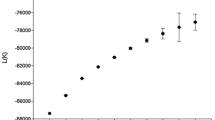
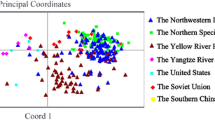
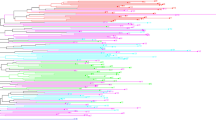
Abstract
Cotton is the world’s leading cash crop, but it lags behind other major crops for marker-assisted breeding due to limited polymorphisms and a genetic bottleneck through historic domestication. This underlies a need for characterization, tagging, and utilization of existing natural polymorphisms in cotton germplasm collections. Here we report genetic diversity, population characteristics, the extent of linkage disequilibrium (LD), and association mapping of fiber quality traits using 202 microsatellite marker primer pairs in 335 G. hirsutum germplasm grown in two diverse environments, Uzbekistan and Mexico. At the significance threshold (r 2 ≥ 0.1), a genome-wide average of LD extended up to genetic distance of 25 cM in assayed cotton variety accessions. Genome wide LD at r 2 ≥ 0.2 was reduced to ~5–6 cM, providing evidence of the potential for association mapping of agronomically important traits in cotton. Results suggest linkage, selection, inbreeding, population stratification, and genetic drift as the potential LD-generating factors in cotton. In two environments, an average of ~20 SSR markers was associated with each main fiber quality traits using a unified mixed liner model (MLM) incorporating population structure and kinship. These MLM-derived significant associations were confirmed in general linear model and structured association test, accounting for population structure and permutation-based multiple testing. Several common markers, showing the significant associations in both Uzbekistan and Mexican environments, were determined. Between 7 and 43% of the MLM-derived significant associations were supported by a minimum Bayes factor at ‘moderate to strong’ and ‘strong to very strong’ evidence levels, suggesting their usefulness for marker-assisted breeding programs and overall effectiveness of association mapping using cotton germplasm resources.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdalla AM, Reddy OUK, El-Zik KM, Pepper AE (2001) Genetic diversity and relationships of diploid and tetraploid cottons revealed using AFLP. Theor Appl Genet 102:222–229. doi:10.1007/s001220051639
Abdurakhmonov IY (2007) Exploiting genetic diversity. In: Ethridge D (ed) Plenary presentations and papers. Proceedings of World Cotton Research Conference-4. Lubbock, TX, USA, 10–14 Sept 2007 p 2153
Abdurakhmonov IY, Abdukarimov A (2008) Application of association mapping to understanding the genetic diversity of plant germplasm resources. Int J Plant Genomics 2008:574927
Abdurakhmonov IY, Buriev ZT, Saha S, Pepper AE, Musaev JA, Almatov A et al (2007a) Microsatellite markers associated with lint percentage trait in cotton, Gossypium hirsutum. Euphytica 156:141–156. doi:10.1007/s10681-007-9361-2
Abdurakhmonov IY, Kushanov FN, Djaniqulov N, Buriev ZT, Pepper AE, Fayzieva N et al (2007b) The role of induced mutation in conversion of photoperiod dependence in cotton. J Hered 98:258–266. doi:10.1093/jhered/esm007
Ball RD (2005) Experimental designs for reliable detection of linkage disequilibrium in unstructured random population association studies. Genetics 170:859–873. doi:10.1534/genetics.103.024752
Barnaud AT, Lacombe , Doligez A (2006) Linkage disequilibrium in cultivated grapevine, Vitis vinifera L. Theor Appl Genet 112:708–716. doi:10.1007/s00122-005-0174-1
Blenda A, Scheffler J, Scheffler B, Palmer M, Lacape JM, Yu JZ et al (2006) CMD: a cotton microsatellite database resource for Gossypium genomics. BMC Genomics 7:132. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-7-132
