Abstract
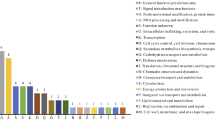
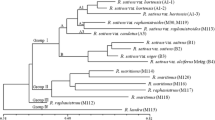
A total of 8117 suitable SSR-contaning ESTs were acquired by screening from a Malus EST database, among which dinudeotide SSRs were the most abundant repeat motif, within which, CT/TC followed by AG/GA were predominant. Based on the suitable sequences, we developed 147 SSR primer pairs, of which 94 pairs gave amplifications within the expected size range while 65 pairs were found to be polymorphic after a preliminary test. Eighteen primer pairs selected randomly were further used to assess genetic relationship among 20 Malus species or cultivars. As a result, these primers displayed high level of polymorphism with a mean of 6.94 alleles per locus and UPGMA cluster analysis grouped twenty Malus accessions into five groups at the similarity level of 0.6800 that were largely congruent to the traditional taxonomy. Subsequently, all of the 94 primer pairs were tested on four accessions of Pyrus to evaluate the transferability of the markers, and 40 of 72 functional SSRs produced polymorphic amplicons from which 8 SSR loci selected randomly were employed to analyze genetic diversity and relationship among a collection of Pyrus. The 8 primer pairs produced expected bands with the similar size in apples with an average of 7.375 alleles per locus. The observed heterozygosity of different loci ranged from 0.29 (MES96) to 0.83 (MES138), with a mean of 0.55 which is lower than 0.63 reported in genome-derived SSR marker analysis in Pyrus. The UPGMA dendrogram was similar to the previous results obtained by using RAPD and AFLP markers. Our results showed that these EST-SSR markers displayed reliable amplification and considerable polymorphism in both Malus and Pyrus, and will contribute to the knowledge of genetic study of Malus and genetically closed genera.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bao L, Chen KS, Zhang D, Cao YF, Yamamoto T, Teng Y (2007) Genetic diversity and similarity of pear (Pyrus L.) cultivars native to East Asia revealed by SSR (simple sequence repeat) markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 54:959–971
Bao L, Chen KS, Zhang D, Li XG, Teng Y (2008) An assessment of genetic variability and relationships within Asian pears based on AFLP (amplified fragment length polymorphism) markers. Sci Hortic 116:374–380
Barrett B, Griffiths A, Schreiber M, Ellison N, Mercer C, Bouton J, Ong B, Forster J, Sawbridge T, Spangenberg G, Bryan G, Woodfield D (2004) A microsatellite map of white clover. Theor Appl Genet 109:596–608
Bassil N, Postman JD (2010) Identification of European and Asian pears using EST-SSRs from Pyrus. Genet Resour Crop Evol. doi:10.1007/s10722-009-9474-7
Bell RL, Quamme HA, Layne REC, Skirvin RM (1996) Pears. In: Janick J, Moore JN (eds) Fruit breeding, tree and tropical fruits, vol 1. John Wiley, London, pp 441–514
Botstein D, White RL, Skolnick M, Davis RW (1980) Construction of genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet 32:314–331
Celton JM, Tustin DS, Chagné D, Gardiner SE (2008) Construction of a dense genetic linkage map for apple rootstocks using SSRs developed from Malus ESTs and Pyrus genomic sequences. Tree Genet Genomes 2:86–97. doi:10.1007/s11295-008-0171-z
Chagné D, Carlisle CM, Blond C, Volz RK, Whitworth CJ, Oraguzie NC, Crowhurst RN, Allan AC, Espley RV, Hellens RP, Gardiner SE (2007) Mapping a candidate gene (MdMYB10) for red flesh and foliage colour in apple. BMC Genomics 8:212. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-8-212
Chen C, Zhou P, Choi YA, Huang S, Gmitter FG Jr (2006) Mining and characterizing microsatellites from Citrus ESTs. Theor Appl Genet 112:1248–1257
DeCandolle AP (1825) Prodromus Systematis Naturalis Regni Vegetabilis. Paris:Sumptibus Sociorum Treuttel et Würtz. Rece de Pourbon No.17. Venitque in Eotumdem Bibliopolüs Argentorati et Londini 2:633–636
Decroocq V, Fave MG, Hagen L, Bordenave L, Decroocq S (2003) Development and transferability of apricot and grape EST microsatellite markers across taxa. Theor Appl Genet 106:912–922
Dellaporta SL, Wood J, Hicks JB (1983) A plant DNA minipreparation: version II. Plant Mol Biol Rep 1:19–21
