Abstract
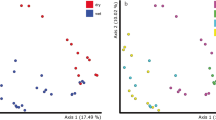
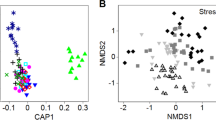
The microbial communities in urban stream ecosystems are subject to complex combinations of stressors. These same microbial communities perform the critical ecosystem service of removing excess reactive nitrogen. We asked whether the denitrifying microbial communities in urban streams differ in their functional resistance to common urban stressors from communities from nonurban streams. We exposed inocula from a highly polluted urban stream and a nearby nonurban stream to three different stressors, added alone and in combination. Stressors represent the common urban impacts of thermal pollution (10°C), trace metal exposure (ionic silver (Ag+)), and salinization (addition of NaCl). We used reduction in nitrite (NO2 −) concentrations under anaerobic conditions as a proxy for denitrification potential. Nonurban stream denitrifying microbial communities were more diverse than their urban counterparts. Denitrification potential for both communities was unaffected by exposure to any individual stressor. However, denitrification rates by the less diverse urban microbial inoculum decreased in response to combined heavy metal and salt stress, while nonurban communities were unaffected. These findings support the hypothesis that higher diversity may confer greater functional resistance in response to multiple stressors and do not support the idea that stressful conditions select for communities that are functionally resilient to multiple stressors.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison, S. D. & J. B. H. Martiny, 2008. Resistance, resilience, and redundancy in microbial communities. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 105: 11512–11519.
Anderson, M. J., 2001. A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral Ecology 26: 32–46.
Blackwood, C. B., D. Hudleston, D. R. Zak & J. S. Buyer, 2007. Interpreting ecological diversity indices applied to terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism data: insights from simulated microbial communities. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 73: 5276–5283.
Blanck, H., S. Wangberg & S. Molander, 1988. Pollution-induced community tolerance – a new ecotoxicological tool. In Cairs Jr., J. & J. R. Pratt (eds), Functional Testing of Aquatic Biota for Estimating Hazards of Chemicals. ASTM STP 988, Philadelphia: 219–230.
Braker, G., A. Fesefeldt & K. P. Witzel, 1998. Development of PCR primer systems for amplification of nitrite reductase genes (nirK and nirS) to detect denitrifying bacteria in environmental samples. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 64: 3769–3775.
Clement, J. L. & P. S. Jarrett, 1994. Antibacterial silver. Metal-Based Drugs 1: 467–582.
Clements, W. H., M. L. Brooks, D. R. Kashian & R. E. Zuellig, 2008. Changes in dissolved organic material determine exposure of stream benthic communities to UV-B radiation and heavy metals: implications for climate change. Global Change Biology 14(9): 2201–2214.
Csonka, L. N., 1989. Physiological and genetic responses of bacteria to osmotic stress. Microbiological Reviews 53: 121–147.
Culman, S., R. Bukowski, H. Gauch, H. Cadillo-Quiroz & D. Buckley, 2009. T-REX: software for the processing and analysis of T-RFLP data. BMC Bioinformatics 10: 171.
Enwall, K., I. N. Throback, M. Stenberg, M. Soderstrom & S. Hallin, 2010. Soil resources influence spatial patterns of denitrifying communities at scales compatible with land management. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 76: 2243–2250.
Fabrega, J., S. N. Luoma, C. R. Tyler, T. S. Galloway & J. R. Lead, 2011. Silver nanoparticles: behaviour and effects in the aquatic environment. Environment International 37: 517–531.
Fierer, N., J. P. Schimel & P. A. Holden, 2003. Variations in microbial community composition through two soil depth profiles. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 35: 167–176.
Fierer, N., M. A. Bradford & R. B. Jackson, 2007. Toward an ecological classification of soil bacteria. Ecology 88(6): 1354–1364.
Gadd, G. M. & A. J. Griffiths, 1977. Microorganisms and heavy metal toxicity. Microbial Ecology 4: 303–317.
Gobel, P., C. Dierkes & W. C. Coldewey, 2007. Storm water runoff concentration matrix for urban areas. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology 91: 26–42.
Johansson, M., M. Pell & J. Stenstrom, 1998. Kinetics of substrate-induced respiration (SIR) and denitrification: applications to a soil amended with silver. Ambio 40: 40–44.
Kaushal, S. S., P. M. Groffman, G. E. Likens, K. T. Belt, W. P. Stack, V. R. Kelly, L. E. Band & G. T. Fisher, 2005. Increased salinization of fresh water in the northeastern United States. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 102: 13517–13520.
Lok, C. N., C. M. Ho, R. Chen, Q. Y. He, W. Y. Yu, H. Sun, P. K. Tam, J. F. Chiu & C. M. Che, 2006. Proteomic analysis of the mode of antibacterial action of silver nanoparticles. Journal of Proteome Research 5: 916–924.
McCann, K. S., 2000. The diversity-stability debate. Nature 405: 228–233.
Mulholland, P. J., A. M. Helton, G. C. Poole, R. O. Hall, S. K. Hamilton, B. J. Peterson, J. L. Tank, L. R. Ashkenas, L. W. Cooper, C. N. Dahm, W. K. Dodds, S. E. G. Findlay, S. V. Gregory, N. B. Grimm, S. L. Johnson, W. H. McDowell, J. L. Meyer, H. M. Valett, J. R. Webster, C. P. Arango, J. J. Beaulieu, M. J. Bernot, A. J. Burgin, C. L. Crenshaw, L. T. Johnson, B. R. Niederlehner, J. M. O’Brien, J. D. Potter, R. W. Sheibley, D. J. Sobota & S. M. Thomas, 2008. Stream denitrification across biomes and its response to anthropogenic nitrate loading. Nature 452(7184): 202–205.
