Abstract
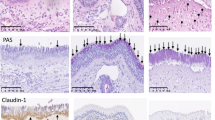
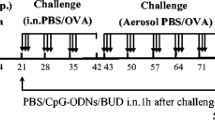
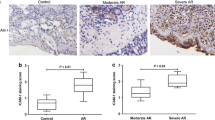
Although CD23-dependent transcytosis of IgE and IgE-derived immune complexes across respiratory epithelial cells is likely to play a pivotal role in the initiation and development of airway allergic inflammation, there is currently a lack of physiological support for this phenomena to suggest that the targeting of CD23 could be used as a means of therapeutic intervention. The present study was designed to detect the CD23 expression in the nasal mucosa of allergic rhinitis (AR) murine model by immunohistochemistry and western blotting, and to investigate whether intranasal anti-CD23 treatment could inhibit allergen-induced upper airway inflammation in the AR model. This is the first report to show that CD23 was constitutively expressed in murine nasal epithelial cells, and its expression was significantly up-regulated in the AR murine model. In vivo, the up-regulation of CD23 expression was correlated with increased serum IL-4 levels. Following intranasal anti-CD23 treatment, nasal symptoms were alleviated and histopathologic examination showed a significant decrease in eosinophilic infiltration. Meanwhile, ELISA analysis showed levels of serum leukotriene C4 (LTC4), eosinophil cation protein (ECP), ovalbumin (OVA)-specific IgE and IL-4 also significantly decreased, as were LTC4 and OVA-specific IgE in the nasal lavage fluid. Furthermore, Western blotting analysis showed that ECP expression in the nasal mucosa was down-regulated. Finally, flow cytometric analysis revealed anti-CD23 treatment inhibited Th2 cell responses. These results indicate that intranasal anti-CD23 treatment can reduce allergic responses in a murine model of allergic rhinitis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonnefoy JY, Lecoanet-Henchoz S, Aubry JP, Gauchat JF, Graber P (1995) CD23 and B-cell activation. Curr Opin Immunol 7(3):355–359
Bousquet J, Van Cauwenberge P, Khaltaev N (2001) Allergic rhinitis and its impact on asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 108(5 Suppl):S147–S334
Brozek JL, Bousquet J, Baena-Cagnani CE, Bonini S, Canonica GW, Casale TB, van Wijk RG, Ohta K, Zuberbier T, Schunemann HJ (2010) Allergic rhinitis and its impact on asthma (ARIA) guidelines: 2010 revision. J Allergy Clin Immunol 126(3):466–476. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2010.06.047
Du D, Ma X, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Zhou X, Li Y (2010) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of 17beta-estradiol postconditioning protection against gastric mucosal injury induced by ischemia/reperfusion in rats. Life Sci 86(1–2):30–38. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2009.11.001
Ford JW, Kilmon MA, Haas KM, Shelburne AE, Chan-Li Y, Conrad DH (2006) In vivo murine CD23 destabilization enhances CD23 shedding and IgE synthesis. Cell Immunol 243(2):107–117. doi:10.1016/j.cellimm.2007.01.004
Galli SJ, Tsai M, Piliponsky AM (2008) The development of allergic inflammation. Nature 454(7203):445–454. doi:10.1038/nature07204
Geha RS, Jabara HH, Brodeur SR (2003) The regulation of immunoglobulin E class-switch recombination. Nat Rev Immunol 3(9):721–732. doi:10.1038/nri1181
Gould HJ, Sutton BJ (2008) IgE in allergy and asthma today. Nat Rev Immunol 8(3):205–217. doi:10.1038/nri2273
Holgate ST (2007) Epithelium dysfunction in asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 120 (6):1233–1244; quiz 1245-1236. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2007.10.025
Kaiserlian D, Lachaux A, Grosjean I, Graber P, Bonnefoy JY (1993) Intestinal epithelial cells express the CD23/Fc epsilon RII molecule: enhanced expression in enteropathies. Immunology 80(1):90–95
Kay AB (2001) Allergy and allergic diseases. First of two parts. N Engl J Med 344(1):30–37. doi:10.1056/nejm200101043440106
Li H, Nowak-Wegrzyn A, Charlop-Powers Z, Shreffler W, Chehade M, Thomas S, Roda G, Dahan S, Sperber K, Berin MC (2006) Transcytosis of IgE-antigen complexes by CD23a in human intestinal epithelial cells and its role in food allergy. Gastroenterology 131(1):47–58. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2006.03.044
