Abstract
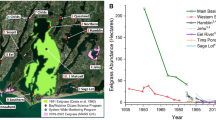
Eelgrass depth limits and water clarity in the Skive Fjord estuarine system have not improved despite nutrient input reductions of 30%. Long-term monitoring data (1989–2010) were used to investigate the underlying causes. Dissolved inorganic and organic nitrogen concentrations decreased significantly over time, whereas particulate organic nitrogen concentration, assumed to consist primarily of phytoplankton and phytoplankton detritus and calculated as a proportional factor to chlorophyll a, did not change. Total organic carbon, mostly of autochthonous origin, remained constant despite reduced nitrogen concentrations, resulting in an increasing C:N ratio of the organic material in the water column. Phytoplankton primary production also remained constant suggesting that phytoplankton growth was only limited by nitrogen to a minor degree. Alleviated grazing pressure caused by a reduction in the blue mussel standing stock and a pelagic food web dominated by jellyfish may have contributed to the constantly high phytoplankton levels. Particulate inorganic matter, likely reflecting sediment resuspension, increased over time, most probably in response to removal of blue mussels and declining eelgrass cover. The Skive Fjord estuarine system is affected by multiple pressures—nutrient enrichment, mussel dredging and climate change that must be addressed together for water clarity to improve and eelgrass to recover.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balsby, T. J. S., J. Carstensen & D. Krause-Jensen, 2012. Sources of uncertainty in estimation of eelgrass depth limits. Hydrobiologia (this issue).
Boström, C., S. P. Baden & D. Krause-Jensen, 2003. The seagrasses of Scandinavia and the Baltic Sea. In Green, E. P. & F. T. Short (eds), World Atlas of Seagrasses. University of California Press, Berkeley: 27–37.
Carr, J., P. D’Odorico, K. McGlathery & P. Wiberg, 2010. Stability and bistability of seagrass ecosystems in shallow coastal lagoons: role of feedbacks with sediment resuspension and light attenuation. Journal of Geophysical Research 115: G03011.
Carstensen, J., 2010. Censored data regression: statistical methods for analyzing Secchi transparency in shallow systems. Limnology & Oceanography: Methods 8: 376–385.
Carstensen, J. & P. Henriksen, 2009. Phytoplankton biomass response to nitrogen inputs: a method for WFD boundary setting applied to Danish coastal waters. Hydrobiologia 633: 137–149.
Carstensen, J., D. J. Conley, J. H. Andersen & G. Ærtebjerg, 2006. Coastal eutrophication and trend reversal: a Danish case study. Limnology & Oceanography 51: 398–408.
Carstensen, J., P. Henriksen & A.-S. Heiskanen, 2007. Summer algal blooms in shallow estuaries: definition, mechanisms, and link to eutrophication. Limnology & Oceanography 52: 370–384.
Carstensen, J., M. Sánchez-Camacho, C. M. Duarte, D. Krause-Jensen & N. Marbà, 2011. Connecting the dots: downscaling responses of coastal ecosystems to changing nutrient concentrations. Environmental Science & Technology 45: 9122–9132.
Conley, D. J., H. Kaas, F. Møhlenberg, B. Rasmussen & J. Windolf, 2000. Characteristics of Danish estuaries. Estuaries 23: 820–837.
Conley, D. J., J. Carstensen, G. Ærtebjerg, P. B. Christensen, T. Dalsgaard, J. L. S. Hansen & A. B. Josefson, 2007. Long-term changes and impacts of hypoxia in Danish coastal waters. Ecological Applications 17: S165–S184.
Dolmer, P., P. S. Kristensen & E. Hoffmann, 1999. Dredging of blue mussels (Mytilus edulis L.) in a Danish sound: stock sizes and fishery-effects on mussel population dynamic. Fisheries Research 40: 73–80.
Duarte, C. M., 1991. Seagrass depth limits. Aquatic Botany 40: 363–377.
Duarte, C. M., 2002. The future of seagrass meadows. Environmental Conservation 29: 192–206.
Duarte, C. M., D. J. Conley, J. Carstensen & M. Sánchez-Camacho, 2009. Return to Neverland: shifting baselines affect ecosystem restoration targets. Estuaries and Coasts 32: 29–36.
Duffy, J. E., 2006. Biodiversity and the functioning of seagrass ecosystems. Marine Ecology Progress Series 311: 233–250.
Fonseca, M. S., P. E. Whitfield, N. M. Kelly & S. S. Bell, 2002. Modelling seagrass landscape pattern and associated ecological attributes. Ecological Applications 12: 218–237.
Fourqurean, J. W., C. M. Duarte, H. Kennedy, N. Marbà, M. Holmer, M. A. Mateo, E. T. Apostolaki, G. A. Kendrick, D. Krause-Jensen, K. J. McGlathery & O. Serrano, 2012. Seagrass ecosystems as a globally significant carbon stock. Nature Geoscience 5: 505–509.
Gacia, E., C. M. Duarte & J. J. Middelburg, 2002. Carbon and nutrient deposition in a Mediterranean seagrass (Posidonia oceanica) meadow. Limnology & Oceanography 47: 23–32.
