Abstract
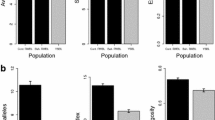
The American mosquitofish, Gambusia holbrooki, is a worldwide invasive species. Multiple paternity might contribute to the invasive success of this species, by locally increasing effective population size. Using microsatellite loci, we examined multiple paternity of mosquitofish in Spanish basins. The percentage of gravid females that mated multiple times (greater than 60%), the average brood size (13.2), and the average number of sires per female brood (3–4) in the invaded basins were similar to values reported in America. Partial correlation showed that female size was not related to the number of sires independent of brood size. In addition, positive correlations between female size and the effective number of sires, or the reproductive skew were dependent on brood size. A relevant percentage of females mating with more than 3 sires suggested enhanced opportunities for transmission of diversity to subsequent generations in Spanish populations. Within broods, a dominant male often sired half of the brood. These results suggest multiple paternity is common in invaded populations. Together with known reproductive tactics of mosquitofish giving to any mature individual the chance for mating regardless of size or age, possibly multiple paternity facilitate the persistence of the genetic diversity of local populations.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrillo, C., M. Dadda & G. Serena, 2008. Choice of female groups by male mosquitofish (Gambusia holbrooki). Ethology 114: 479–488.
Alcaraz, C. & E. Garcia-Berthou, 2007. Life-history variation of invasive mosquitofish (Gambusia holbrooki) along a salinity gradient. Biological Conservation 139: 83–92.
Becher, S. A. & A. E. Magurran, 2004. Multiple mating and reproductive skew in Trinidadian guppies. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 271: 1009–1014.
Belk, M. C. & R. C. Tuckfiled, 2010. Changing costs of reproduction: age-based differences in reproductive allocation and escape performance in a livebearing fish. Oikos 119: 163–169.
Benejam, L., C. Alcaraz, P. Sasal, G. Simon-Levert & E. García-Berthou, 2009. Life history and parasites of the invasive mosquitofish (Gambusia holbrooki) along a latitudinal gradient. Biological Invasions 11: 2265–2277.
Billman, E. J. & M. C. Belk, 2014. Effect of age-based and environment-based cues on reproductive investment in Gambusia affinis. Ecology and Evolution 4: 1611–1622.
Bisazza, A. & G. Marin, 1991. Male size and female mate choice in the eastern mosquitofish (Gambusia holbrooki: Poeciliidae). Copeia 1991(3): 730–735.
Bisazza, A., G. Vaccari & A. Pilastro, 2001. Female mate choice in a mating system dominated by male sexual coercion. Behavioral Ecology 12: 59–64.
Booksmythe, I., P. R. Y. Backwell & M. D. Jennions, 2013. Competitor size, male mating success and mate choice in eastern mosquitofish, Gambusia holbrooki. Animal Behaviour 85: 371–375.
Cabral, J. A. & J. C. Marques, 1999. Life history, population dynamics and production of eastern mosquitofish, Gambusia holbrooki (Pisces, Poeciliidae), in rice fields of the Lower Mondego River Valley, West Portugal. Acta Oecologica 20: 607–620.
Carlsson, J., 2007. The effect of family structure on the likelihood for kin-biased distribution: an empirical study of brown trout populations. Journal of Fish Biology 71(Supplement A): 98–110.
Carmona-Catot, G., J. Benito & E. García-Berthou, 2011. Comparing latitudinal and upstream-downstream gradients: life history traits of invasive mosquitofish. Diversity and Distributions 17: 214–224.
Chesser, R. K., M. W. Smith & M. H. Smith, 1984. Biochemical genetics of mosquitofish III. Incidence and significance of multiple insemination. Genetica 64: 77–81.
Deacon, A. E., I. W. Ramnarine & A. E. Magurran, 2011. How reproductive ecology contributes to the spread of a globally invasive fish. PLoS ONE 6(9): e24416.
Deaton, R., 2008. Factors influencing male mating behaviour in Gambusia affinis (Baird & Girard) with a coercive mating system. Journal of Fish Biology 72: 1607–1622.
Diez-del-Molino, D., G. Carmona-Catot, R. M. Araguas, O. Vidal, N. Sanz, E. García-Berthou & J. L. García-Marín, 2013. Gene flow and maintenance of genetic diversity in invasive mosquitofish (Gambusia holbrooki). PLoS ONE 8(12): e82501.
