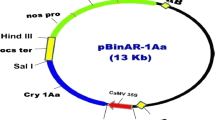
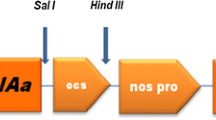
Abstract
Cultivating insect pest-resistant varieties is one of the most effective ways to prevent or mitigate pest infestation in Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris ssp. chinensis). Via the agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation method, this study introduced the protease inhibitor encoding gene sporamin into two widely cultured cultivars ‘Youdonger’ and ‘Shanghaiqing’, of the common variety of Chinese cabbages (B. campestriss ssp. chinensis var. communis), getting transgenic plants with high sporamin expression. In vitro insect bioassays indicated that, compared with the wild type plants, the transgenic plants exhibited improved resistance to diamondback moth (Plutella xylostella L.) The analysis of inheritance pattern of exogenous sporamin in the progenies of single copy insertion transgenic lines demonstrated that sporamin could be inherited and expressed stably in transgenic progenies. Field survey of the insect resistance under the normal culture condition confirmed the enhanced resistance in transgenic progenies to diamondback moth. Our results strongly suggest that sporamin is an efficient candidate gene for insect-resistant genetic engineering in Chinese cabbage.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cannell ME, Doherty A, Lazzeri PA, Barcelo P (1999) A population of wheat and tritordeum transformants showing a high degree of marker gene stability and heritability. Theor Appl Genet 99:772–784. doi:10.1007/s001220051296
Cao J, Zhao JZ, Tang J, Shelton A, Earle E (2002) Broccoli plants with pyramided cry1Ac and cry1C Bt genes control diamondback moths resistant to Cry1A and Cry1C proteins. Theor Appl Genet 105:258–264. doi:10.1007/s00122-002-0942-0
Chen HJ, Wang SJ, Chen CC, Yeh KW (2006) New gene construction strategy in T-DNA vector to enhance expression level of sweet potato sporamin and insect resistance in transgenic Brassica oleracea. Plant Sci 171:367–374. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2006.04.003
Cordero MJ, Raventós D, San Segundo B (1994) Expression of a maize proteinase-inhibitor gene is induced in response to wounding and fungal infection: systemic wound-response of a monocot gene. Plant J 6:141–150 doi:10.1046/j.1365-313X.1994.6020141.x
Doyle J (1991) DNA protocols for plants. In: Hewitt G, Johnson AWB, Young JPW (eds) Molecular techniques in taxonomy. NATO ASI series H, cell biology, vol 57. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 283–293
Hilder VA, Barker RF, Samour RA, Gatehouse AMR, Gatehouse JA, Boulter D (1989) Protein and cDNA sequences of Bowman-Birk protease inhibitors from the cowpea (Vigna unguiculata Walp.) Plant Mol Biol 13:701–710. doi:10.1007/BF00016025
Hu R, Wang J, Ji Y, Song Y, Yang S (2012) Overexpression of poplar wounding-inducible genes in Arabidopsis caused improved resistance against Helicoverpa armigera (Hubner) larvae. Breed Sci 62:288–291. doi:10.1270/jsbbs.62.288
Huang F, Shi MY, Li JY, Chen XX (2009) Changes in hemocytes of Plutella xylostella after parasitism by Diadegma semiclausum. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 70:177–187. doi:10.1002/arch.20284
Karban R, Anurag AA, Mangel M (1997) The benefits of induced defenses against herbivores. Ecology 78:1351–1355. doi:10.1890/0012-9658(1997)078
Koiwa H, Bressan RA, Hasegawa PM (1997) Regulation of protease inhibitors and plant defense. Trends Plant Sci 2:379–384 doi:10.1016/S1360-1385(97)90052-2
Littell RC, Milliken GA, Stroup WW, Wolfinger RD, Schabenberger O (2006) SAS® for mixed models, 2nd edn. Cary, NC: SAS Institute Inc.