Gallegos, C. L., 2001. Calculating optical water quality targets to restore and protect submersed aquatic vegetation: overcoming problems in partitioning the diffuse attenuation coefficient for photosynthetically active radiation. Estuaries 24: 381–397.
Grasshoff, K., 1976. Methods in Seawater Analysis. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim.
Green, E. P. & F. T. Short, 2003. World Atlas of Seagrasses. University of California Press, Berkeley.
Greening, H. & A. Janicki, 2006. Toward reversal of eutrophic conditions in a subtropical estuary: water quality and seagrass response to nitrogen loading reductions in Tampa Bay, Florida, USA. Environmental Management 38: 163–178.
Greening, H. S., L. M. Cross & E. T. Sherwood, 2011. A multiscale approach to seagrass recovery in Tampa Bay, Florida. Ecological Restoration 29: 1–2.
Hansen, J. W. & D. L. J. Petersen, 2011. Marine areas 2010. NOVANA. Status and trends in the natural and environmental quality (in Danish). Scientific Report No. 6, DCE, National Centre for Environment and Energy, Aarhus University, Silkeborg.
Hemminga, M. A. & C. M. Duarte, 2000. Seagrass Ecology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Hiratsuka, J., M. Yamamuro & Y. Ishitobi, 2007. Long-term change in water transparency before and after the loss of eelgrass beds in an estuarine lagoon, Lake Nakaumi, Japan. Limnology 8: 53–58.
Kirk, J. T. O., 1994. Light and Photosynthesis in Aquatic Ecosystems. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Krause-Jensen, D., M. F. Pedersen & C. Jensen, 2003. Regulation of eelgrass (Zostera marina) cover along depth gradients in Danish coastal waters. Estuaries 26: 866–877.
Krause-Jensen, D., J. Carstensen, S. L. Nielsen, T. Dalsgaard, P. B. Christensen, H. Fossing & M. B. Rasmussen, 2011. Sea bottom characteristics affect depth limits of eelgrass Zostera marina. Marine Ecology Progress Series 425: 91–102.
Krause-Jensen, D., S. Markager & T. Dalsgaard, 2012. Benthic and pelagic primary production in different nutrient regimes. Estuaries and Coasts 35: 527–545.
Kristensen, P. S. & E. Hoffmann, 2004. Standing stock of blue mussels in Limfjorden 1993–2003 (in Danish). Report No. 130 from DTU-Aqua. www.aqua.dtu.dk.
Kronvang, B. & J. A. Bruhn, 1996. Choice of sampling strategy and estimation method when calculating nitrogen and phosphorus transport in small lowland streams. Hydrological Processes 10: 1483–1501.
Marbà, N., D. Krause-Jensen, T. Alcoverro, S. Birk, A. Pedersen, J. M. Neto, S. Orfanidis, J. M. Garmendia, I. Muxika, A. Borja, K. Dencheva, & C. M. Duarte, 2012. Diversity of European seagrass indicators – patterns within and across regions. Hydrobiologia (this issue).
Markager, S., W. Vincent & E. Y. Tang, 1999. Carbon fixation by phytoplankton in high Arctic lakes: implications of low temperature for photosynthesis. Limnology & Oceanography 44: 597–607.
Markager, S., L. M. Storm, & C. A. Stedmon, 2006. Limfjorden state of the environment from 1985 to 2003 – empirical models relating nutrients to climate and hydrography (in Danish). Report No. 577, National Environmental Research Institute, Silkeborg. www.dce.au.dk.
Markager, S., C. A. Stedmon & M. Søndergaard, 2011. Seasonal dynamics and conservative mixing of dissolved organic matter in the temperate eutrophic estuary Horsens Fjord. Estuarine Coastal Shelf Science 92: 376–388.
Møhlenberg, F., 1995. Regulating mechanisms of phytoplankton growth and biomass in a shallow estuary. Ophelia 42: 239–256.
Nielsen, S. L., K. Sand-Jensen, J. Borum & O. Geertz-Hansen, 2002. Depth colonization of eelgrass (Zostera marina) and macroalgae as determined by water transparency in Danish coastal waters. Estuaries 25: 1025–1032.
Nixon, S. W., 1995. Coastal marine eutrophication: a definition, social causes, and future concerns. Ophelia 41: 199–219.
Nixon, S. W., 2009. Eutrophication and the macroscope. Hydrobiologia 629: 5–19.
Olesen, B., 1996. Regulation of light attenuation and eelgrass Zostera marina depth distribution in a Danish embayment. Marine Ecology Progress Series 134: 187–194.
Orth, R. J., T. J. B. Carruthers, W. C. Dennison, C. M. Duarte, J. W. Fourqurean, K. L. Heck Jr, A. R. Hughes, G. A. Kendrick, W. J. Kenworthy, S. Olyarnik, F. T. Short, M. Waycott & S. L. Williams, 2006a. A global crisis for seagrass ecosystems. Bioscience 56: 987–996.
