Abstract
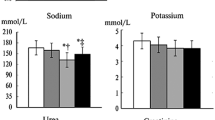
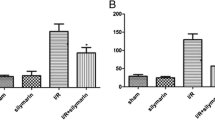
Renal ischemia–reperfusion (I/R) injury may occur after renal transplantation, thoracoabdominal aortic surgery, and renal artery interventions. This study was designed to investigate the effect of Urtica dioica L. (UD), in I/R induced renal injury. A total of 32 male Sprague–Dawley rats were divided into four groups: control, UD alone, I/R and I/R + UD; each group contain 8 animals. A rat model of renal I/R injury was induced by 45-min occlusion of the bilateral renal pedicles and 24-h reperfusion. In the UD group, 3 days before I/R, UD (2 ml/kg/day intraperitoneal) was administered by gastric gavage. All animals were sacrificed at the end of reperfusion and kidney tissues samples were obtained for histopathological investigation in all groups. To date, no more histopathological changes on intestinal I/R injury in rats by UD treatment have been reported. Renal I/R caused severe histopathological injury including tubular damage, atrophy dilatation, loss of brush border and hydropic epithelial cell degenerations, renal corpuscle atrophy, glomerular shrinkage, markedly focal mononuclear cell infiltrations in the kidney. UD treatment significantly attenuated the severity of intestinal I/R injury and significantly lowered tubulointerstitial damage score than the I/R group. The number of PCNA and TUNEL positive cells in the control and UD alone groups was negligible. When kidney sections were PCNA and TUNEL stained, there was a clear increase in the number of positive cells in the I/R group rats in the renal cortical tissues. However, there is a significant reduction in the activity of PCNA and TUNEL in kidney tissue of renal injury induced by renal I/R with UD therapy. Our results suggest that administration of UD attenuates renal I/R injury. These results suggest that UD treatment has a protective effect against renal damage induced by renal I/R. This protective effect is possibly due to its ability to inhibit I/R induced renal damage, apoptosis and cell proliferation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam A, Raij L (2000) Nitric oxide-angiotensin II axis in renal and cardiovascular injury. J Nephrol 13:211–220
Ak A, Caliskan O, Cırak C (2006) Economical importance of stinging netle (Urtica spp.) and its cultivation. J Fac Agric OMU 21:357–363
Alan C, Kocoglu H, Altintas R, Alici B, Resit Ersay A (2011) Protective effect of decorin on acute ischaemia-reperfusion injury in the rat kidney. Arch Med Sci 7(2):211–216
Bacallo R, Fine LG (1989) Molecular events in the organization of renal tubular epithelium from nephrogenesis to regeneration. Am J Physiol 257:913–924
Bagheri F, Gol A, Dabiri S, Javadi A (2011) Preventive effect of garlic juice on renal reperfusion injury. Iran J Kidney Dis 5(3):194–200
Barnes JL, Osgood RW, Reineck HJ, Stein JH (1981) Glomerular alterations in an ischemic model of acute renal failure. Lab Invest 45:378–386
Beeri R, Symon Z, Brezis M, Ben-Sasson SA, Baehr PH, Rosen S, Zager RA (1995) Rapid DNA fragmentation from hypoxia along the thick ascending limb of rat kidneys. Kidney Int 47:1806–1810
Bird JE, Milhoan K, Wilson CB, Young SG, Mundy CA, Parthasarathy S, Blantz RC (1988) Ischemic acute renal failure and antioxidant therapy in the rat: the relation between glomerular and tubular dysfunction. J Clin Invest 81:1630–1638
Bonegio R, Lieberthal W (2002) Role of apoptosis in the pathogenesis of acute renal failure. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 11:301–308
Bowen ID, Bowen SM, Jones AH (1988) Mitosis and apoptosis. Published by Chapman and Hall, London
Chatterjee PK, Cuzzocrea S, Thiemermann C (1999) Inhibitors of poly (ADPribose) synthetase protect rat proximal tubular cells against oxidant stress. Kidney Int 56:973–984
Daemen MA, van’t Veer C, Denecker G, Heemskerk VH, Wolfs TG, Clauss M, Vandenabeele P, Buurman WA (1999) Inhibition of apoptosis induced by ischemiareperfusion prevents inflammation. J Clin Invest 104:541–549
Dorai T, Fishman AI, Ding C, Batinic-Haberle I, Goldfarb DS, Grasso M (2011) Amelioration of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury with a novel protective cocktail. J Urol 186(6):2448–2454
Finn WF (1981) Nephron heterogeneity in polyuric acute renal failure. J Lab Clin Med 98:21–29
Gollackner B, Sedivy R, Rockenschaub S, Casati B, Wrba F, Langer F, Mittermayer C, Mittlböck M, Mühlbacher F, Steininger R (2000) Increased apoptosis of hepatocytes in vascular occlusion after orthotopic liver transplantation. Transpl Int 13:49–53
Gulçın I, Kufrevioglu OI, Oktay M, Buyukokuroglu ME (2004) Antioxidant, antimicrobial, antiulcer and analgesic activities of nettle (Urtica dioica L.). J Ethnopharmacol 90:205–215
