Abstract
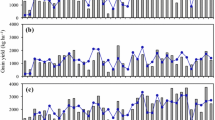
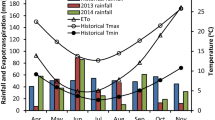
Sensitivity analysis of DSSAT outputs to inputs parameters was conducted in two Canadian locations: one for spring wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) in the semi-arid Prairies in Swift Current, Saskatchewan and the second for maize (Zea mays L.) under humid conditions in Woodslee, Ontario. The nominal range sensitivity method, regression, and graphical analysis were used to assess the sensitivity of crop yields, biomass, soil inorganic N, nitrate leaching and soil water contents to soil hydraulic properties, management practices and precipitation. Wheat and maize yields were highly sensitive to soil water drainage upper limit, fertilizer nitrogen rate and precipitation at both locations. At Swift Current, very high soil nitrate leaching (25–140 kg N ha−1) was found in 1994, 1996, 1997 and 2003 as affected by high precipitation in the previous years (i.e., 1993, 1995, 1996 and 2002). Soil N leaching was greater in 2011, a wet year at Woodslee, Ontario, with 20–85 kg N ha−1 than in the normal rainfall years of 2010 and 2012. Based on the fitted N response curves, the maximum yields were obtained at 112 kg N ha−1 for spring wheat at Swift Current and 150–210 kg N ha−1 for maize at Woodslee. The optimum planting date for maize at Woodslee was predicted to be from late May to early June. Sensitivity analysis was found to be useful in assessing the influence of crop management practices, soil parameters and precipitation on crop production and potential environment risks.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banterng P, Patanothai A, Pannangpetch K, Jogloy S, Hoogenboom G (2004) Determination of genetic coefficients for peanut lines for breeding applications. Eur J Agron 21:297–310
Benke KK, Lowell KE, Hamilton AJ (2008) Parameter uncertainty, sensitivity analysis and prediction error in a water-balance hydrological model. Math Comput Model 47:1134–1149
Bert FE, Laciana CE, Podesta GP, Satorre EH, Menendez AN (2007) Sensitivity of CERES-maize simulated yields to uncertainty in soil properties and daily solar radiation. Agric Syst 94:141–150
Boote KJ, Jones JW, Pickering NB (1996) Potential uses and limitations of crop models. Agron J 88:704–716
Boote KJ, Jones JW, Batchelor WD, Nafziger ED, Myers O (2003) Genetic coefficients in the CROPGRO–Soybean model: links to field performance and genomics. Agron J 95:32–51
Bootsma A, De Jong R (1988) Estimates of seeding dates of spring wheat on the Canadian Prairies from climate data. Can J Plant Sci 68:513–517
Cacuci DG (2003) Sensitivity and uncertainty analysis, vol II. Chapman andHall/CRC, Boca Roton, pp 33487–33742
Campbell CA, Read DWL, Biederbeck VO, Winkleman GE (1983a) The first 12 years of a long-term crop rotation study in southwestern Saskatchewan: nitrate-N distribution in soil and N uptake by the plant. Can J Soil Sci 63:563–578
Campbell CA, Read DWL, Zentner RP, Leyshon AJ, Ferguson WS (1983b) First 12 years of a long-term crop rotation study in southwestern Saskatchewan: yields and quality of grain. Can J Plant Sci 63:91–108
Campbell CA, Selles F, Zentner RP, McConkey BG, Brandt SA, McKenzie RC (1997) Regression model for predicting yield of hard red spring wheat grown on stubble in the semiarid prairie. Can J Plant Sci 77:43–52
Campbell CA, Zentner RP, Liang BC, Roloff G, Gregorich EC, Blomert B (2000) Organic C accumulation in soil over 30 years in semiarid southwestern Saskatchewan: effect of crop rotations and fertilizers. Can J Soil Sci 80:179–192
Campbell CA, Selles F, Zentner RP, De Jong R, Lemke R, Hamel C (2006) Nitrate leaching in the semiarid prairie: effect of cropping frequency, crop type, and fertilizer after 37 years. Can J Soil Sci 86:701–710
Campbell CA, VandenBygaart AJ, Grant B, Zentner RP, McConkey BG, Lemke R, Gregorich EG, Fernandez MR (2007) Quantifying carbon sequestration in a conventionally tilled crop rotation study in southwestern Saskatchewan. Can J Soil Sci 87:23–38