Orth, R. J., M. L. Luckenbach, S. R. Marion, K. A. Moore & D. J. Wilcox, 2006b. Seagrass recovery in the Delmarva Coastal Bays, USA. Aquatic Botany 84: 26–36.
Preisendorfer, R. W., 1986. Secchi disk science: visual optics of natural waters. Limnology & Oceanography 31: 909–926.
Pulido, C. & J. Borum, 2010. Eelgrass (Zostera marina) tolerance to anoxia. Journal of experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 385: 8–13.
Riisgaard, H. U., D. F. Seerup, M. H. Jensen, E. Glob & P. S. Larsen, 2004. Grazing impact of filter-feeding zoobenthos in a Danish fjord. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 307: 261–271.
Riisgaard, H. U., P. Andersen, & E. Hoffmann, 2012. From fish to jellyfish in the eutrophicated Limfjorden (Denmark). Estuaries and Coasts 35, doi:10.1007/s12237-012-9480-4.
Scheffer, M., S. Carpenter, S. A. Foley, C. Folke & B. Walker, 2001. Catastrophic shifts in ecosystems. Nature 413: 591–596.
Schneider, B., R. Schlitzer, G. Fischer & E. M. Nothig, 2003. Depth-dependent elemental compositions of particulate organic matter (POM) in the ocean. Global Biogeochemical Cycles 17: 1032.
Searle, S. R., F. M. Speed & G. A. Milliken, 1980. Populations marginal means in the linear model: an alternative to least squares means. American Statistician 34: 216–221.
Short, F. T. & S. Wyllie-Echeverria, 1996. Natural and human induced disturbances of seagrass. Environmental Conservation 23: 17–27.
Smith, R. C. & K. S. Baker, 1978. The bio-optical state of ocean waters and remote sensing. Limnology & Oceanography 23: 247–259.
Smith, R. C. & K. S. Baker, 1981. Optical properties of the clearest natural waters (200–800 nm). Applied Optics 20: 177–184.
Stæhr, P. A. & J. Borum, 2011. Seasonal acclimation in metabolism reduces light requirements of eelgrass (Zostera marina). Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 407: 139–146.
Steemann Nielsen, E., 1952. The use of radio-active carbon (C14) for measuring organic production in the sea. Journal Conseil International pour l’Exploration de la Mer 18: 117–140.
Strickland, J. D. & T. R. Parsons, 1972. A Practical Handbook of Seawater Analysis. Fisheries Research Board of Canada, Ottawa: 1–310.
Terrados, J. & C. M. Duarte, 2000. Experimental evidence of reduced particle resuspension within a seagrass (Posidonia oceanica L.) meadow. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 243: 45–53.
Thom, R. M., H. L. Diefenderfer, J. Vavrinec & A. B. Borde, 2012. Restoring resiliency: case studies from Pacific Northwest estuarine eelgrass (Zostera marina L.) ecosystems. Estuaries and Coasts 35: 78–91.
Vaudrey, J. M. P., J. N. Kremer, B. F. Branco & F. T. Short, 2010. Eelgrass recovery and nutrient enrichment reversal. Aquatic Botany 93: 237–243.
Waycott, M., C. M. Duarte, T. J. B. Carruthers, R. J. Orth, W. C. Dennison, S. Olyarnik, A. Calladine, J. W. Fourqurean, K. L. Heck Jr, A. R. Hughes, G. A. Kendrick, W. J. Kenworthy, F. T. Short & S. L. Williams, 2009. Accelerating loss of seagrasses across the globe threatens coastal ecosystems. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 106: 12377–12381.
Widdows, J., J. S. Lucas, M. D. Brinsley, P. N. Salkeld & F. J. Staff, 2002. Investigation of the effects of current velocity on mussel feeding and mussel bed stability using an annular flume. Helgoland Marine Research 56: 3–12.
Windolf, J., H. Thodsen, L. Troldborg, S. E. Larsen, J. Bøgestrand, N. B. Ovesen & B. Kronvang, 2011. A distributed modelling system for simulation of monthly runoff and nitrogen sources, loads and sinks for ungauged catchments in Denmark. Journal of Environmental Monitoring 13: 2645–2658.
Acknowledgments
This research is a contribution to the WISER project (contract #FP7-226273), funded by the European Commission, and the REELGRASS project (contract #09-063190), funded by the Danish Agency for Science, Technology and Innovation. Additional founding was provided by the Danish Council for Strategic Research to the project IMAGE (Integrated Management of Agriculture, Fishery, Environment and Economy, Grant No. 09-067259). We are grateful to the Danish Environmental Centers responsible for data collection under the Danish Nationwide Aquatic Monitoring and Assessment Program. This is a contribution from the Baltic Nest Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guest editors: C. K. Feld, A. Borja, L. Carvalho & D. Hering / Water bodies in Europe: integrative systems to assess ecological status and recovery
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carstensen, J., Krause-Jensen, D., Markager, S. et al. Water clarity and eelgrass responses to nitrogen reductions in the eutrophic Skive Fjord, Denmark. Hydrobiologia 704, 293–309 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-012-1266-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-012-1266-y