Abstract
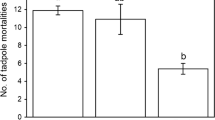
The non-indigenous red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) has been shown to be a threat for amphibian conservation. Many amphibian species breed in temporary ponds to diminish predation risk as such ecosystems are free of large predators. However P. clarkii, occurring as an invasive species in the Camargue delta, can readily disperse on the ground and thus colonize isolated ponds. We studied the current impact of the exotic crayfish on the reproductive success of the Mediterranean tree frog (Hyla meridionalis). In a mesocosm experiment, we tested the effect of two crayfish densities (1 and 3 crayfish/m2) on tadpole abundance. We also tested in a field experiment, within a temporary pond, the crayfish’s predation on the tree frog’s eggs. Finally, we developed site occupancy models using data from 20 ponds to assess the effect of crayfish abundance on tadpole abundance. Neither the experiments, nor the site occupancy models showed a negative impact of the current crayfish abundance on the tree frog populations breeding in ponds. We found that recorded crayfish densities were lower than in other areas where crayfish has impacted amphibian populations, but we hypothesize that current crayfish abundance in the area may increase in the future, thus impacting tree frog populations.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
ACEMAV coll, R. Duguet & F. Melik (eds), 2003. Les amphibiens de France, Belgique et Luxembourg, Collection Pasthénope. Editions Biotope, Mèze (France).
Aquiloni, L., M. Ilhéu & F. Gheradi, 2005. Habitat use and dispersal of the invasive crayfish Procambarus clarkii in ephemeral water bodies of Portugal. Marine & Freshwater Behaviour & Physiology 38(4): 225–236.
Bates, D. M., M. Maechler & B. M. Bolker, 2011. lme4: Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using S4 Classes. R package version 0.9999375-42.
Biek, R., W. C. Funk, B. A. Maxell & L. S. Mills, 2002. What is missing in amphibian decline research: insights from ecological sensitivity analysis. Conservation Biology 16: 728–734.
Blaustein, A. R., B. A. Han, R. A. Relyea, P. T. J. Johnson, J. C. Buck, S. S. Gervasi & L. B. Kats, 2011. The complexity of amphibian population declines: understanding the role of cofactors in driving amphibian losses. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1223: 108–119.
Bolker, B. M., M. E. Brooks, C. J. Clark, S. W. Geange, J. R. Poulsen, M. H. H. Stevens & J.-S. S. White, 2009. Generalized linear mixed models: a practical guide for ecology and evolution. Trends in Ecology & Evolution 24: 127–135.
Bonis, A., J. Lepart & P. Grillas, 1995. Seed bank dynamics and coexistence of annual macrophytes in a temporary and variable habitat. Oikos 74: 81–92.
Boogert, N. J., D. M. Paterson & K. N. Laland, 2006. The implications of niche construction and ecosystem engineering for Conservation Biology. BioScience 56: 570–578.
Byers, J. E., S. Reichard, J. M. Randall, I. M. Parker, C. S. Smith, W. M. Lonsdale, I. A. E. Atkinson, T. R. Seastedt, M. Williamson, E. Chornesky & D. Hayes, 2002. Directing research to reduce the impacts of nonindigenous species. Conservation Biology 16: 630–640.
Cayuela, H., A. Besnard, A. Béchet, V. Devictor & A. Olivier, 2012. Reproductive dynamics of three amphibian species in Mediterranean wetlands: the role of local precipitation and hydrological regime. Freshwater Biology 57(2): 2629–2640.
Céréghino, R., B. Oertli, M. Bazzanti, C. Coccia, A. Compin, J. Biggs, N. Bressi, P. Grillas, A. Hull, T. Kalettka & O. Scher, 2012. Biological traits of European pond macroinvertebrates. Hydrobiologia 689: 51–61.
Cruz, M. J. & R. Rebelo, 2005. Vulnerability of Southwest Iberian amphibians to an introduced crayfish, Procambarus clarkii. Amphibia-Reptilia 26: 293–303.
Cruz, M. J., S. Pascoal, M. Tejedo & R. Rebelo, 2006a. Predation by an exotic crayfish, Procambarus clarkii, on Natterjack Toad, Bufo calamita, embryos: its role on the exclusion of this amphibian from its breeding ponds. Copeia 2: 274–280.
Cruz, M. J., R. Rebelo & E. G. Crespo, 2006b. Effects of an introduced crayfish, Procambarus clarkii, on the distribution of south-western Iberian amphibians in their breeding habitats. Ecography 29: 329–338.
Cruz, M. J., P. Segurado, M. Sousa & R. Rebelo, 2008. Collapse of the amphibian community of the Paul do Boquilobo Natural Reserve (central Portugal) after the arrival of the exotic American crayfish Procambarus clarkii. The Herpetological Journal 18: 197–204.
