Abstarct
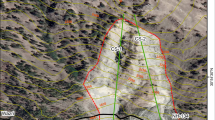
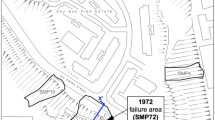
Several cases of subsidence occurred in greater Tehran resulting from collapse of walls of underground water channel system known locally as qanat. Many mechanisms contribute to the qanat collapse, which add to the complexity of the problem. The present research focuses on identifying the main factors that influence qanat collapse and the parameters that should be considered in modeling their behavior. Some of the important factors that influence the stability and performance of qanats and considered in the analysis presented here include: qanat geometrical characteristics; loading due to surface structures; underground water level and geotechnical properties of the soil. A suitable model was chosen and deformational behavior of qanat walls was simulated. The stability of qanats was evaluated considering both elastic and elasto-plastic soil models. It was found that qanats in north and northeastern parts of Tehran have high strength and qanats in south and southwestern parts have low strength. A GIS-based qanat collapse hazard zonation map was prepared. It was found that the hazard of collapse increases for shallow qanats with any structural loads imposed at the ground surface. As expected, this hazard is much higher for qanats situated in weak soils. Furthermore, the hazard of collapse is much higher for qanats with larger diameter.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arc View GIS, Version 3.1, GeoCommunity™, Wireless Developer Network TM, GIS Data Depot®, and Spatial News
Davis JC (1986) Statistics and Data Analysis in Geology. John Wiley & Sons, New York, p. 646
Dearman WR (1979) The engineering geological mapping commission of the international association of engineering geology. Bull Intl Assoc Eng Geol 19:II.5—II.29
Goodman RE (1989) Introduction to rock mechanics. University of California at Berkeley, Press John Wiley & Sons, New York
Geological Survey of Iran (GSI) (1979) Geological and Seismo-tectonic Features of Tehran Area, Report no. 56, Tehran, Iran
IIEES (2003) Reconnaissance report on 26 December 2003 Bam earthquake. International Institute of Earthquake Engineering (IIEES)
ILWIS V3.1, The remote sensing and GIS software, International Institute for Geo-Information Science and Earth Observation, ITC
Itasca (2000) FLAC (Fast Lagrangian Analysis of Continua) ver.2.27, Itasca consulting group, Minneapolis, USA
Maleki A (1973) Hydro geological Investigation of Tehran Area. Report no. 36, Ground Water Deparmentt, Ministry of Water
Nadim F, Moghtaderi M, Lindholm C, Andresen A, Remseth S, Bolorchi M, Mokhtari M, Tvedt E (2004) The Bam Earthquake of 26 December 2003. Bull Earthquake Eng 2(2):119–153
Rayhani MT, Shiroodi S, Farajpour V (2003) Qanat Collapse Hazard Zonation Map in Tehran Area. Annual research report, Geotechnical Deparment, Building and Housing Research Center, Iran
Vesic AS (1972) Expansion of cavities in infinite soil mass. J Soil Mech Found Div ASCE, 98(SM3):265–290
Voughan PR, Fookes PG (1982) Engineering geomorphology. Surrey University Press
Acknowledgements
The first author expresses his thanks to Eng. V. Farajpour and Eng. S. Shiroodi for their cooperation and help in data analyses of the research. The funding for this research has been provided by the Building and Housing Research Center, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rayhani, M.H.T., El Naggar, M.H. Collapse hazard zonation of qanats in greater Tehran area. Geotech Geol Eng 25, 327–338 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-006-9113-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-006-9113-4