Abstract
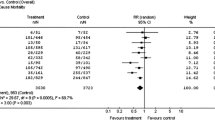
Previous studies of implantable cardiac resynchronization therapy plus defibrillator (CRT-D) therapy used for primary prevention of sudden cardiac death have suggested that CRT-D therapy is less effective in patients with mild heart failure and a wide QRS complex. However, the long-term benefits are variable. We performed a meta-analysis of randomized trials identified in systematic searches of MEDLINE, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Database. Three studies (3858 patients) with a mean follow-up of 66 months were included. Overall, CRT-D therapy was associated with significantly lower all-cause mortality than was implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) therapy (OR, 0.78; 95 % CI, 0.63–0.96; P = 0.02; I 2 = 19 %). However, the risk of cardiac mortality was comparable between two groups (OR, 0.74; 95 % CI, 0.53–1.01; P = 0.06). CRT-D treatment was associated with a significantly lower risk of hospitalization for heart failure (OR, 0.67; 95 % CI, 0.50–0.89; P = 0.005; I 2 = 55 %). The composite outcome of all-cause mortality and hospitalization for heart failure was also markedly lower with CRT-D therapy than with ICD treatment alone (OR, 0.67; 95 % CI, 0.57–0.77; P < 0.0001; I 2 = 0 %). CRT-D therapy decreased the long-term risk of mortality and heart failure events in patients with mild heart failure with a wide QRS complex. However, long-term risk of cardiac mortality was similar between two groups. More randomized studies are needed to confirm these findings, especially in patients with NYHA class I heart failure or patients without LBBB.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fan X, Hua W, Xu Y, Ding L, Niu H, Chen K, Xu B, Zhang S (2014) Incidence and predictors of sudden cardiac death in patients with reduced left ventricular ejection fraction after myocardial infarction in an era of revascularisation. Heart 100(16):1242–1249
Earley A, Persson R, Garlitski AC, Balk EM, Uhlig K (2014) Effectiveness of implantable cardioverter defibrillators for primary prevention of sudden cardiac death in subgroups a systematic review. Ann Intern Med 160(2):111–121
Leyva F, Nisam S, Auricchio A (2014) 20 years of cardiac resynchronization therapy. J Am Coll Cardiol 64(10):1047–1058
Higgins SL, Hummel JD, Niazi IK, Giudici MC, Worley SJ, Saxon LA, Boehmer JP, Higginbotham MB, De Marco T, Foster E, Yong PG (2003) Cardiac resynchronization therapy for the treatment of heart failure in patients with intraventricular conduction delay and malignant ventricular tachyarrhythmias. J Am Coll Cardiol 42(8):1454–1459
Linde C, Abraham WT, Gold MR, St John Sutton M, Ghio S, Daubert C, REVERSE (REsynchronization reVErses Remodeling in Systolic left vEntricular dysfunction) Study Group (2008) Randomized trial of cardiac resynchronization in mildly symptomatic heart failure patients and in asymptomatic patients with left ventricular dysfunction and previous heart failure symptoms. J Am Coll Cardiol 52(23):1834–1843
Moss AJ, Hall WJ, Cannom DS, Klein H, Brown MW, Daubert JP, Estes NA 3rd, Foster E, Greenberg H, Higgins SL, Pfeffer MA, Solomon SD, Wilber D, Zareba W, MADIT-CRT Trial Investigators (2009) Cardiac-resynchronization therapy for the prevention of heart-failure events. N Engl J Med 361(14):1329–1338
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. J Clin Epidemiol 62(10):1006–1012
Hardy RJ, Thompson SG (1998) Detecting and describing heterogeneity in meta-analysis. Stat Med 17(8):841–856
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 327(7414):557–560
Tang AS, Wells GA, Talajic M, Arnold MO, Sheldon R, Connolly S, Hohnloser SH, Nichol G, Birnie DH, Sapp JL, Yee R, Healey JS, Rouleau JL, Resynchronization-Defibrillation for Ambulatory Heart Failure Trial Investigators (2010) Cardiac-resynchronization therapy for mild-to-moderate heart failure. N Engl J Med 363(25):2385–2395
Goldenberg I, Kutyifa V, Klein HU, Cannom DS, Brown MW, Dan A, Daubert JP, Estes NA 3rd, Foster E, Greenberg H, Kautzner J, Klempfner R, Kuniss M, Merkely B, Pfeffer MA, Quesada A, Viskin S, McNitt S, Polonsky B, Ghanem A, Solomon SD, Wilber D, Zareba W, Moss AJ (2014) Survival with cardiac-resynchronization therapy in mild heart failure. N Engl J Med 370(18):1694–1701
Gold MR, Padhiar A, Mealing S, Sidhu MK, Tsintzos SI, Abraham WT (2015) Long-term extrapolation of clinical benefits among patients with mild heart failure receiving cardiac resynchronization therapy: analysis of the 5-Year Follow-Up From the REVERSE Study. JACC Heart Fail 3(9):691–700
Kutyifa V, Pouleur AC, Knappe D, Al-Ahmad A, Gibinski M, Wang PJ, McNitt S, Merkely B, Goldenberg I, Solomon SD, Moss AJ, Zareba W (2013) Dyssynchrony and the risk of ventricular arrhythmias. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 6(4):432–444