Dirlewanger E, Cosson P, Tavaud M, Aranzana J, Poizat C, Zanetto A, Arus P, Laigret F (2002) Development of microsatellite markers in peach [Prunus persica (L.) Batsch] and their use in genetic diversity analysis in peach and sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.). Theor Appl Genet 105:127–138
Ellegren H, Moore S, Robinson N, Byrne K, Ward W, Sheldon BC (1997) Microsatellites evolution—a reciprocal study of repeat lengths at homologous loci in cattle and sheep. Mol Biol Evol 14:854–860
Gonzalez-Martinez SC, Robledo-Arnuncio JJ, Collada C, Diaz A, Williams CG, Alia R, Cervera MT (2004) Cross-amplification and sequence variation of microsatellite loci in Eurasian hard pines. Theor Appl Genet 109:103–111
Gupta PK, Rustgi S, Sharma S, Singh R, Kumar N, Balyan HS (2003) Transferable EST-SSR markers for the study of polymorphism and genetic diversity in bread wheat. Mol Genet Genomics 270:315–323
Hackauf B, Wehling P (2002) Identification of microsatellite polymorphisms in an expressed portion of the rye genome. Plant Breed 121:17–25
Huckins CA (1972) A revision of the sections of the genus Malus Miller. Ph.D. Thesis, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY
Jang JT, Tanabe K, Tamura F, Banno K (1992) Identification of Pyrus species by leaf peroxidase isozyme phenotypes (in Japanese with English summary). J Jpn Soc Hortic Sci 61:273–286
Jia XP, Shi YS, Song YC, Wang GY, Wang TY, Li Y (2007) Development of EST-SSR in foxtail millet (Setaria italica). Genet Resour Crop Evol 54:233–236
Jiang D, Zhong GY, Hong QB (2006) Analysis of microsatellites in Citrus Unigenes. Acta Genetica Sinica 33:345–353 (in Chinese)
Kajiura I, Sato Y (1990) Recent progress in Japanese pear (Pyrus pyrifolia Nakai) breeding and descriptions of cultivars based on literature review (in Japanese with English summary). Bull Fruit Tree Res Stn Extra 1:1–329
Kantety RV, Rota ML, Matthews DE, Sorrells ME (2002) Data mining for simple sequence repeats in expressed sequence tags from barley, maize, rice, sorghum and wheat. Plant Mol Biol 48:501–510
Kikuchi A (1948) Horticulture of fruit trees, vol 1. Yokendo, Tokyo (in Japanese)
Langenfeld WT (1991) Apple trees. Morphological evolution, phylogeny, geography and systematics. Riga (Zinatne) 232 (in Russian)
Lewin B (1994) Genes V. Oxford University Press, New York
Li Y (1996) A critical review of the species and the classification of the genus Malus Mill. in the world. Journal of Fruit Science, Vol 10 (Suppl) Zhengzhou Fruit Research Institute, pp 63–81 (in Chinese)
Li Y (1999) An investigation and studies on the origin and evolution of Malus domestica Borkh. in the world. Acta Hortic Sinica 26:213–220
Li Y (2001) Researches of germplasm resources of Malus Mill. Agriculture Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Linnaeus C (1753) Species plantarum. Bernard Quaritch, London
Miyao A, Zhong HS, Monna L, Yano M, Yamamoto K, Havukkala I, Minobe Y, Sasaki T (1996) Characterization and genetic mapping of simple sequence repeats in the rice genome. DNA Res 3:233–238
Nei M, Li WH (1979) Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:5269–5273
Newcomb RD, Crowhurst RN, Gleave AP, Rikkerink EHA, Allan AC, Beuning LL, Bowen JH, Gera E, Jamieson KR, Janssen BJ, Laing WA, McArtney S, Nain B, Ross GS, Snowden KC, Souleyre EJF, Walton EF, Yauk YK (2006) Analysis of expressed sequence tags from apple. Plant Physiol 141:147–166
Pierantoni L, Cho KH, Shin IS, Chiodini R, Tartarini S, Dondini L, Kang SJ, Sansavini S (2004) Characterisation and transferability of apple SSRs to two European pear F1 populations. Theor Appl Genet 109:1519–1524
Pillen K, Binder A, Kreuzkam B, Ramsay L, Waugh R, Förster J, Léon J (2000) Mapping new EMBL-derived barley microsatellites and their use in differentiating German barley cultivars. Theor Appl Genet 101:652–660
Poncet V, Hamon P, Minier J, Carasco C, Hamon S, Noirot M (2004) SSR cross-amplification and variation within coffee trees (Coffea spp.). Genome 47:1071–1081
Powell W, Machray GC, Provan J (1996) Polymorphism revealed by simple sequence repeats. Trends Plant Sci 1:215–222
Pu F, Wang Y (1963) Pomology of China. Pears, vol 3. Shanghai Science and Technology Press, Shanghai (in Chinese)
