Abstract
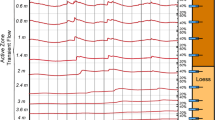
As one of the issues, the evolutions of humidity field must be studied to avoid roadbed water damage. To study the influences of groundwater depth differences on the subgrade humidity field infiltrated by rainfall, five scale-down laboratory subgrade physical models with different initial groundwater depths were tested. The effects and mechanisms of different initial groundwater depths on the humidity values of disturbed zone, extended distances, and humidity gradients were explored. The results show that the influences of initial depths on humidity fields get more significant along with subgrade depths. With decrease of initial depths, the amplifications of subgrade humidity maximum differences increase quadratically to a steady value while the extended distances of humidity disturbed zone decrease quadratically to a steady value. A balanced groundwater depth should exist according to a given field situation. The influences of groundwater on humidity fields are vary slight while initial depths are deeper than the balanced one, otherwise, with increase of initial depths the amplifications of subgrade humidity increase logarithmically and the humidity gradients increase linearly.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Samahiji D, Houston SL, Houston WN (2007) Degree and extent of wetting due to capillary rise in soils. Transp Res Rec 1709:114–120
Cho SE, Lee SR (2001) Instability of unsaturated soil slopes due to infiltration. Comput Geotech 28:185–208
Deng YC, Hao PW, He LB (2011) Study on capillarity water rise in subgrade soil. Adv Mater Res 250–253:1702–1706
Han YP (2006) Resilient modulus estimation system for fine-grained soils. Transp Res Rec 1967:69–77
Hu ML, Yao HL, Liu J, Lu Z (2012) Influence of variation of groundwater level on deformation of subgrade based on hydromechanical coupling. Adv Mater Res 457–458:30–33
Khoury N, Brooks R, Khoury C (2012) Modeling resilient modulus hysteretic behavior with moisture variation.Int J Geomech 12(5):519–527
Ling Z, Fu HY, Li T, Qin YQ (2012) The analysis of seepage characteristics and stability of carbonaceous mudstone embankment slope in rainfall condition. Adv Mater Res 446–449:1864–1868
Liu J, Yao HL, Chen P, Lu Z, Luo XW (2013) Theoretical analysis and experimental study of subgrade moisture variation and underground antidrainage technique under groundwater fluctuations. Hindawi Publ Corp J Appl Math 51:1–8
Mahmood K, Ryu JH, Kim JM (2013) Effect of anisotropic conductivity on suction and reliability index of unsaturated slope exposed to uniform antecedent rainfall. Landslides 10:15–22
Nguyen Q, Fredlund DG, Samarasekera L (2010) Seasonal pattern of matric suctions in highway subgrades. Can Geotech J 47(3):267–280
Qian JS, Qiu X, Ling JM (2010) In-situ testing and evaluation of moisture content in existing subgrade. ASCE Geo Shanghai International Conference: paving materials and pavement analysis 203:379–384
Tsai TL, Chen HF (2010) Effects of degree of saturation on shallow landslides triggered by rainfall [J]. Environ Earth Sci 59(6):1285–1295
Won TO, Vanapalli SK (2010) Influence of rain infiltration on the stability of compacted soil slopes [J]. Comput Geotech 37(5):649–657
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, ZJ. Numerical Study of Subgrade Humidity Field Evolution Under Different Initial Groundwater Depths. Geotech Geol Eng 33, 79–86 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-014-9824-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-014-9824-x