Díez-del-Molino, D., R. M. Araguas, M. Vera, O. Vidal, N. Sanz & J.-L. García-Marín, 2016. Temporal genetic dynamics among mosquitofish (Gambusia holbrooki) populations in invaded watersheds. Biological Invasions 18: 841–855.
Eales, J., R. S. Thorpe & A. Malhotra, 2010. Colonization history and genetic diversity: adaptive potential in early stage invasions. Molecular Ecology 19: 2858–2869.
Edwards, T. M., H. D. Miller, G. Toft & L. J. Guillette, 2013. Seasonal reproduction of male Gambusia holbrooki (eastern mosquitofish) from two Florida lakes. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry 39: 1165–1180.
Evans, J. P. & A. E. Magurran, 2000. Multiple benefits of multiple mating in guppies. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 97: 10074–10076.
Evans, J. P. & A. E. Magurran, 2001. Patterns of sperm precedence and predictors of paternity in the Trinidadian guppy. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 268: 719–724.
Fernandez-Delgado, C. & S. Rossomanno, 1997. Reproductive biology of the mosquitofish in a permanent natural lagoon in south-west Spain: two tactics for one species. Journal of Fish Biology 51: 80–92.
Fraile, B., F. J. Sáez, C. A. Vicentini, A. González, M. P. de Miguel & R. Paniagua, 1994. Effects of Temperature and Photoperiod on the Gambusia affinis holbrooki Testis during the Spermatogenesis period. Copeia 1994: 216–221.
Greene, J. M. & K. L. Brown, 1991. Demographic and genetic characteristics of multiply inseminated female mosquitofish (Gambusia affinis). Copeia 1991: 434–444.
Hayden, M. J., T. M. Nguyen, A. Waterman & K. J. Chalmers, 2008. Multiplex-ready PCR: a new method for multiplexed SSR and SNP genotyping. BMC Genomics 9: 80.
Hoysak, D. J. & J.-G. J. Godin, 2007. Repeatability of male mate choice in the mosquitofish, Gambusia holbrooki. Ethology 113: 1007–1018.
Johnson, A. M., G. Chappell, A. C. Price, F. H. Rodd, R. Olendorf & K. A. Hughes, 2010. Inbreeding depression and inbreeding avoidance in a natural population of guppies (Poecilia reticulata). Ethology 116: 448–457.
Jones, A. G., 2005. GERUD 2.0: a computer program for the reconstruction of parental genotypes from half-sib progeny arrays with known or unknown parents. Molecular Ecology Notes 5: 708–711.
Jones, O. & J. Wang, 2009. COLONY: a program for parentage and sibship inference from multilocus genotype data. Molecular Ecology Resources 10: 551–555.
Kalinowski, S. T., M. L. Taper & T. C. Marshall, 2007. Revising how the computer program CERVUS accommodates genotyping error increases success in paternity assignment. Molecular Ecology 16: 1099–1106.
Koya, Y. & E. Kamiya, 2000. Environmental regulation of annual reproductive cycle in the mosquitofish, Gambusia affinis. The Journal of Experimental Zoology 286: 204–211.
Marsh-Matthews, E., M. Brooks, R. Deaton & H. Tan, 2005. Effects of maternal and embryo characteristics on post-fertilization provisioning in fishes of the genus Gambusia. Oecologia 144: 12–24.
Neff, B. D. & T. E. Pitcher, 2002. Assessing the statistical power of genetic analyses to detect multiple mating in fishes. Journal of Fish Biology 61: 739–750.
Neff, B. D., T. E. Pitcher & I. W. Ramnarine, 2008. Inter-population variation in multiple paternity and reproductive skew in the guppy. Molecular Ecology 17: 2975–2984.
Norazmi-Lokman, N. H., G. J. Purser & J. G. Patil, 2016. Gravid spot predicts developmental progress and reproductive output in a livebearing fish, Gambusia holbrooki. PLoS ONE 11(1): e0147711.
Ojanguren, A. F., J. P. Evans & A. E. Magurran, 2005. Multiple mating influences offspring size in guppies. Journal of Fish Biology 67: 1184–1188.
Pearse, D. E. & E. C. Anderson, 2009. Multiple paternity increases effective population size. Molecular Ecology 18: 3124–3127.
Pérez-Bote, J. & M. López, 2005. Life-history pattern of the introduced eastern mosquitofish, Gambusia holbrooki (Baird & Girard, 1854), in a Mediterranean-type river: the River Guadiana (SW Iberian Peninsula). Italian Journal of Zoology 72: 241–248.
