibition of TLR4-mediated NF-κB signaling pathways.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baumann, W.R., R.C. Jung, M. Koss, C.T. Boylen, L. Navarro, and O.P. Sharma. 1986. Incidence and mortality of adult respiratory distress syndrome: a prospective analysis from a large metropolitan hospital. Critical Care Medicine 14: 1–4.
Ware, L.B. 2006. Pathophysiology of acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Seminars in Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 27: 337–349.
Tomashefski Jr., J.F. 2000. Pulmonary pathology of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Clinics in Chest Medicine 21: 435–466.
Mei, S.H., S.D. McCarter, Y. Deng, C.H. Parker, W.C. Liles, and D.J. Stewart. 2007. Prevention of LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice by mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing angiopoietin 1. PLoS Medicine 4: e269.
Imai, Y., K. Kuba, G.G. Neely, R. Yaghubian-Malhami, T. Perkmann, G. van Loo, M. Ermolaeva, R. Veldhuizen, Y.H. Leung, H. Wang, et al. 2008. Identification of oxidative stress and Toll-like receptor 4 signaling as a key pathway of acute lung injury. Cell 133: 235–249.
Gunnarsson, P.S., K. Sigvaldason, K.I. Reynisson, and A.D. Moller. 2013. The incidence and mortality of ARDS at Landspitali—The National University Hospital of Iceland 2004–2008. Læknablađiđ 99: 443–448.
Seeram, N.P., L.S. Adams, S.M. Henning, Y. Niu, Y. Zhang, M.G. Nair, and D. Heber. 2005. In vitro antiproliferative, apoptotic and antioxidant activities of punicalagin, ellagic acid and a total pomegranate tannin extract are enhanced in combination with other polyphenols as found in pomegranate juice. Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry 16: 360–367.
Cerda, B., R. Llorach, J.J. Ceron, J.C. Espin, and F.A. Tomas-Barberan. 2003. Evaluation of the bioavailability and metabolism in the rat of punicalagin, an antioxidant polyphenol from pomegranate juice. European Journal of Nutrition 42: 18–28.
Lin, C.C., Y.F. Hsu, and T.C. Lin. 1999. Effects of punicalagin and punicalin on carrageenan-induced inflammation in rats. American Journal of Chinese Medicine 27: 371–376.
Xu, X, Yin, P, Wan, C, Chong, X, Liu, M, Cheng, P, Chen, J, Liu, F, Xu, J. 2014. Punicalagin inhibits inflammation in LPS-induced RAW264.7 macrophages via the suppression of TLR4-mediated MAPKs and NF-kappaB activation. Inflammation
Lee, C., L. Chen, and C. Wang. 2010. Anti-inflammatory effects of Punica granatum Linne in LPS-induced primary human chondrocytes. Planta Medica 76: 1376–1376.
Jean-Gilles, D., L. Li, V.G. Vaidyanathan, R. King, B. Cho, D.R. Worthen, C.O. Chichester 3rd, and N.P. Seeram. 2013. Inhibitory effects of polyphenol punicalagin on type-II collagen degradation in vitro and inflammation in vivo. Chemico-Biological Interactions 205: 90–99.
Lee, W.L., and G.P. Downey. 2001. Neutrophil activation and acute lung injury. Current Opinion in Critical Care 7: 1–7.
Zmijewski, J.W., E. Lorne, X. Zhao, Y. Tsuruta, Y. Sha, G. Liu, and E. Abraham. 2009. Antiinflammatory effects of hydrogen peroxide in neutrophil activation and acute lung injury. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 179: 694–704.
Graff, G., D.A. Gamache, M.T. Brady, J.M. Spellman, and J.M. Yanni. 1998. Improved myeloperoxidase assay for quantitation of neutrophil influx in a rat model of endotoxin-induced uveitis. Journal of Pharmacological and Toxicological Methods 39: 169–178.
Goodman, R.B., J. Pugin, J.S. Lee, and M.A. Matthay. 2003. Cytokine-mediated inflammation in acute lung injury. Cytokine & Growth Factor Reviews 14: 523–535.
Giebelen, I.A.J., D.J. van Westerloo, G.J. LaRosa, A.F. de Vos, and T. van der Poll. 2007. Local stimulation of alpha 7 cholinergic receptors inhibits LPS-induced TNF-alpha release in the mouse lung. Shock 28: 700–703.
Kolb, M., P.J. Margetts, D.C. Anthony, F. Pitossi, and J. Gauldie. 2001. Transient expression of IL-1beta induces acute lung injury and chronic repair leading to pulmonary fibrosis. Journal of Clinical Investigation 107: 1529–1536.
Parsons, P.E., M.D. Eisner, B.T. Thompson, M.A. Matthay, M. Ancukiewicz, G.R. Bernard, and A.P. Wheeler. 2005. Network NARDSCT: Lower tidal volume ventilation and plasma cytokine markers of inflammation in patients with acute lung injury. Critical Care Medicine 33: 1–6. discussion 230–232.
Lu, Y.C., W.C. Yeh, and P.S. Ohashi. 2008. LPS/TLR4 signal transduction pathway. Cytokine 42: 145–151.
Medzhitov, R., and J.C. Kagan. 2006. Phosphoinositide-mediated adaptor recruitment controls Toll-like receptor signaling. Cell 125: 943–955.
Gilmore, T.D. 2006. Introduction to NF-kappaB: players, pathways, perspectives. Oncogene 25: 6680–6684.
Conflict of Interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, J., Wei, D., Fu, Z. et al. Punicalagin Ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Mice. Inflammation 38, 493–499 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-9955-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-9955-5