Li H, Chehade M, Liu W, Xiong H, Mayer L, Berin MC (2007) Allergen-IgE complexes trigger CD23-dependent CCL20 release from human intestinal epithelial cells. Gastroenterology 133(6):1905–1915. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2007.09.024
Mo JH, Kang EK, Quan SH, Rhee CS, Lee CH, Kim DY (2011) Anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha treatment reduces allergic responses in an allergic rhinitis mouse model. Allergy 66(2):279–286. doi:10.1111/j.1398-9995.2010.02476.x
Montagnac G, Yu LC, Bevilacqua C, Heyman M, Conrad DH, Perdue MH, Benmerah A (2005) Differential role for CD23 splice forms in apical to basolateral transcytosis of IgE/allergen complexes. Traffic 6(3):230–242. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0854.2005.00262.x
Palaniyandi S, Tomei E, Li Z, Conrad DH, Zhu X (2011) CD23-dependent transcytosis of IgE and immune complex across the polarized human respiratory epithelial cells. J Immunol 186(6):3484–3496. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1002146
Rao M, Lee WT, Conrad DH (1987) Characterization of a monoclonal antibody directed against the murine B lymphocyte receptor for IgE. J Immunol 138(6):1845–1851
Rivera J, Gilfillan AM (2006) Molecular regulation of mast cell activation. J Allergy Clin Immunol 117 (6):1214–1225; quiz 1226. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2006.04.015
Sokol CL, Barton GM, Farr AG, Medzhitov R (2008) A mechanism for the initiation of allergen-induced T helper type 2 responses. Nat Immunol 9(3):310–318. doi:10.1038/ni1558
Stelekati E, Orinska Z, Bulfone-Paus S (2007) Mast cells in allergy: innate instructors of adaptive responses. Immunobiology 212(6):505–519. doi:10.1016/j.imbio.2007.03.012
Takano K, Kojima T, Go M, Murata M, Ichimiya S, Himi T, Sawada N (2005) HLA-DR- and CD11c-positive dendritic cells penetrate beyond well-developed epithelial tight junctions in human nasal mucosa of allergic rhinitis. J Histochem Cytochem 53(5):611–619. doi:10.1369/jhc.4A6539.2005
Tu Y, Salim S, Bourgeois J, Di Leo V, Irvine EJ, Marshall JK, Perdue MH (2005) CD23-mediated IgE transport across human intestinal epithelium: inhibition by blocking sites of translation or binding. Gastroenterology 129(3):928–940. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2005.06.014
Wang YH, Angkasekwinai P, Lu N, Voo KS, Arima K, Hanabuchi S, Hippe A, Corrigan CJ, Dong C, Homey B, Yao Z, Ying S, Huston DP, Liu YJ (2007) IL-25 augments type 2 immune responses by enhancing the expansion and functions of TSLP-DC-activated Th2 memory cells. J Exp Med 204(8):1837–1847. doi:10.1084/jem.20070406
Yang PC, Berin MC, Yu LC, Conrad DH, Perdue MH (2000) Enhanced intestinal transepithelial antigen transport in allergic rats is mediated by IgE and CD23 (FcepsilonRII). J Clin Invest 106(7):879–886. doi:10.1172/jci9258
Yu LC, Yang PC, Berin MC, Di Leo V, Conrad DH, McKay DM, Satoskar AR, Perdue MH (2001) Enhanced transepithelial antigen transport in intestine of allergic mice is mediated by IgE/CD23 and regulated by interleukin-4. Gastroenterology 121(2):370–381
Yu LC, Montagnac G, Yang PC, Conrad DH, Benmerah A, Perdue MH (2003) Intestinal epithelial CD23 mediates enhanced antigen transport in allergy: evidence for novel splice forms. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 285(1):G223–G234. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00445.2002
Zhang M, Murphy RF, Agrawal DK (2007) Decoding IgE Fc receptors. Immunol Res 37(1):1–16
Zheng Y, Guo C, Zhang Y, Qi H, Sun Q, Xu E, Ma D, Wang Y (2011) Alleviation of murine allergic rhinitis by C19, a C-terminal peptide of chemokine-like factor 1 (CKLF1). Int Immunopharmacol 11(12):2188–2193. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2011.09.017
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Prof. Yulai Tian for his kind assistance in statistical analysis of the data. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30973281, 81271060).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, M., Du, D., Zhao, K. et al. In vivo intranasal anti-CD23 treatment inhibits allergic responses in a murine model of allergic rhinitis. J Mol Hist 44, 327–338 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-013-9484-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-013-9484-9