Abstract
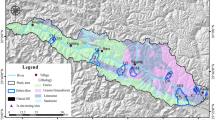
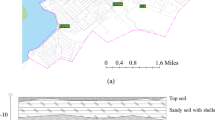
This study provides geotechnical characteristics of recent lahar deposits on which the city of Arequipa (South Peru) is built. Geological and sedimentological observations point out the existence of three types of lahar deposits in the Arequipa region: fine hyperconcentrated-flow deposits, coarse hyperconcentrated-flow deposits, and debris-flow deposits. The mineral components identified in the three types of lahars show that they are linked to the outcropping volcanic rocks around Arequipa city. Physical measurements (dry density, grain-size distribution, specific surface of the grains based on methylene blue tests) and mechanical tests (in situ dynamic cone penetration soundings, oedometric and Casagrande shear-box tests) were performed on the three main categories of soils. Our results highlight that hyperconcentrated-flow deposits are fine sand- and silt-rich deposits that lack clay particles. Their dry density is low (ρd = 1.25 g/cm3) and their friction angle is high (ϕ = 38°) which contribute to the peculiar dynamics of lahar flows and to their high erosive power. The low apparent density provides a better capacity for the debulking process, whereas the high friction angle takes part in the erosion process. Finally, the geotechnical properties observed here suggest that the high contents in silica pyroclastic particles and the lack of clay or fine particles control the rheological behavior of lahar deposits. We can also consider that the rheological behavior of lahars through time is complex and that existing older lahars can be remobilized by heavy rain or future stream flows and lahars.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bardou E, Boivin P, Pfeifer HR (2007) Properties of debris-flow deposits and source materials compared: implications for debris flow characterization. Sedimentology 54:469–480
Cattoni E, Cecconi M, Pane V (2007) Geotechnical properties of an unsaturated pyroclastic soil from Roma. Bull Eng Geol Environ 66:403–414
Cecconi M, Scarapazzi M, Viggiani GMB (2010) On the geology and the geotechnical properties of pyroclastic flow deposits of the Colli Albani. Bull Eng Geol Environ 69:185–206
Chaigneau L, Bacconnet C, Gourvès R, (2000) Penetration test coupled with geotechnical classification for compacting control. An international conference on geotechnical and geological engineering, Geo Eng 2000, Melbourne, Australia
Cobeñas G, Thouret JC, Bonadonna C, Boivin P (2012) The c.2030 yr. BP-old Plinian eruption of El Misti, Peru: characteristics of the fallout and pyroclastic flows, and eruption dynamics. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 241–242:105–120. doi:10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2012.06.006
Cuadros-Paz J, Meza-Arestegui P (2009) Puente Chilina : geologia del proyecto. Technical report (unpublished). Regional Government of Arequipa, p 33
Delaite G, Thouret JC, Sheridan M, Labazuy P, Stinton A, Souriot T, Van Westen C (2005) Assessment of volcanic hazards of El Misti and in the city of Arequipa, Peru, based on GIS and simulations, with emphasis on lahars. Zeitschrift für Geomorphologie NF Suppl 140:209–231
Doyle EE, Cronin SJ, Cole SE, Thouret JC (2010) The coalescence and organization of lahars at Semeru volcano. Indonesia Bull Volcanol. 72(8):961–970
Dumaisnil C, Thouret JC, Chambon G, Doyle EE, Cronin SJ, Surono (2010) Hydraulic, physical and rheological characteristics of rain-triggered lahars at Semeru volcano. Indonesia. Earth Surf. Process. Landforms 35:1573–1590
Chester D, Degg M, Duncan, AM, Guest JE (2001) The increasing exposure of cities to the effects of volcanic eruptions: a global survey. Global Env Change, part B: Environmental hazards, pp 89–103
Enjolras G, Thouret JC, Martelli K, Santoni O, Luque JA, Nagata M, Arguedas A, Macedo L (2013) Combined criteria for assessing lahar and flood-prone hazard and risk zones in the city area of Arequipa, Peru. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci. (EGU), Accepted 7 Jan 2013
Espinace R, Villavicencio G, Palma J, Breul P, Bacconnet C, Benz MA, Gourvès R (2013) Stability of chilean’s tailings dams with the Panda® penetrometer. Experiences of the last 10th, Proceedings of the 18th international conference on soil mechanics and geotechnical engineering, Paris
Fabre D, Ritzenthaler A, Maquaire O, Ambroise B, Thiery Y, Truchet E, Malet JP, Monnet J (2002) Apport du pénétromètre dynamique léger pour la connaissance du manteau d’altération des marnes. Application au bassin-versant du Laval, Draix (Alpes de Haute Provence). Proc. Int. Symp. “Geomorphology: from expert opinion to modelling”. Strasbourg, Delahaye et al. pp 185–192
Gourvès R, Barjot B (1995) Le pénétromètre dynamique léger Panda. Proc. Int. Conf. on Soil Mech & Found. Eng, Copenhagen, pp 83–88