Pu F, Huang L, Sun B, Li S (1989) Pear cultivars. Agriculture Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Rallo P, Tenzer I, Gessler C, Baldoni L, Dorado G, Martin A (2003) Transferability of olive microsatellite loci across the genus Olea. Theor Appl Genet 107:940–946
Rehder A (1940) Manual of cultivated trees and shrubs, 2nd edn. Macmillan, New York
Robinson JP, Harris SA, Juniper BE (2001) Taxonomy of the genus Malus Mill. (Rosaceae) with emphasis on the cultivated apple, M. domestica Borkh. Plant Syst Evol 226:35–58
Roder MS, Korzun V, Wendehake K, Plaschke J, Tixier MH, Leroy P, Ganal MW (1998) A microsatellite map of wheat. Genetics 149:2007–2023
Rohlf FJ (1998) Numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system. Version 2.0. Exeter Software, Setauket
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Scott KD, Eggler P, Seaton G, Rossetto M, Ablett EM, Lee LS, Henry RJ (2000) Analysis of SSRs derived from grape ESTs. Theor Appl Genet 100:723–726
Silfverberg-Dilworth E, Matasci CL, Van DE, Weg WE, Kaauwen MPW, Walser M, Kodde LP, Soglio V, Gianfranceschi L, Durel CE, Costa F, Yamamoto T, Koller B, Gessler C, Patocchi A (2006) Microsatellite markers spanning the apple (Malus × domestica Borkh.) genome. Tree Genet Genomes 2:202–224
Teng Y, Tanabe K (2004) Reconsideration on the origin of cultivated pears native to East Asia. Acta Hortic 634:175–182
Teng Y, Tanabe K, Tamura F, Itai A (2001) Genetic relationships of pear cultivars in Xinjiang, China as measured by RAPD markers. J Hortic Sci Biotechnol 76:771–779
Teng Y, Tanabe K, Tamura F, Itai A (2002) Genetic relationships of Pyrus species and cultivars native to East Asia revealed by randomly amplified polymorphic DNA markers. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 127:262–270
Thiel T, Michalek W, Varshney RK, Graner A (2003) Exploiting EST databases for the development and characterization of gene-derived SSR-markers in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Theor Appl Genet 106:411–422
Varshney RK, Graner A, Sorrells ME (2005) Genic microsatellite markers in plants: features and applications. Trends Biotechnol 23:48–55
Vendramin E, Dettori MT, Giovinazzi J, Micali S, Quarta R, Verde I (2007) A set of EST-SSRs isolated from peach fruit transcriptome and their transportability across Prunus species. Mol Ecol Notes 7:307–310
Watkins R (1981) The main species of Malus. In: Hora B (ed) The Oxford encyclopedia of trees of the world. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 188–192
Way RD, Aldwinckle HS, Lamb RC, Rejman A, Sansavini S, Shen T, Watkins R, Westwood MN, Yoshida Y (1991) Apples (Malus). In: Moore JN, Ballington JR (eds) Genetic resources of temperate fruit and nut crops 1. International Society of Horticultural Science, Wageningen, pp 3–62
Yamamoto T, Kimura T, Sawamura Y, Kotobuki K, Ban Y, Hayashi T, Matsuta N (2001) SSRs isolated from apple can identify polymorphism and genetic diversity in pear. Theor Appl Genet 102:865–870
Yamamoto T, Kimura T, Terakami S, Nishitani C, Sawamura Y, Saito T, Kotabuki K, Hayashi T (2007) Integrated reference genetic linkage maps of pear based on SSR and AFLP markers. Breed Sci 57:321–329
Yang RC, Yeh FC (1993) Multilocus structure in Pinus contorta Dougl. Theor Appl Genet 87:568–576
Yu T (1979) Taxonomy of the fruit tree in China. Agriculture Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge Prof. David Spooner of Department of Horticulture, University of Wisconsin, for critical review of the manuscript. This research work was funded by the project (30871690) of the National Natural Science Foundation of China, project (R307605) from Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province, China, the grant (2008C32011) from Science & Technology Department of Zhejiang Province and the earmarked fund for Modern Agro-industry Technology Research System of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, L., Zheng, X., Cai, D. et al. Exploitation of Malus EST-SSRs and the utility in evaluation of genetic diversity in Malus and Pyrus . Genet Resour Crop Evol 57, 841–851 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-009-9524-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-009-9524-1