Diaz-Paniagua, C., 1990. Temporary ponds as breeding sites of amphibians at a locality in southwestern Spain. Herpetological Journal 1: 447–453.
Díaz-Paniagua, C., R. Fernández-Zamudio, M. Florencio, P. Gacía-Murillo, C. Gómez-Rodríguez, A. Portheault, L. Serrano & P. Siljeström, 2010. Temporary ponds from Doñana National Park: a system of natural habitats for the preservation of aquatic flora and fauna. Limnetica 29: 41–58.
Ficetola, F. G., M. E. Siesa, R. Manenti, L. Bottoni, F. De Bernardi & E. Padoa-Schioppa, 2011. Early assessment of the impact of alien species: differential consequences of an invasive crayfish on adult and larval amphibians. Diversity and Distributions 17: 1141–1151.
Fiske, I. & R. Chandler, 2011. Unmarked: an R package for fitting hierarchical models of wildlife occurrence and abundance. Journal of Statistical Software 43: 1–23.
Fox, J. & S. Weisberg, 2011. An R Companion to Applied Regression, 2nd ed. SAGE, Thousand Oaks, CA.
Gamradt, S. C. & L. B. Kats, 1996. Effect of introduced crayfish and Mosquito fish on California Newts. Conservation Biology 10: 1155–1162.
Gamradt, S. C., L. B. Kats & C. B. Anzalone, 1997. Aggression by non-native crayfish deters breeding in California Newts. Conservation Biology 11: 793–796.
Geiger, W., P. Alcorlo, A. Baltanás & C. Montes, 2005. Impact of an introduced crustacean on the trophic webs of Mediterranean wetlands. Biological Invasions 7: 49–73.
Gherardi, F., 2002. Behaviour. In Holdich, D. M. (ed.), Biology of Freshwater Crayfish. Springer, Cornwall: 258–290.
Gherardi, F. & S. Barbaresi, 2000. Invasive crayfish: activity patterns of Procambarus clarkii in the rice fields of the Lower Guadalquivir (Spain). Archiv für Hydrobiolgie 150: 153–168.
Gibelin, A. L. & M. Deque, 2003. Anthropogenic climate change over the Mediterranean region simulated by a global variable resolution model. Climate Dynamics 20: 327–339.
Gómez-Rodríguez, C., C. Díaz-Paniagua, L. Serrano, M. Florencio & A. Portheault, 2009. Mediterranean temporary ponds as amphibian breeding habitats: the importance of preserving pond networks. Aquatic Ecology 43: 1179–1191.
Gómez-Rodríguez, C., C. Díaz-Paniagua, J. Bustamante, A. Portheault & M. Florencio, 2010. Inter-annual variability in amphibian assemblages: implications for diversity assessment and conservation. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 20: 668–677.
Gosner, K. L., 1960. A simplified table for staging anuran embryos and larvae with notes on identification. Herpetologica 16: 183–190.
Guillera-Arroita, G., M. S. Ridout & B. J. T. Morgan, 2010. Design of occupancy studies with imperfect detection. Methods in Ecology and Evolution 1: 131–139.
Habsurgo-Lorena, A. S., 1979. Present situation of exotic species of crayfish introduced into Spanish continental waters. Freshwater Crayfish 4: 175–184.
Holdich, D. M. (ed.), 2002. Biology of Freshwater Crayfish. Blackwell Science, Cornwall, UK.
Holdich, D. M., J. D. Reynolds, C. Souty-Grosset & P. J. Sibley, 2010. A review of the ever increasing threat to European crayfish from non-indigenous crayfish species. Knowledge and Management of Aquatic Ecosystems 11: 394–395.
Jakob, C., G. Poizat, M. Veith, A. Seitz & A. J. Crivelli, 2003. Breeding phenology and larval distribution of amphibians in a Mediterranean pond network with unpredictable hydrology. Hydrobiologia 499: 51–61.
Kats, L. B. & R. P. Ferrer, 2003. Alien predators and amphibian declines: review of two decades of science and the transition to conservation. Diversity and Distributions 9: 99–110.
Kendall, W. L. & G. C. White, 2009. A cautionary note on substituting spatial subunits for repeated temporal sampling in studies of site occupancy. Journal of Applied Ecology 46: 1182–1188.
Kreider, J. L. & S. A. Watts, 1998. Behavioral (feeding) responses of the crayfish, Procambarus clarkii, to natural dietary items and common components of formulated crustacean feeds. Journal of Chemical Ecology 24: 91–111.
Martino, A., J. Syväranta, A. Crivelli, R. Céréghino & F. Santoul, 2011. Is European catfish a threat to eels in southern France? Aquatic Conservation: Marine Freshwater Ecosystems 21: 276–281.