Naeem, S. & S. B. Li, 1997. Biodiversity enhances ecosystem reliability. Nature 390(6659): 507–509.
Oskanen, J., F. G. Blanchet, R. Kindt, et al., 2010. Vegan: community ecology package. R package version 1: 17.
Paine, R. T., M. J. Tegner & E. A. Johnson, 1998. Compounded perturbations yield ecological surprises. Ecosystems 1: 535–545.
Paul, M. J. & J. L. Meyer, 2001. Streams in the urban landscape. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics 32: 333–365.
Peterson, B. J., W. M. Wollheim, P. J. Mulholland, J. R. Webster, J. L. Meyer, J. L. Tank & E. Marti, 2001. Control of nitrogen export from watersheds by headwater streams. Science 292: 86–90.
Philippot, L. & S. Hallin, 2005. Finding the missing link between diversity and activity using denitrifying bacteria as a model functional community. Current Opinion in Microbiology 8: 234–239.
Poolman, B. & E. Glaasker, 1998. Regulation of compatible solute accumulation in bacteria. Molecular Microbiology 29: 397–407.
Rosenberg, D. & V. H. Resh (eds), 1993. Freshwater Biomonitoring and Benthic Macroinvertebrates. Chapman and Hall, New York.
Seo, D. C., K. Yu & R. D. Delaune, 2008. Influence of salinity level on sediment denitrification in a Louisiana estuary receiving diverted Mississippi River water. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science 54: 249–257.
Somers, K. A., E. S. Bernhardt, J. B. Grace, B. A. Hassett, E. B. Sudduth, S. Y. Wang & D. L. Urban, 2013. Streams in the urban heat island: spatial and temporal variability in temperature. Freshwater Science 32(1): 309–326.
Sousa, W. P., 1984. The role of disturbance in natural communities. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics 15: 353–391.
Sudduth, E. B., B. A. Hassett, P. Cada & E. S. Bernhardt, 2011. Testing the field of dreams hypothesis: functional responses to urbanization and restoration in stream ecosystems. Ecological Applications 6: 1972–1988.
Throback, I. N., M. Johansson, M. Rosenquist, M. Pell, M. Hansson & S. Hallin, 2007. Silver (Ag+) reduces denitrification and induces enrichment of novel nirK genotypes in soil. FEMS Microbiology Letters 270: 189–194.
Tsuzuki, M., O. V. Moskvin, M. Kuribayashi, K. Sato, S. Retamal, M. Abo, J. Zeilstra-Ryalls & M. Gomelsky, 2011. Salt stress-induced changes in the transcriptome, compatible solutes, and membrane lipids in the facultatively phototrophic bacterium Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 29: 397–407.
Vinebrooke, R. D., K. L. Cottingham, J. Norberg, M. Scheffer, S. I. Dodson, S. C. Maberly & U. Sommer, 2004. Impacts of multiple stressors on biodiversity and ecosystem functioning: the role of species co-tolerance. Oikos 104: 451–457.
Violin, C. R., P. Cada, E. B. Sudduth, B. A. Hassett, D. L. Penrose & E. S. Bernhardt, 2011. Effects of urbanization and urban stream restoration on the physical and biological structure of stream ecosystems. Ecological Applications 21(6): 1932–1949.
Walsh, C. J., A. H. Roy, J. W. Feminella, P. D. Cottingham, P. M. Groffman & R. P. Morgan, 2005. The urban stream syndrome: current knowledge and the search for a cure. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 24: 706–723.
West, A. & G. Sparling, 1986. Modifications to the substrate-induced respiration method to permit measurement of microbial biomass in soils of differing water contents. Journal of Microbiological Methods 5: 177–189.
White, P., 1979. Pattern, process and natural disturbance in vegetation. Botanical Review 45: 229–299.
Wittebolle, L., M. Marzorati, L. Clement, A. Balloi, D. Daffonchio, K. Heylen, P. De Vos, W. Verstraete & N. Boon, 2009. Initial community evenness favours functionality under selective stress. Nature 458(7238): 623–626.
Yachi, S. & M. Loreau, 1999. Biodiversity and ecosystem productivity in a fluctuating environment: the insurance hypothesis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 96(4): 1463–1468.
Ye, Y., L. Zhang, F. Hao, J. Zhang, Y. Wang & H. Tang, 2012. Global metabolomic responses of Escherichia coli to heat stress. Journal of Proteome Research 11: 2559–2566.
Yura, T., H. Nagai & H. Mori, 1993. Regulation of the heat-shock response in bacteria. Annual Review of Microbiology 47: 321–350.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank B. Colman, B. Hassett, and S. Hayward for field and lab assistance. This research was supported by grants from the National Science Foundation NSF DEB 0546251 to ESB and NSF DEB 3320160 to SW and JPW.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: Stefano Amalfitano
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, SY., Bernhardt, E.S. & Wright, J.P. Urban stream denitrifier communities are linked to lower functional resistance to multiple stressors associated with urbanization. Hydrobiologia 726, 13–23 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-013-1747-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-013-1747-7