Abstract
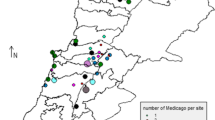
The wild species in general is considered to be the reservoir of genes especially for biotic and abiotic stresses. In okra, the predominant biotic stresses are yellow vein mosaic disease (YVMD), shoot and fruit borer and leaf hopper. Sixty eight (68) accessions belonging to four wild Abelmoschus species [Abelmoschus caillei (A. Chev.) Stevels, Abelmoschus manihot (L.) Medik., Abelmoschus moschatus (L.) Medik. and Abelmoschus tuberculatus Pal et Singh] and eight okra varieties were characterized and evaluated for phenological characters including biotic stresses under natural epiphytotic condition. The wild species examined consisted of 18 accessions (16 exotic and 2 indigenous) of A. caillei, 29 accessions of A. manihot, 16 accessions of A. moschatus and 5 accessions of A. tuberculatus. All the wild Abelmoschus species exhibited high diversity (as measured by Shannon Diversity Index) for 3 qualitative characters viz. intensity of stem colour, leaf shape, epicalyx shape, 13 quantitative characters and 3 biotic stress parameters. Among the wild species, A. caillei and A. tuberculatus showed maximum and minimum diversity for qualitative characters, respectively. There was significant variation for 19 out of 24 quantitative characters studied. Inter-species diversity pattern as estimated through Ward’s Minimum Variance Dendrogram and Principal Component Analysis revealed clear differentiation among the species with minimum overlapping indicating close association between geographical origins and clustering pattern. Intra-species diversity indicated role of specific adaptation in sub-clustering. Resistance to YVMD was found in accessions belonging to three wild species viz. A. caillei, A. manihot and A. moschatus while resistance to shoot and fruit borer and leaf hopper was found in accessions of all the four wild species. The resistant accessions can further be used for introgressing biotic stress resistance through pre-breeding into cultivated okra species.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adeoluwa O, Kehinde O (2011) Genetic variability studies in West African okra (Abelmoschus caillei). Agric Biol J North Am 2:1326–1335
Aladele SE, Ariyo O, de Lapena R (2008) Genetic relationships among West African okra (Abelmoschus caillei) and Asian genotypes (Abelmoschus esculentus) using RAPD. Afr J Biotechnol 7:10
Anitha K, Nandihalli B (2009) Evaluation of some okra hybrids against leafhopper and aphid Karnataka. J Agric Sci 22:718–719
Ariyo OJ (1990) Variation and heritability of fifteen characters on okra (Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench). Trop Agric 67:213–216
Ariyo O (1993) Genetic diversity in West African okra (Abelmoschus caillei (A. Chev.) Stevels)—Multivariate analysis of morphological and agronomic characteristics. Genet Resour Crop Evol 40:25–32
Bag MK, Gautam N, Prasad T, Pandey S, Dutta M, Roy A (2014) Evaluation of an Indian collection of black gram germplasm and identification of resistance sources to Mungbean yellow mosaic virus. Crop Prot 61:92–101
Bas T, Koludar J (2001) Characterisation on okra (Hibiscus esculentus L.) germplasm in Turkey. Acta Hort 560:133–136
Bisht IS, Bhat KV (2006) Okra (Abelmoschus species). In: Singh RJ (ed) Genetic resources, chromosome engineering, and crop improvement: vegetable crops. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 148–162
Bisht I, Patel D, Mahajan R (1997) Classification of genetic diversity in Abelmoschus tuberculatus germplasm collection using morphometric data. Ann Appl Biol 130:325–335
Borssum Waalkes Jv (1966) Malesian Malvaceae revised. Blumea 14:1–213
Burton GW (1952) Quantitative inheritance in grasses. Proc 6th Int Grassland Cong 1:277–283
Camciuc M, Deplagne M, Vilarem G, Gaset A (1998) Okra—Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench. a crop with economic potential for set aside acreage in France. Ind Crops Prod 7:257–264
Charrier A (1984) Genetic resources of the genus Abelmoschus Med. (okra)
Clifford HT, Stephenson W (1975) An introduction to numerical classification, vol 229. Academic Press, New York
Dhankar BS, Mishra JP (2004) Objectives of okra breeding. In: Singh PK (ed) Hybrid vegetable development. Haworth Press, Binghamton NY, pp 195–209
Dhankar BS, Mishra JP (2005) Okra. In: Narendra S, Thamburaj T (eds) Textbook of vegetables, tuber crops and spices. ICAR, New Delhi, pp 222–237