Mazerolle, M. J., 2011. AICcmodavg: Model Selection and Multimodel Inference Based on (Q) AIC(c). Version 1.15.
Mazerolle, M. J., L. L. Bailey, W. L. Kendall, J. Andrew Royle, S. J. Converse & J. D. Nichols, 2007. Making great leaps forward: accounting for detectability in herpetological field studies. Journal of Herpetology 41: 672–689.
Miaud, C. & J. Muratet, 2004. Identifier les oeufs et les larves des amphibiens de France. INRA, Nancy.
Nyström, P., 2002. Ecology. In Holdich, D. M. (ed.), Biology of Freshwater Crayfish. Springer, Cornwall: 192–235.
Ottonello, D., S. Salvidio & E. Rosecchi, 2005. Feeding habits of the European pond terrapin Emys orbicularis in Camargue (Rhone delta, Southern France). Amphibia-Reptilia 26: 562–565.
Pechmann, J. H. K. & H. M. Wilbur, 1994. Putting declining populations in perspective, natural fluctuations and human impacts. Herpetologica 50(1): 65–84.
Pleguezuelos, J. M., 1997. Distribución y biogeografía de los anfíbios y reptiles en España y Portugal. Universidad de Granada; Asociación Herpetológica Española, Granada, España.
Portheault, A., C. Díaz-Paniagua & C. Gómez-Rodríguez, 2007. Predation on amphibian eggs and larvae in temporary ponds: the case of Bufo calamita in Southwestern Spain. Revue d’Ecologie (Terre et Vie) 62: 315–322.
Poulin, B., G. Lefebvre & A. J. Crivelli, 2007. The invasive red swamp crayfish as a predictor of Eurasian bittern density in the Camargue, France. Journal of Zoology 273: 98–105.
Quinn, G. P. & M. J. Keough, 2002. Experimental Design and Data Analysis for Biologist. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK.
R Development Core Team, 2012. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing, Vienna.
Rhazi, L., P. Grillas, E.-R. Saber, M. Rhazi, L. Brendonck & A. Waterkeyn, 2012. Vegetation of Mediterranean temporary pools: a fading jewel? Hydrobiologia 689: 23–36.
Richter-Boix, A., G. A. Llorente & A. Montori, 2006. Breeding phenology of an amphibian community in a Mediterranean area. Amphibia-Reptilia 27: 549–559.
Rodríguez, C., E. Bécares, M. Fernández-Aláez & C. Fernández-Aláez, 2005. Loss of diversity and degradation of wetlands as a result of introducing exotic crayfish. Biological Invasions 7: 75–85.
Rosecchi, E., G. Poizat & A. J. Crivelli, 1997. Introductions de poissons d’eau douce et d’écrevisses en Camargue: historique, origines et modifications des peuplements. Bulletin Français de la Pêche et de la Pisciculture 344(345): 221–232.
Royle, J. A. & J. D. Nichols, 2003. Estimating abundance from repeated presence-absence data or point counts. Ecology 84: 777–790.
Savini, D., A. Occhipinti-Ambrogi, A. Marchini, E. Tricarico, F. Gherardi, S. Olenin & S. Gollasch, 2010. The top 27 animal alien species introduced into Europe for aquaculture and related activities. Journal of Applied Ichthyology 26: 1–7.
Semlitsch, R. D., 2002. Critical elements fro biologically based recovery plans of aquatic-breeding amphibians. Conservation Biology 16: 619–629.
Stuart, S. N., J. S. Chanson, N. A. Cox, B. E. Young, A. S. L. Rodrigues, D. L. Fischman & R. W. Waller, 2004. Status and trends of amphibian declines and extinctions worldwide. Science 306: 1783–1786.
Wilbur, H. M., 1997. Experimental ecology of food webs: complex systems in temporary ponds. Ecology 78: 2279–2302.
Zuur, A. F., E. N. Ieno, N. J. Walker, A. A. Savaliev & G. M. Smith, 2009. Mixed Effects Models and Extensions in Ecology with R. Springer, New York.
Acknowledgments
We thank Eric Meineri and two anonymous referees for their helpful comments which helped us to improve the manuscript. We also thank Michael Paul for improving the English. This study was funded by the MAVA Foundation .
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guest editors: R. Céréghino, D. Boix, H.-M. Cauchie, K. Martens & B. Oertli / Understanding the role of ponds in a changing world
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodriguez-Perez, H., Cayuela, H., Hilaire, S. et al. Is the exotic red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) a current threat for the Mediterranean tree frog (Hyla meridionalis) in the Camargue (Southern France)?. Hydrobiologia 723, 145–156 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-013-1481-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-013-1481-1