Liu HB, Guo X, Naeem MS, Xu L, Zhang W, Tang G, Zhou W (2011a) Transgenic Brassica napus L. lines carrying a two gene construct demonstrate enhanced resistance against Plutella xylostellaa and Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 106:143–151. doi:10.1007/s11240-010-9902-6
Liu HB, Naeem MS, Liu D, Zhu YN, Guo X, Cui P, Zhou WJ (2011b) Analyses of inheritance patterns and consistent expression of sporamin and chitinase PjChi-1 genes in Brassica napus. Plant Breeding 130:345–351. doi:10.1111/j.1439-05232010.01827.x
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2–∆∆ C T method. Methods 25:402–408. doi:10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Maqbool SB, Riazuddin S, Loc NT, Gatehouse AMR, Gatehouse JA, Christou P (2001) Expression of multiple insecticidal genes confers broad resistance againsta range of different rice pests. Mol Breeding 7:85–93. doi:10.1023/A:1009644712157
Qiu L, Wu T, Dong H, Wu L, Cao J, Huang L (2013) High-level expression of sporamin in transgenic Chinese cabbage enhances resistance against diamondback moth. Plant Mol Biol Rep 31:657–664. doi:10.1007/s11105-012-0536-1
Quilis J, Belen LG, Meynard D, Guiderdoni E, Segundo BS (2014) Inducible expression of a fusion gene encoding two proteinase inhibitors leads to insect and pathogen resistance in transgenic rice. Plant Biotechnol J 12:367–377. doi:10.1111/pbi.12143
Rajendran SK, Lin IW, Chen MJ, Chen CY, Yeh KW (2014) Differential activation of sporamin expression in response to abiotic mechanical wounding and biotic herbivore attack in the sweet potato. BMC Plant Biol 14:297–300. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-14-112
Rooke L, Barro F, Tatham AS, Fido R, Steele S, Békés F, Gras P, Martin A, Lazzeri PA, Shewry PR, Barcelo P (1999) Altered functional properties of tritordeum by transformation with HMW glutenin subunit genes. Theor Appl Genet 99:851–858. doi:10.1007/s001220051305
Roush RT, Shelton AM (1997) Assessing the odds: the emergence of resistance to Bt transgenic plants. Nat Biotechnol 15:816–817. doi:10.1038/nbt0997-816
Senthilkumar R, Cheng CP, Yeh KW (2010) Genetically pyramiding protease-inhibitor genes for dual broad-spectrum resistance against insect and phytopathogens in transgenic tobacco. Plant Biotechnol J 8:65–75. doi:10.1111/j.1467-76522009.00466.x
Seo SG, Bea SH, Jun BK, Kim ST, Kwon SY, Kim SH (2015) Overexpression of ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase (IbAGPaseS) affects expression of carbohydrate regulated genes in sweet potato [Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam. cv. Yulmi]. Gene Genomics 37:595–605. doi:10.1007/s13258-015-0289-y
Shelton AL (2004) Variation in chemical defenses of plants may improve the effectiveness of defense. Evol Ecol Res 6:709–726
Stewart SD, Adamczyk JJ, Knighten KS, Davis FM (2001) Impact of Bt cottons expressing one or two insecticidal proteins of Bacillus thuringiensis Berliner on growth and survival of noctuid (Lepidoptera) larvae. J Econ Entomol 94:752–760. doi:10.1603/0022-0493-94.3.752
Stoger E, Williams S, Keen D, Christou P (1997) Molecular characteristics of transgenic wheat and the effect on transgene expression. Transgenic Res 7:463–471. doi:10.1023/A:1008833324193
Tang JD, Gilboa S, Roush RT, Shelton AM (1997) Inheritance, stability, and lack-of-fitness costs of field-selected resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis in diamondback moth (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae) from florida. J Econ Entomol 90:732–741. doi:10.1093/jee/90.3.732
Wang SJ, Lan YC, Chen SF, Chen YM, Yeh KW (2002) Wound-response regulation of the sweet potato sporamin gene promoter region. Plant Mol Biol 48:223–231. doi:10.1023/A:1013359227041
Wang EH, Zhou Y, Jing H, Hai BX (2013) Effects of 90-day feeding of transgenic Bt rice TT51 on the reproductive system in male rats. Food Chem Toxicol 62:390–396. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2013.08.032
Wu Y, Llewellyn D, Mathews A, Dennis ES (1997) Adaptation of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) to a proteinase inhibitor expressed in transgenic tobacco. Mol Breeding 3:371–380. doi:10.1023/A:1009681323131
Yeh KW, Lin MI, Tuan SJ, Chen YM, Lin CY, Kao SS (1997) Sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas) trypsin inhibitors expressed in transgenic tobacco plants confer resistance against Spodoptera litura. Plant Cell Rep 16:696–699. doi:10.1007/s002990050304
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Key Technology Innovation Team of Zhejiang Province (No. 2013TD05), the Sci-Technology Project of Zhejiang Province (2009C32026), and the Grand Science and Technology Special Project of Zhejiang Province (No. 2012C12903). The authors would like to thank Dr. Kai-Wun Yeh (Taiwan University) and Dr. Xuexin Cheng (Zhejiang University) for providing the vector and diamondback moth larvae, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, J., Li, M., Qiu, L. et al. Stable expression of exogenous imported sporamin in transgenic Chinese cabbage enhances resistance against insects. Plant Growth Regul 81, 543–552 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-016-0231-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-016-0231-6