Düzyaman E (2005) Phenotypic diversity within a collection of distinct okra (Abelmoschus esculentus) cultivars derived from Turkish landraces. Genet Resour Crop Evol 52:1019–1030
Duzyaman E, Vural H (2002) Different approaches in the improvement process of local okra varieties. Acta Hort 579:139–144
Federer WT (1956) Augmented designs. Hawaii Planters Record 55:191–208
Fougat RS, Purohit AR, Kumar S, Parekh MJ, Kumar M (2015) SSR based genetic diversity in Abelmoschus species. Indian J Agric Sci 85:1223–1228
Hamon S, Van Stolen DH (1989) Characterization and evaluation of okra. In: Brown AHD (ed) The use of plant genetic resources. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 173–196
Hamon S, Charrier A, Koechlin J, Van Sloten D (1991) [Potential improvement of okra (Abelmoschus spp.) through the study of its genetic resources] Plant Genetic Resources Newsletter (IBPGR/FAO)
Iqbal J, Mansoor H, Muhammad A, Shahbaz T, Amjad A (2008) Screening of Okra genotypes against Jassid, Amrasca biguttula biguttula (Ishida) (Homoptera: Cicadellidae). Pak J Agric Sci 45:448–451
Jalgaonkar VN, Patil PD, Munj AY, Naik KV (2002) Screening of new germplasm of okra, Abelmoschus esculentus L. against shoot and fruit borer Earias vitella and flea beetle Monolepta signata. Pestology 26:21–25
Jambhale N, Nerkar Y (1986) Parbhani Kranti, a yellow vein mosaic-resistant Okra. Hort Sci 21:1470–1471
Kumar S, Reddy MT (2015) Morphological characterization and agronomic evaluation of yellow vein mosaic virus resistant single cross hybrids for yield and quality traits in Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench.). doi:10.4236/oalib.1101720
Kumar S, Dagnoko S, Haougui A, Ratnadass A, Pasternak D, Kouame C (2010) Okra (Abelmoschus spp.) in West and Central Africa: potential and progress on its improvement. Afr J Agric Res 25:3590–3598
Kyriakopoulou OG, Arens P, Pelgrom KT, Karapanos I, Bebeli P, Passam HC (2014) Genetic and morphological diversity of okra (Abelmoschus esculentus [L.] Moench.) genotypes and their possible relationships, with particular reference to Greek landraces. Sci Hortic 171:58–70
Mahajan R, Sapra R, Umesh S, Singh M, Sharma G (2000) Minimal descriptors (for characterization and evaluation) of agri-horticultural crops (Part I). National Bureau of Plant Genetic Resources, New Delhi
Mastoi AH, Memon SA, Haq WH (2013) Varietal resistance of okra against white fly (Bemisia tabaci) and fruit borer (Earias spp.). Sch J Agric Sci 3:78–82
Mishra P, Singh Y, Nautiyal M (1988) Screening of brinjal varieties for resistance to shoot and fruit borer (Leucinodes orbonalis Guen.) (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). South Indian Hortic 36:188–192
Mishra D, Naik S, Kumar S, Kukreja A, Dwivedi S, Singh A (2000) Cultivation and processing of Abelmoschus moschatus. J Med Aromatic Plant Sci 22:624–628
Nene Y, Srivastava S, Naresh J (1972) Evaluation of black-gram (Phaseolus mungo Roxb.) and greengram (Phaseolus aureus Roxb.) varieties and germplasms for resistance to yellow-mosaic virus of green-gram. Indian J Agric Sci 42:251–254
Omonhinmin C, Osawaru M (2005) Morphological characterization of two species of Abelmoschus: Abelmoschus esculentus and Abelmoschus caillei. Plant Genet Resour Newsl (IPGRI/FAO) 144:51–55
Oppong-Sekyere D, Akromah R, Nyamah E, Brenya E, Yeboah S (2011) Characterization of okra (Abelmoschus spp. L.) germplasm based on morphological characters in Ghana. J Plant Breed Crop Sci 3:367–378
Osawaru M, Ogwu M, Dania-Ogbe F (2014) Morphological assessment of the genetic variability among 53 Accessions of West African okra [Abelmoschus caillei (A. Chev.) Stevels] from South Western Nigeria. Nigerian J Basic Appl Sci 21:227–238
Pandit M, Das B, Ghosh S (2012) Nutritional cum medicinal properties and insect-pest complex of Abelmoschus moschatus - an underutilized vegetable. In: Proceedings of the international symposium on minor fruits and medicinal plants for health and ecological security (ISMF & MP), West Bengal, India, 19-22 December, 2011. Bidhan Chandra Krishi Viswandyalaya, pp 47–50
Priyanka DK, Animesh DK, Mandal A, Saha A, Sengupta S (2011) Morphological anatomical cytological and palynological characterization of two cultivars of Abelmoschus moschatus (L.) Medik. (Malvaceae). Int J Res Ayurveda Pharm (IJRAP) 2:670–676