Bradbury PJ, Zhang Z, Kroon DE, Casstevens TM, Ramdoss Y, Buckler ES (2007) TASSEL: software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 23:2633–2635. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btm308
Breseghello F, Sorrells ME (2006) Association mapping of kernel size and milling quality in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars. Genetics 172:1165–1177. doi:10.1534/genetics.105.044586
Brubaker CL, Wendel JF (1994) Re-evaluating the origin of domesticated cotton (Gossypium hirsutum, Malvaceae) using nuclear restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP). Am J Bot 81:1309–1326. doi:10.2307/2445407
Brubaker CL, Paterson AH, Wendel JF (1999) Comparative genetic mapping of allotetraploid cotton and its diploid progenitors. Genome 42:184–203. doi:10.1139/gen-42-2-184
Chen ZJ, Scheffler BE, Dennis E, Triplett BA, Zhang T, Guo W et al (2007) Toward sequencing cotton (Gossypium) genomes. Plant Physiol 145:1303–1310. doi:10.1104/pp.107.107672
Ching A, Caldwell KS, Jung M, Dolan M, Smith OS, Tingey S et al (2002) SNP frequency, haplotype structure and linkage disequilibrium in elite maize inbred lines. BMC Genet 3:1–14. doi:10.1186/1471-2156-3-19
Conneely KN, Boehnke M (2007) So many correlated tests, so little time! Rapid adjustment of P values for multiple correlated tests. Am J Hum Genet 81:1158–1168. doi:10.1086/522036
Culp TW, Lewis CF (1973) Breeding methods for improving yield and fiber quality of upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum). Crop Sci 13:686–689
Dellaporta SL, Wood J, Hicks JP (1983) A plant DNA minipreparation: version II. Plant Mol Biol Rep 1:19–21. doi:10.1007/BF02712670
Excoffier L, Smouse P, Quattro J (1992) Analysis of molecular variance inferred from metric distances among DNA haplotypes: application to human mitochondrial DNA restriction data. Genetics 131:479–491
Flint-Garcia SA, Thornsberry JM, Buckler ESIV (2003) Structure of linkage disequilibrium in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 54:357–374. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.54.031902.134907
Goodman SN (2001) Of P-values and Bayes: a modest proposal. Epidemiology 12:295–297. doi:10.1097/00001648-200105000-00006
Gupta PK, Rustgi S, Kulwal PL (2005) Linkage disequilibrium and association studies in higher plants: present status and future prospects. Plant Mol Biol 57:461–485. doi:10.1007/s11103-005-0257-z
Gutierrez OA, Basu S, Saha S, Jenkins JN, Shoemaker DB, Cheatham CL et al (2002) Genetic distance among selected cotton genotypes and its relationship with F2 performance. Crop Sci 42:1841–1847
Hamblin MT, Mitchell SE, White GM, Gallego J, Kukatla R, Wing RA et al (2004) Comparative population genetics of the panicoid grasses: sequence polymorphism, linkage disequilibrium and selection in a diverse sample of Sorghum bicolor. Genetics 167:471–483. doi:10.1534/genetics.167.1.471
Han ZG, Guo W, Song XL, Zhang T (2004) Genetic mapping of EST-derived microsatellites from the diploid Gossypium arboreum in allotetraploid cotton. Mol Genet Genomics 272:308–327. doi:10.1007/s00438-004-1059-8
Hansen M, Kraft T, Ganestam S, Sall S, Nilsson NO (2001) Linkage disequilibrium mapping of the bolting gene in sea beet using AFLP markers. Genet Res 77:s61–s66. doi:10.1017/S0016672300004857
Hardy OJ (2003) Estimation of pairwise relatedness between individuals and characterization of isolation by distance processes using dominant genetic markers. Mol Ecol 12:1577–1588. doi:10.1046/j.1365-294X.2003.01835.x
Hardy OJ, Vekemans X (2002) SpaGeDi: a versatile computer program to analyze spatial genetic structure at the individual or population levels. Mol Ecol Notes 2:618–620. doi:10.1046/j.1471-8286.2002.00305.x
