Abstract
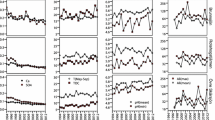
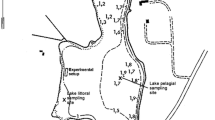
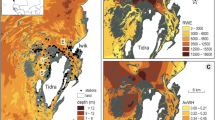
Since the discovery of the green alga Caulerpa taxifolia in Lake Macquarie (New South Wales, Australia) in 2001, the New South Wales Department of Primary Industries (Fisheries) has attempted various control methods, including covering the alga with granulated sea salt to induce osmotic shock and cell lysis. In Lake Macquarie, C. taxifolia often occurs in patches within beds of the native seagrass Zostera capricorni. Although the effects of the salt treatment on blades of Z. capricorni and infauna have been shown to be minimal, there have been no tests of any effects on other native biota, including seagrass epifauna. In this study, we tested the general hypothesis that the abundance and diversity of epifauna would be reduced by salting. We used a ‘Beyond BACI’ experimental design whereby epifaunal invertebrates were sampled 3 months, 6 weeks and 6 days before and then again after salting. Epifaunal abundances at the putatively impacted (salted) location were compared to those at 4 control locations (where no salt was applied). Abundances of most organisms varied significantly among times and locations with no evidence of the consistent effect of salting on diversity or abundance of epifauna. The study represents an example of the use of large-scale managerial action as a scientific experiment.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ceccherelli, G. & F. Cinelli, 1999. Effects of Posidonia oceanica canopy on Caulerpa taxifolia in a north-western Mediterranean bay. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 240: 19–36.
Clarke, K. R. & R. M. Warwick, 2001. Change in marine communities: an approach to statistical analysis and interpretation, 2nd edn. PRIMER-E, Plymouth.
Clarke, K. R. & R. H. Green, 1988. Statistical design and analysis for a ‘biological effects’ study. Marine Ecology Progress Series 46: 213–226.
Connell, J. H. & M. J. Keough, 1985. Disturbance and patch dynamics of subtidal marine animals on hard substrata. In Pickett S. T. A. & P. S. White (eds), The Ecology of Natural Disturbance and Patch Dynamics. Academic Press, Inc., New York, 125–151.
Creese, R. G., A. R. Davis & T.M. Glasby, 2004. Eradicating and Preventing the Spread of Caulerpa taxifolia in NSW. NSW Fisheries Final Report Series, No. 64, 110 pp.
de Villèle, X. & M. Verlaque, 1995. Changes and degradation in a Posidonia oceanica bed invaded by the introduced tropical alga Caulerpa taxifolia in the north western Mediterranean. Botanica Marina 38: 79–87.
Glasby, T. M., 1997. Analysing data from post-impact studies using asymmetrical analysis of variance: a case study of epibiota on marinas. Australian Journal of Ecology 22: 448–459.
Glasby, T. M., R. G. Creese & P. T. Gibson, 2005. Experimental use of salt to control the invasive marine alga Caulerpa taxifolia in New South Wales, Australia. Biological Conservation 122: 573–580.
Hanski, I., 1991. Single-species meta population dynamics: concepts, models and observations. Biological Journal of Linnaean Society 42: 17–38.
Jaubert, J. M., J. R. M. Chisholm, D. Ducrot, H. T. Ripley, L. Roy & G. Passeron-Seitre, 1999. No deleterious alterations in Posidonia beds in the Bay of Menton (France) eight years after Caulerpa taxifolia colonization. Journal of Phycology 35: 1113–1119.
Jaubert, J. M., J. R. M. Chisholm, A. Minghelli-Roman, M. Marchioretti, J. H. Morrow & H. T. Ripley, 2003. Re-evaluation of the extent of Caulerpa taxifolia development in the northern Mediterranean using airborne spectrographic sensing. Marine Ecology Progress Series 263: 75–82.
Martin-Smith, K. M., 1994. Short-term dynamics of tropical macroalgal epifauna: patterns and processes in recolonisation of Sargassum fissifolium. Marine Ecology Progress Series 110: 177–185.
Meinesz, A., J. de Vaugelas, B. Hesse & X. Nmarin, 1993. Spread of the introduced tropical green alga Caulerpa taxifolia in the northern Mediterranean water. Journal of Applied Phycology 5: 141–147.
Phillips, J. A. & I. R. Price, 2002. How different is Mediterranean Caulerpa taxifolia (Caulerpales: Chlorophyta) to other populations of the species? Marine Ecology Progress Series 238: 61–71.
Smith, C. M. & L. J. Walters, 1999. Fragmentation as a strategy for Caulerpa species: fates of fragments and implications for management of an invasive weed. Marine Ecology 20: 307–319.
Underwood, A. J., 1991. Beyond BACI: experimental designs for detecting human environmental impacts on temporal variations in natural populations. Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 42: 569–587.
Underwood, A. J., 1992 Beyond BACI: the detection of environmental impacts on populations in the real, but variable, world. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 161: 145–178.
Underwood, A. J., 1994. On Beyond BACI: sampling designs that might reliably detect environmental disturbance. Ecological Applications 412: 3–15.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Vanessa Hannan for her valuable assistance in the field and NSW Department of Primary Industries (formerly NSW Fisheries) for assistance with co-ordination of salting and sampling. Bob Creese provided valuable comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below are the electronic supplementary materials.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
O’Neill, K.M., Schreider, M.J., Glasby, T.M. et al. Lack of epifaunal response to the application of salt for managing the noxious green alga Caulerpa taxifolia in a coastal lake. Hydrobiologia 580, 135–142 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-006-0458-8
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-006-0458-8