Hauet T, Mothes D, Goujon JM, Caritez JC, Carretier M, le Moyec L, Eugene M, Tillement JP (1997) Trimetazidine prevents renal injury in the isolated perfused pig kidney exposed to prolonged cold ischemia. Transplantation 64:1082–1086
Hsu SM, Raine L, Fanger H (1981) Use of Avidin-Biotin-Peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem 29:577–580
Iwata M, Myerson D, Torok-Storb B, Zager RA (1994) An evaluation of renal tubular DNA laddering in response to oxygen deprivation and oxidant injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 5:1307–1313
Kahraman A, Erkasap N, Serteser M, Köken T (2003) Protective effect of quercetin on renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. J Nephrol 16(2):219–224
Kanter M, Coskun O, Budancamanak M (2005) Hepatoprotective effects of Nigella sativa L and Urtica dioica L on lipid peroxidation, antioxidant enzyme systems and liver enzymes in carbon tetrachloride-treated rats. World J Gastroenterol 11(42):6684–6688
Maghsoudi S, Gol A, Dabiri S, Javadi A (2011) Preventive effect of ginger (Zingiber officinale) pretreatment on renal ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Eur Surg Res 46(1):45–51
Matsuno T, Nakagawa K, Sasaki H (1994) Apoptosis in acute tubular necrosis and acute renal allograft rejection. Transpl Proc 26:2170–2173
Maxwell SR, Lip GY (1997) Reperfusion injury: a review of the pathophysiology, clinical manifestations and therapeutic options. Int J Cardiol 58:95–117
Mittman P (1990) Randomized, double-blind study of freeze-dried Urtica dioica in the treatment of allergic rhinitis. Planta Med 56:44–47
Okusa MD (2002) The inflammatory cascade in acute ischemic renal failure. Nephron 90:133–138
Padanilam BJ (2003) Cell death induced by acute renal injury: a perspective on the contributions of apoptosis and necrosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 284:608–627
Paller MS (1998) Acute renal failure: controversies, clinical trials and future directions. Semin Nephrol 18:482–489
Radhakrishnan J, Kiryluk K (2006) Acute renal failure outcomes in children and adults. Kidney Int 69:17–19
Roso NC, Correa RR, Castiglia YM, Carvalho LR, Scatena LM, de Souza AV, de Oliveira CC, Vianna PT (2012) Caffeic Acid phenethyl ester effects in the kidney during ischemia and reperfusion in rats anesthetized with isoflurane. Transpl Proc 44(5):1211–1213
Schierle GS, Hansson O, Leist M, Nicotera P, Widner H, Brundin P (1999) Caspase inhibition reduces apoptosis and increases survival of nigral transplants. Nat Med 5:97–100
Schumer M, Colombel MC, Sawczuk IS, Gobe G, Connor J, O’Toole KM, Olsson CA, Wise GJ, Buttyan R (1992) Morphologic, biochemical, and molecular evidence of apoptosis during the reperfusion phase after brief periods of renal ischemia. Am J Pathol 140:831–838
Singh D, Chopra K (2004) The effect of naringin, a bioflavonoid on ischemia-reperfusion induced renal injury in rats. Pharmacol Res 50(2):187–193
Singh D, Chander V, Chopra K (2004) The effect of quercetin, a bioflavonoid on ischemia/reperfusion induced renal injury in rats. Arch Med Res 35(6):484–494
Terzi A, Yildiz F, Coban S, Taskin A, Bitiren M, Aksoy N (2010) Protective effect of Urtica dioica on liver injury induced by hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury in rats. Duzce Med J 12:43–47
Thadhani R, Pascual M, Bonventre JV (1996) Acute renal failure. N Engl J Med 334:1448–1460
Toback FG (1992) Regeneration after acute tubular necrosis. Kidney Int 41:226–246
Wallin A, Zhang G, Jones TW, Jaken S, Stevens JL (1992) Mechanism of the nephrogenic repair response: studies on proliferation and vimentin expression after 35S-(1,2-dichlorovinyl)-l-cysteine nephrotoxicity in vivo and in cultured proximal tubule epithelial cells. Lab Invest 66:474–484
Weinberg JM (1991) The cell biology of ischemic renal injury. Kidney Int 39:476–500
Yaoita H, Ogawa K, Maehara K, Maruyama Y (1998) Attenuation of ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats by a caspase inhibitor. Circulation 97:276–281
Yildiz F, Coban S, Terzi A, Savas M, Bitiren M, Celik H, Aksoy N (2010) Protective effects of Nigella sativa against ischemia-reperfusion injury of kidneys. Ren Fail 32(1):126–131
Ysebaert DK, De Greef KE, Vercauteren SR, Verhulst A, Kockx M, Verpooten GA, De Broe ME (2003) Effect of immunosuppression on damage, leukocyte infiltration, and regeneration after severe warm ischemia/reperfusion renal injury. Kidney Int 64:864
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sayhan, M.B., Kanter, M., Oguz, S. et al. Protective effect of Urtica dioica L. on renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat. J Mol Hist 43, 691–698 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-012-9436-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-012-9436-9