He DH, Zhong-Xu L, Zhang XL, Nie YC, Guo XP, Feng CD et al (2005) Mapping QTLs of traits contributing to yield and analysis of genetic effects in tetraploid cotton. Euphytica 144:141–149. doi:10.1007/s10681-005-5297-6
He DH, Lin ZX, Zhang XL, Nie YC, Guo XP, Feng CD et al (2007) QTL mapping for economic traits based on a dense genetic map of cotton with PCR-based markers using the interspecific cross of Gossypium hirsutum × Gossypium barbadense. Euphytica 153:181–197. doi:10.1007/s10681-006-9254-9
Hollingsworth PM, Ennos RA (2004) Neighbor joining trees, dominant markers and population genetic structure. Heredity 92:490–498. doi:10.1038/sj.hdy.6800445
Holsinger KE, Lewis PO (2003) HICKORY: a package for analysis of population genetic data, version 1.0. Department of Ecology and evolutionary Biology, University of Connecticut, Storrs, Connecticut, USA
Holsinger KE, Lewis PO, Dey DK (2002) A Bayesian approach to inferring population structure from dominant markers. Mol Ecol 11:1157–1164. doi:10.1046/j.1365-294X.2002.01512.x
Huttley GA, Smith MW, Carrington M, O’Brien SJ (1999) A scan for linkage disequilibrium across the human genome. Genetics 152:1711–1722
Iqbal MJ, Aziz N, Saeed NA, Zafar Y, Malik KA (1997) Genetic diversity evaluation of some elite cotton varieties by RAPD analysis. Theor Appl Genet 94:139–144. doi:10.1007/s001220050392
Iqbal J, Reddy OUK, El-Zik KM, Pepper AE (2001) A genetic bottleneck in the ‘evolution under domestication’ of Upland cotton Gossypium hirsutum L. examined using DNA fingerprinting. Theor Appl Genet 103:547–554. doi:10.1007/PL00002908
Iwata H, Uga Y, Yoshioka Y, Ebana K, Hayashi T (2007) Bayesian association mapping of multiple quantitative trait loci and its application to the analysis of genetic variation among Oryza sativa L. germplasms. Theor Appl Genet 114:1437–1449. doi:10.1007/s00122-007-0529-x
Kantartzi SK, Stewart JM (2008) Association analysis of fibre traits in Gossypium arboreum accessions. Plant Breed 127:173–179. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0523.2008.01490.x
Katki HA (2008) Invited commentary: evidence-based evaluation of P values and Bayes factors. Am J Epidemiol 268:384–388. doi:10.1093/aje/kwn148
Kraakman ATW, Niks RE, Van den Berg PMMM, Stam P, Van Eeuwijk FA (2004) Linkage disequilibrium mapping of yield and yield stability in modern spring barley cultivars. Genetics 168:435–446. doi:10.1534/genetics.104.026831
Kraakman ATW, Martinez F, Mussiraliev B, van Eeuwijk FA, Niks RE (2006) Linkage disequilibrium mapping of morphological, resistance and other agronomically relevant traits in modern spring barley cultivars. Mol Breed 17:41–58. doi:10.1007/s11032-005-1119-8
Kraft TM, Hansen , Nilsson NO (2000) Linkage disequilibrium and fingerprinting in sugar beet. Theor Appl Genet 101:323–326. doi:10.1007/s001220051486
Kruglyak L (1999) Prospects for whole-genome linkage disequilibrium mapping of common disease genes. Nat Genet 22:139–144. doi:10.1038/9642
Lacape JM, Nguyen TB, Courtois B, Belot JL, Giband M, Gourlot JP et al (2005) QTL analysis of cotton fiber quality using multiple Gossypium hirsutum × Gossypium barbadense backcross generations. Crop Sci 45:123–140
Lacape JM, Dessauw D, Rajab M, Noyer JL, Hau B (2007) Microsatellite diversity in tetraploid Gossypium germplasm: assembling a highly informative genotyping set of cotton SSRs. Mol Breed 19:45–58. doi:10.1007/s11032-006-9042-1
Lewis H (1962) Catastrophic selection as a factor in speciation. Evol Int J Org Evol 16:257–271. doi:10.2307/2406275
Li Y, Li Y, Han K, Wang Z, Hou W, Zeng Y et al (2007) Estimation of multilocus linkage disequilibria in diploid populations with dominant markers. Genetics 176:1811–1821. doi:10.1534/genetics.106.068890