Pilastro, A., E. Giacomello & A. Bisazza, 1997. Sexual selection for small size in male mosquitofish (Gambusia holbrooki). Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 264: 1125–1129.
Pitcher, T. E., B. D. Neff, F. H. Rodd & L. Rowe, 2003. Multiple mating and sequential mate choice in guppies: females trade up. Proceedings of the Royal Society B 270: 1623–1629.
Purcell, K. M., S. L. Lance, K. L. Jones & C. A. Stockwell, 2011. Ten novel microsatellite markers for the western mosquitofish Gambusia affinis. Conservation Genetic Resources 3: 361–363.
Pyke, G. H., 2005. A review of the biology of Gambusia affinis and G. holbrooki. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries 15: 339–365.
Rehage, J. S. & A. Sih, 2004. Dispersal behavior, boldness, and the link to invasiveness: a comparison of four Gambusia species. Biological Invasions 6: 379–391.
Reznick, D., E. Schultz, S. Morey & D. Roff, 2006. On the virtue of being the first born: the influence of date of birth on fitness in the mosquitofish, Gambusia affinis. Oikos 114: 135–147.
Ruesink, J. L., 2005. Global analysis of factors affecting the outcome of freshwater fish introductions. Conservation Biology 19: 1883–1893.
Sanz, N., R. M. Araguas, O. Vidal, D. Diez-del-Molino, R. Fernández-Cebrián & J.-L. García-Marín, 2013. Genetic characterization of the invasive mosquitofish (Gambusia spp.) introduced to Europe: population structure and colonization routes. Biological invasions 15: 2333–2346.
Sefc, K. M. & S. Koblmüller, 2009. Assessing the parent numbers from offspring genotypes: the importance of marker polymorphism. Journal of Heredity 100: 197–205.
Simmons, L. W., M. Beveridge & J. P. Evans, 2008. Molecular evidence for multiple paternity in a feral population of green swordtails. Journal of Heredity 99: 610–615.
Spencer, C. C., C. A. Chlan, J. E. Neigel, K. T. Scribner, M. C. Wooten & P. L. Leberg, 1999. Polymorphic microsatellite markers in the western mosquitofish, Gambusia affinis. Molecular Ecology 8: 157–158.
Stockwell, C. A. & S. C. Weeks, 1999. Translocations and rapid evolutionary responses in recently established populations of western mosquitofish (Gambusia affinis). Animal Conservation 2: 103–110.
Trexler, J. C., J. Travis & A. Dinep, 1997. Variation among populations of the sailfin molly in the rate of concurrent multiple paternity and its implications for mating-system evolution. Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology 40: 297–305.
Vargas, M. J. & A. de Sostoa, 1996. Life history of Gambusia holbrooki (Pisces, Poeciliidae) in the Ebro delta (NE Iberian Peninsula). Hydrobiologia 341: 215–224.
Vera, M., D. Díez-del-Molino & J. L. García-Marín, 2016. Genomic survey provides insights into the evolutionary changes that occurred during European expansion of the invasive mosquitofish (Gambusia holbrooki). Molecular Ecology 25: 1089–1105.
Vidal, O., E. García-Berthou, P. A. Tedesco & J.-L. García-Marín, 2009. Origin and genetic diversity of mosquitofish (Gambusia holbrooki) introduced to Europe. Biological Invasions 12: 841–851.
Wang, J., 2004. Sibship reconstruction from genetic data with typing errors. Genetics 166: 1963–1979.
Wang, J., 2013. An improvement on the maximum likelihood reconstruction of pedigrees from marker data. Heredity 111: 165–174.
Zane, L., W. S. Nelson, A. G. Jones & J. C. Avise, 1999. Microsatellite assessment of multiple paternity in natural populations of a live-bearing fish, Gambusia holbrooki. Journal of Evolutionary Biology 12(1): 61–69.
Zarev, V. Y., 2012. Some life-history traits of Gambusia holbrooki (Pisces: Poeciliidae) from Bulgaria. Acta Zoologica Bulgarica 64(3): 263–272.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: Christian Sturmbauer
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, Y., Díez-del-Molino, D., Vidal, O. et al. Multiple paternity and reproduction opportunities for invasive mosquitofish. Hydrobiologia 795, 139–151 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-017-3125-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-017-3125-3