Langton DD (1999) The Panda lightweight penetrometer for soil investigation and monitoring material compaction. Ground Eng 32:33–37
Lavigne F, Thouret JC (2000) Les lahars : dépôts, origines et dynamique. Bull Soc Géol Fra 1741:545–557
Legros F, Cantagrel JM, Devouard B (2000) Pseudotachylite (frictionite) at the base of the Arequipa volcanic landslide deposit (Peru): Implications for emplacement mechanisms. J Geol 108:601–611
Maquaire O, Ritzenthaler A, Fabre D, Ambroise B, Thiery Y, Truchet E, Malet JP, Monnet J (2002) Caractérisation des profils d’altération par pénétromètrie dynamique. Application aux marnes noires à Draix (Alpes de Haute Provence). C. R. Geoscience 334:1–7
Martelli K (2011) The physical vulnerability of urban areas facing the threat of lahars and flash floods: application to the case study of Arequipa, Peru. PhD thesis, University Blaise Pascal, Clermont-Ferrand p 341
O’ Rourke TD (1988) Geotechnical properties of cemented volcanic soil. ASCE J Geotech Eng 114(10):1126–1147
Olalla C, Hernandez LE, Rodriguez-Losada JA, Perucho A (2010) Volcanic rock mechanics: rock mechanics and geo-engineering in volcanic environments. CRC Press, Madrid 368
Paquereau P, Thouret JC, Wörner G, Fornari M, Macedo O, Roperch P (2005) Caractérisation des ignimbrites néogènes du bassin d’Arequipa, Pérou. Geosci 337:477–486
Paquereau-Lebti P, Thouret JC, Wörner G, Fornari M (2006) Neogene and quaternary ignimbrites in the area of Arequipa, southern Peru: stratigraphical and petrological correlations. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 154:251–275
Paquereau-Lebti P, Fornari M, Roperch P, Thouret JC, Macedo O (2008) Paleomagnetic, magnetic fabric properties, and 40 Ar/39 Ar dating, of Neogene: quaternary ignimbrites in the Arequipa area, Southern Peru. Flow directions and implications for the emplacement mechanisms. Bull Volcanol 70:977–997
Pierson TC (2005) Hyperconcentrated flow: transitional process between water flow and debris flow. In: Jakob M, Hungr O (eds) Debris-flow hazards and related phenomena. Springer, Berlin
Powers MC (1953) A new roundness scale for sedimentary particles. J Sediment Petrol 23:117–119
Schmertmann JH, (1978) Guidelines for CPT in: Performance and Design. U.S. Dept. of transportation, FHA, Washington
Scott KM (1988) Origins, behavior and sedimentology of lahars and lahar–runout flows in Toutle Cowlitz river system, Mount St-Helens, Washington, US Geological Survey, pp 1447A
Serrano A, Olalla C, Perucho A (2002) Mechanical collapsible rocks. Symp. I.S.R.M. “Eurock 2002”: Madeira Portugal
Shepard FP (1963) Submarine geology. Harper & Row, Evanston
Smith GA, Fritz WJ (1989) Volcanic influences on terrestrial sedimentation. Geology 17:375–376
Thouret JC, Finizola A, Fornari M, Legeley-Padovani A, Suni J, Frechen M (2001) Geology of El Misti volcano near the city of Arequipa. Peru Geol Soc Am Bull 113(12):1593–1610
Thouret JC, Fabre D, Willinger M, Talon A. Pallares C, Bacconnet C, Bchir MA, Enjolras G, Heitz C, Cespedes X, Martelli K, Nagata M, (2012) Assessing Lahar and flood hazards as a contribution to risk management in the city of Arequipa, Peru. 12th Congress INTERPRAEVENT 2012 Grenoble/France—Extended Abstracts. www.interpraevent, Extended Abstracts, pp 390–391
Tilling RI (2005) Volcano hazards. In: Marti J, Ernst GJE (eds) Volcanoes and the environment. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 55–89
Vallance JW (2000) Lahars. In: Sigurdsson H, Houghton B, McNutt SR, Rymer H, Stix J (eds) Encyclopedia of volcanoes. Academic Press, New York, pp 601–616
Vargas Franco R, Thouret JC, Delaite G, van Westen C, Sheridan MF, Siebe C, Marino J, Souriot T, Stinton A (2010) Mapping and assessing volcanic hazards and risks in the city of Arequipa, Peru, based on GIS techniques. In G. Groppelli & L. Viereck-Goette, eds.,’ Stratigraphy and Geology of volcanic areas’, Geol Soc Am Special Paper 464: 265–280
Villavicencio G, Bacconnet C, Breul P, Boissier D, Espinace R (2011) Estimation of the variability of tailings dams properties in order to perform probabilistic assessment. Geotech Geol Eng 29(6):1073–1084
Acknowledgments
We thank the Project Laharisk (2010–2013) funded by the French National Agency for Research (ANR—RiskNat) and all our Peruvian colleagues in Arequipa for their help, especially during the work field. The first author wishes also to thank especially V. Pallares and X. Quidelleur.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pallares, C., Fabre, D., Thouret, JC. et al. Geological and geotechnical characteristics of recent lahar deposits from El Misti volcano in the city area of Arequipa, South Peru. Geotech Geol Eng 33, 641–660 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-015-9848-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-015-9848-x