Lin Z, He D, Zhang X, Nie Y, Guo X, Feng C et al (2005) Linkage map construction and mapping QTL for cotton fiber quality using SRAP, SSR and RAPD. Plant Breed 124:180–187. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0523.2004.01039.x
Liu K, Muse SV (2005) PowerMarker: an integrated analysis environment for genetic marker analysis. Bioinformatics 21:2128–2129. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bti282
Liu S, Saha S, Stelly D, Burr B, Cantrell RG (2000a) Chromosomal assignment of microsatellite loci in cotton. J Hered 91:326–332. doi:10.1093/jhered/91.4.326
Liu S, Cantrell RG, McCarty JCJ, Stewart JM (2000b) Simple sequence repeat-based assessment of genetic diversity in cotton race stock accessions. Crop Sci 40:1459–1469
Liu KJ, Goodman M, Muse S, Smith JS, Buckler E, Doebley J (2003) Genetic structure and diversity among maize inbred lines as inferred from DNA microsatellites. Genetics 165:2117–2128
Maccaferri M, Sanguineti MC, Noli E, Tuberosa R (2005) Population structure and long-range linkage disequilibrium in a drum wheat elite collection. Mol Breed 15:271–289. doi:10.1007/s11032-004-7012-z
Malosetti M, van der Linden CG, Vosman B, van Eeuwijk FA (2007) A mixed-model approach to association mapping using pedigree information with an illustration of resistance to Phytophthora infestans in potato. Genetics 175:879–889. doi:10.1534/genetics.105.054932
Malysheva-Otto LV, Ganal MW, Roder MS (2006) Analysis of molecular diversity, population structure and linkage disequilibrium in a worldwide survey of cultivated barley germplasm (Hordeum vulgare L.). BMC Genet 7:6. doi:10.1186/1471-2156-7-6
McRae AF, McEwan JC, Dodds KG, Wilson T, Crawford AM, Slate J (2002) Linkage disequilibrium in domestic sheep. Genetics 160:1113–1122
Mei M, Syed NH, Gao W, Thaxton PM, Smith CW, Stelly DM et al (2004) Genetic mapping and QTL analysis of fiber-related traits in cotton (Gossypium). Theor Appl Genet 108:280–291. doi:10.1007/s00122-003-1433-7
Mohlke KL, Lange EM, Valle TT, Ghosh S, Magnuson VL, Silander K et al (2001) Linkage disequilibrium between microsatellite markers extends beyond 1 cM on chromosome 20 in Finns. Genome Res 11:1221–1226. doi:10.1101/gr.173201
Nei M (1973) Analysis of gene diversity in subdivided populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 70:3321–3323. doi:10.1073/pnas.70.12.3321
Nordborg M, Borevitz JO, Bergelson J, Berry CC, Chory J, Hanblad J et al (2002) The extent of linkage disequilibrium in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat Genet 30:90–193. doi:10.1038/ng813
Nordborg M, Hu TT, Ishino Y, Jhaveri J, Toomajian C, Zheng H et al (2005) The pattern of polymorphism in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS Biol 3:el96. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0030196
Paterson AH, Smith RH (1999) Future horizons: biotechnology of cotton improvement. In: Smith CW, Cothren JT (eds) Cotton: origin, history, technology, and production. Wiley, New York, pp 415–432
Pillay M, Myers GO (1999) Genetic diversity in cotton assessed by variation in ribosomal RNA genes and AFLP markers. Crop Sci 39:1881–1886
Preetha S, Raveendren TS (2008) Molecular marker technology in cotton. Biotechnol Mol Biol Rev 3:032–045
Pritchard JK, Wen W (2004) Documentation for Structure software. The University of Chicago Press, Chicago
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multi-locus genotype data. Genetics 155:945–959
Rafalski A, Morgante M (2004) Corn and humans: recombination and linkage disequilibrium in two genomes of similar size. Trends Genet 20:103–111. doi:10.1016/j.tig.2003.12.002