Protection of Plant Varieties and Farmers’ Rights Authority (2009) Guidelines for the Conduct of Test for distinctiveness, uniformity and stability on okra/lady’s finger (Abelmoschus moschatus (L.) Moench.). Chandu Press, Delhi P.18
Rana RS, Thomas TA, Arora RK (1991) Plant genetic resources activities in okra: an Indian perspective. International Crop Network Series. 5. Report of an international workshop on okra genetic resources. International Board for Plant Genetic Resources, Rome
Reddy TM, Hari Babu K, Ganesh M, Chandrasekhar Reddy K, Begum H, Purushothama Reddy B, Narshimulu G (2012) Genetic variability analysis for the selection of elite genotypes based on pod yield and quality from the germplasm of okra (Abelmoschus esculentus L. Moench). J Agric Technol 8:639–655
Ren J, McFerson JR, Li R, Kresovich S, Lamboy WF (1995) Identities and relationships among Chinese vegetable Brassicas as determined by random amplified polymorphic DNA markers. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 120:548–555
R.H.S. (1986) Colour Chart, 1 and 2 edn. Royal Horticultural Society, London
Samarajeewa P, Rathnayaka R (2004) Disease resistance and genetic variation of wild relatives of okra (Abelmoschus esculentus L.). Ann Sri Lanka Depart Agric 6:167–176
SAS (2009) Statistical analysis software system, Version 9.3. SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA
Shannon CE, Weaver W (1949) The mathematical theory of communication. University of Illinois Press, Urbana
Sharma B, Sharma O (1984) Breeding for resistance to yellow-vein mosaic virus in okra. Indian J Agric Sci 54:917–920
Shukla A, Pathak S, Agrawal R (1997) Seasonal incidence of okra shoot and fruit borer Earias vittella (Fab.) and effect of temperature on its infestation level. Adv Plant Sci 10:169–172
Singh A, Singh K (2000) Screening for desease incidence of yellow vein mosaic virus (YVMV) in okra [Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench] treated with gamma rays and EMS. Veg Sci 27:72–75
Singh GS, Sahni M, Shah BR (1988) Biochemical and morphological basis of resistance to okra plant. Euphytica 21:147–153
Singh B, Rai M, Kalloo G, Satpathy S, Pandey K (2006) Wild taxa of okra (Abelmoschus species): reservoir of genes for resistance to biotic stresses. Acta Hortic 752:323–328
Sivasubramanian S, Menon M (1973) Heterosis and inbreeding depression in rice. Madras Agric J 60:1339
Sowei J, Osilis P (1993) Aibika (Abelmoschus manihot) germplasm in Papua New Guinea Papua New Guinea. J Agric For Fisheries (Papua New Guinea) 36:60–69
Srinivasa N, Sugeetha G (2001) Field screening of certain okra varieties for resistance against major pests. Insect Environ 7:74–76
Stalker HT (1980) Utilization of wild species for crop improvement. Adv Agron 33:1–147
Thakur MR (1976) Inheritance of resistance to Yellow Vein Mosaic (YVM) in a cross of okra species, Abelmoschus esculentus × A. manihot ssp. manihot. SABRAO J 8:69–73
Velayudhan K, Amalraj V, Thomas T (1996) Collecting germplasm of okra and its wild relatives in southern India. Indian J Plant Genet Resour 9:261–268
Velayudhan K, Nizar MA, John J, Latha M, Abraham Z (2007) A note on taxonomy of the genus Abelmoschus in India with special reference to the vulnerable status of Abelmoschus moschatus subsp. tuberosus (Span) Borss. Plant Genetic Resources Newsletter = Bulletin de Ressources Phytogénétiques = Noticiario de Recursos Fitogenéticos 152:77–81
Yuan CY, Ping W, Chen PP et al (2015) Genetic diversity revealed by morphological traits and ISSR markers in 48 Okras (Abelmoschus esculentus L.). Physiol Mol Biol Plants 21:359–364. doi:10.1007/s12298-015-0303-5
Zhou Z et al (2015) Resequencing 302 wild and cultivated accessions identifies genes related to domestication and improvement in soybean. Nat Biotechnol 33:408–414
Acknowledgments
The authors are highly thankful to Director, NBPGR, New Delhi for providing facilities and support. The authors acknowledge Head, Germplasm Conservation Division, NBPGR; and Officer Incharge(s) of NBPGR Regional Station Thrissur and Akola for timely supplying germplasm of wild species.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gangopadhyay, K.K., Singh, A., Bag, M.K. et al. Diversity analysis and evaluation of wild Abelmoschus species for agro-morphological traits and major biotic stresses under the north western agro-climatic condition of India. Genet Resour Crop Evol 64, 775–790 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-016-0400-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-016-0400-5