Ruschitzka F, Abraham WT, Singh JP, Bax JJ, Borer JS, Brugada J, Dickstein K, Ford I, Gorcsan J 3rd, Gras D, Krum H, Sogaard P, Holzmeister J, EchoCRT-Study-Group (2013) Cardiac-resynchronization therapy in heart failure with a narrow QRS complex. N Engl J Med 369(15):1395–1405
Abraham WT, Fisher WG, Smith AL, Delurgio DB, Leon AR, Loh E, Kocovic DZ, Packer M, Clavell AL, Hayes DL, Ellestad M, Trupp RJ, Underwood J, Pickering F, Truex C, McAtee P, Messenger J, MIRACLE Study Group. Multicenter InSync Randomized Clinical Evaluation (2002) Cardiac resynchronization in chronic heart failure. N Engl J Med 346(24):1845–1853
Cleland JG, Daubert JC, Erdmann E, Freemantle N, Gras D, Kappenberger L, Tavazzi L, Cardiac Resynchronization-Heart Failure (CARE-HF) Study Investigators (2005) The effect of cardiac resynchronization on morbidity and mortality in heart failure. N Engl J Med 352(15):1539–1549
Bristow MR, Saxon LA, Boehmer J, Krueger S, Kass DA, De Marco T, Carson P, DiCarlo L, DeMets D, White BG, DeVries DW, Feldman AM, Comparison of Medical Therapy, Pacing, and Defibrillation in Heart Failure (COMPANION) Investigators (2004) Cardiac-resynchronization therapy with or without an implantable defibrillator in advanced chronic heart failure. N Engl J Med 350(21):2140–2150
Brignole M, Auricchio A, Baron-Esquivias G, Bordachar P, Boriani G, Breithardt OA, Cleland J, Deharo JC, Delgado V, Elliott PM, Gorenek B, Israel CW, Leclercq C, Linde C, Mont L, Padeletti L, Sutton R, Vardas P, ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines (CPG), Zamorano JL, Achenbach S, Baumgartner H, Bax JJ, Bueno H, Dean V, Deaton C, Erol C, Fagard R, Ferrari R, Hasdai D, Hoes AW, Kirchhof P, Knuuti J, Kolh P, Lancellotti P, Linhart A, Nihoyannopoulos P, Piepoli MF, Ponikowski P, Sirnes PA, Tamargo JL, Tendera M, Torbicki A, Wijns W, Windecker S, Document Reviewers, Kirchhof P, Blomstrom-Lundqvist C, Badano LP, Aliyev F, Bänsch D, Baumgartner H, Bsata W, Buser P, Charron P, Daubert JC, Dobreanu D, Faerestrand S, Hasdai D, Hoes AW, Le Heuzey JY, Mavrakis H, McDonagh T, Merino JL, Nawar MM, Nielsen JC, Pieske B, Poposka L, Ruschitzka F, Tendera M, Van Gelder IC, Wilson CM (2013) 2013 ESC Guidelines on cardiac pacing and cardiac resynchronization therapy: the Task Force on cardiac pacing and resynchronization therapy of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Developed in collaboration with the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA). Eur Heart J 34(29):2281–2329
Abraham WT, Young JB, León AR, Adler S, Bank AJ, Hall SA, Lieberman R, Liem LB, O’Connell JB, Schroeder JS, Wheelan KR, Multicenter InSync ICD II Study Group (2004) Effects of cardiac resynchronization on disease progression in patients with left ventricular systolic dysfunction, an indication for an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator, and mildly symptomatic chronic heart failure. Circulation 110(18):2864–2868
Al-Majed NS, McAlister FA, Bakal JA, Ezekowitz JA (2011) Meta-analysis: cardiac resynchronization therapy for patients with less symptomatic heart failure. Ann Intern Med 154(6):401–412
Bradley DJ, Bradley EA, Baughman KL, Berger RD, Calkins H, Goodman SN, Kass DA, Powe NR (2003) Cardiac resynchronization and death from progressive heart failure: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. JAMA 289(6):730–740
Salukhe TV, Dimopoulos K, Francis D (2004) Cardiac resynchronisation may reduce all-cause mortality: meta-analysis of preliminary COMPANION data with CONTAK-CD, InSync ICD, MIRACLE and MUSTIC. Int J Cardiol 93(2–3):101–103
Rivero-Ayerza M, Theuns DA, Garcia-Garcia HM, Boersma E, Simoons M, Jordaens LJ (2006) Effects of cardiac resynchronization therapy on overall mortality and mode of death: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur Heart J 27(22):2682–2688
Wells G, Parkash R, Healey JS, Talajic M, Arnold JM, Sullivan S, Peterson J, Yetisir E, Theoret-Patrick P, Luce M, Tang AS (2011) Cardiac resynchronization therapy: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. CMAJ 183(4):421–429
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the grants from Natural Science Foundation of china (81373076) and Beijing Municipal Commission of Education (SQKM201210025010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, WP., Li, CL., Guo, JC. et al. Long-term efficacy of implantable cardiac resynchronization therapy plus defibrillator for primary prevention of sudden cardiac death in patients with mild heart failure: an updated meta-analysis. Heart Fail Rev 21, 447–453 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10741-016-9550-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10741-016-9550-y