Remington DL, Thornsberry JM, Matsuoka Y, Wilson LM, Whitt SR, Doebley J et al (2001) Structure of linkage disequilibrium and phenotypic associations in the maize genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:11479–11484. doi:10.1073/pnas.201394398
Reynolds J, Weir BS, Cockerham CC (1983) Estimation for the coancestry coefficient: basis for a short-term genetic distance. Genetics 105:7767–7779
Rungis D, Llewellyn D, Dennis ES, Lyon BR (2005) Simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers reveal low levels of polymorphism between cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) cultivars. J Agric Res 56:301–307. doi:10.1071/AR04190
Saitou M, Nei N (1987) The neighbor joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sand PG (2007) A lesson not learned: allele misassignment. Behav Brain Funct 3:65. doi:10.1186/1744-9081-3-65
Schneider S, Roessll D, Excoffier L (2000) ARLEQUIN: a software for population genetics data analysis, version 2.0. Genetics and Biometry Laboratory, Department of Anthropology, Geneva, Switzerland, University of Geneva
Schulze TG, McMahon FJ (2002) Genetic association mapping at the crossroad: which test and why? Overview and practical guidelines. Am J Med Genet 114:1–11. doi:10.1002/ajmg.10042
Shen X, Guo W, Zhu X, Yuan Y, Yu JZ, Kohel RJ et al (2005) Molecular mapping of QTLs for fiber qualities in three diverse lines in Upland cotton using SSR markers. Mol Breed 15:169–181. doi:10.1007/s11032-004-4731-0
Stich B, Melchinger AE, Frisch M, Maurer HP, Heckenberger M, Reif JC (2005) Linkage disequilibrium in European elite maize germplasm investigated with SSRs. Theor Appl Genet 111:723–730. doi:10.1007/s00122-005-2057-x
Stich B, Maurer HP, Melchinger AE, Frisch M, Heckenberger M, van der Voort JR et al (2006) Comparison of linkage disequilibrium in elite European maize inbred lines using AFLP and SSR markers. Mol Breed 17:217–226. doi:10.1007/s11032-005-5296-2
Storey JD, Tibshirani R (2003) Statistical significance for genome-wide experiments. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:9440–9445. doi:10.1073/pnas.1530509100
Swofford DL (2002) Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (*and other methods). Sinauer, Sunderland
Tatineni V, Canlrell RG, Davis DD (1996) Genetic diversity in elite cotton germplasm determined by morphological characteristics and RAPD. Crop Sci 36:186–192
Tenaillon MI, Sawkins MC, Long AD, Gaut RL, Doebley JF, Gaut BS et al (2001) Patterns of DNA sequence polymorphism along chromosome 1 of maize (Xea mays ssp. mays L.). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:9161–9166. doi:10.1073/pnas.151244298
Thornsberry JM, Goodman MM, Doebley J, Kresovich S, Nielsen D, Buckler ES (2001) Dwarf 8 polymorphisms associate with variation in flowering time. Nat Genet 28:286–289. doi:10.1038/90135
Tommasini L, Schnurbusch T, Fossati D, Mascher F, Keller B (2007) Association mapping of Stagonospora nodorum blotch resistance in modern European winter wheat varieties. Theor Appl Genet 115:697–708. doi:10.1007/s00122-007-0601-6
Wang B, Guo W, Zhu X, Wu Y, Huang N, Zhang T (2006) QTL mapping of fiber quality in an elite hybrid derived-RIL population of Upland cotton. Euphytica 152:367–378. doi:10.1007/s10681-006-9224-2
Weir BS, Cockerham CC (1984) Estimating F statistics for the analysis of population structure. Evol Int J Org Evol 38:1358–1370. doi:10.2307/2408641
Weiss KM, Clark AG (2002) Linkage disequilibrium and mapping of human traits. Trends Genet 18:19–24. doi:10.1016/S0168-9525(01)02550-1
Wendel JF, Brubaker CL, Percival AE (1992) Genetic diversity in Gossypium hirsutum and the origin of upland cotton. Am J Bot 79:1291–1310.
Witt SR, Buckler ES (2003) Using natural allelic diversity to evaluate gene function. Methods Mol Biol 236:123–139
Young FW, Bann CM (1996) Data analyses with ViSta. In: Fox J, Stine R (eds) Statistical computing environments for social research. Sage Publications, California, pp 207–235
Yu J, Pressoir G, Briggs WH, Vroh BI, Yamasaki M, Doebley JF et al (2006) A unified mixed-model method for association mapping that accounts for multiple levels of relatedness. Nat Genet 38:203–208. doi:10.1038/ng1702
Zhang K, Deng M, Chen T, Waterman MS, Sun F (2002) A dynamic programming algorithm for haplotype block partitioning. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:7335–7339. doi:10.1073/pnas.102186799
Zhang ZS, Xiao YH, Luo M, Li XB, Luo XY, Hou L et al (2005a) Construction of a genetic linkage map and QTL analysis of fiber-related traits in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Euphytica 144:91–99. doi:10.1007/s10681-005-4629-x
Zhang J, Lu Y, Cantrell RG, Hughs E (2005b) Molecular marker diversity and field performance in commercial cotton cultivars evaluated in the Southwestern USA. Crop Sci 45:1483–1490. doi:10.2135/cropsci2004.0581
Zhang HB, Li Y, Wang B, Chee PW (2008) Recent advances in cotton genomics. Int J Plant Genomics 2008:742304
Zhao K, Aranzana MJ, Kim S, Lister C, Shindo C, Tang C et al (2007) An Arabidopsis example of association mapping in structured samples. PLoS Genet 31:e4. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.0030004
Zhu YL, Song QJ, Hyten DL, Van Tassell CP, Matukumalli LK, Grimm DR et al (2003) Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in soybean. Genetics 163:1123–1134
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the Science and Technology Center of Ukraine for the project coordination, and the technical assistance of project participants of P120/P120A. We also thank the administration of Academy of Sciences of Uzbekistan for their continual support of the research efforts. We thank Drs. A. Abdullaev (Uzbek cotton germplasm curator), and S. M. Rizaeva for valuable suggestions on germplasm selection and phenotypic analyses in the Uzbekistan environment. We thank Ms Linda Ballard, Genomics laboratory, USDA ARS at Mississippi for useful suggestions during manuscript edition.
Funding
This project was funded by the Office of International Research Programs (OIRP) of United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) in the frame of USDA-Former Soviet Union (FSU) cooperation programs with the research grant of P120/P120A to IYA, RJK, JZY, SS, and AEP.
Disclaimer
Mention of trademark or proprietary product does not constitute a guarantee or warranty of the product by the United States Department of Agriculture and does not imply its approval to the exclusion of other products that may also be suitable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdurakhmonov, I.Y., Saha, S., Jenkins, J.N. et al. Linkage disequilibrium based association mapping of fiber quality traits in G. hirsutum L. variety germplasm. Genetica 136, 401–417 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-008-9337-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-008-9337-8