Ciampitti IA, Vyn TJ (2012) Physiological perspectives of changes over time in maize yield dependency on nitrogen uptake and associated nitrogen efficiencies: a review. Field Crops Res 133:4867
Confalonieri R, Bellocchi G, Tarantola S, Acutis M, Donatelli M, Genovese G (2010) Sensitivity analysis of the rice model WARM in Europe: exploring the effects of different locations, climates and methods of analysis on model sensitivity to crop parameters. Environ Model Softw 25:479–488
DeJong KC, Ascough JC, Ahmadia M, Andalesc AA, Arabia M (2012) Global sensitivity and uncertainty analysis of a dynamic agroecosystem model under different irrigation treatments. Ecol Model 231:113–125
Drury CF, Tan CS (1995) Long-term (35 years) effects of fertilization, rotation and weather on corn yields. Can J Plant Sci 75:355–362
Drury CF, Reynolds WD, Yang XM, McLaughlin NB, Welacky TW, Calder W, Grant CA (2011) Nitrogen source, application time, and tillage effects on soil nitrous oxide emissions and corn grain yields. Soil Sci Soc Am J 76:1268–1279
Drury CF, Reynolds WD, Tan CS, McLaughlin NB, Yang XM, Calder W, Oloya TO, Yang JY (2014) Impacts of 49–51 years of fertilization and crop rotation on growing season nitrous oxide emissions, nitrogen uptake and corn yields. Can J Soil Sci 94:421–433
Dubus IG, Brown CD (2002) Sensitivity and first-step uncertainty analyses for the preferential flow model MACRO. J Environ Qual 31:227–240
Dzotsi KA, Bassob B, Jones JW (2013) Development, uncertainty and sensitivity analysis of the simple SALUS crop model in DSSAT. Ecol Model 260:62–76
Esprey LJ, Sands PJ, Smith CW (2004) Understanding 3-PG using a sensitivity analysis. For Ecol Manag 193:235–250
Fitton N, Datta A, Smith K, Williams JR, Hastings A, Kuhnert M, Topp CFE, Smith P (2014) Assessing the sensitivity of modelled estimates of N2O emissions and yield to input uncertainty at a UK cropland experimental site using the DailyDayCent model. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 99:119–133
Frey HC, Patil SR (2002) Identification and review of sensitivity analysis methods. Risk Anal 22(3):553–578
Gourley JJ, Vieux BE (2006) A method for identifying sources of model uncertainty in rainfall-runoff simulations. J Hydrol 327:68–80
Hoogenboom G, Jones JW, Wilkens PW, Porter CH, Boote KJ, Hunt LA, Singh U, Lizaso JL, White JW, Uryasev O, Royce FS, Ogoshi R, Gijsman AJ, Tsuji GY, Koo J (2012) Decision support system for agrotechnology transfer (DSSAT) Version 4.5.1.023 [CD-ROM]. University of Hawaii, Honolulu
Jones JW, Hoogenboom G, Porter CH, Boote KJ, Batchelor WD, Hunt LA, Wilkens PW, Singh U, Gijsman AJ, Ritchie JT (2003) The DSSAT cropping system model. Eur J Agron 18:235–265
Kang SZ, Zhang L, Liang YL, Hu XT, Cai HJ, Gu BJ (2002) Effects of limited irrigation on yield and water use efficiency of winter wheat on the loess plateau of China. Agric Water Manag 55:203–216
Kassie BT, Asseng S, Rotter RP, Hengsdijk H, Ruane AC, Ittersum MK (2015) Exploring climate change impacts and adaptation options for maize production in the Central Rift Valley of Ethiopia using different climate change scenarios and crop models. Clim Change 129:145–158
Katz RW (2002) Techniques for estimating uncertainty in climate change scenarios and impact studies. Clim Res 20:167–185
Li C, Salas W, Zhang R, Krauter C, Rotz A, Mitloehner F (2012) Manure-DNDC: a biogeochemical process model for quantifying greenhouse gas and ammonia emissions from livestock manure systems. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 93:163–200
Li ZT, Yang JY, Smith WN, Drury CF, Lemke RL, Grant B, He WT, Li XG (2015) Simulation of long-term spring wheat yields, soil organic C, N and water dynamics using DSSAT-CSM in a semi-arid region of the Canadian prairies. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 101:401–419
Liu HL, Yang JY, Drury CF, Reynolds WD, Tan CS, Bai YL, He P, Jin J, Hoogenboom G (2011) Using the DSSAT-CERES-Maize model to simulate crop yield and nitrogen cycling in fields under long-term continuous maize production. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 89:313–328
Liu S, Yang JY, Drury CF, Liu HL, Reynolds WD (2014) Simulating maize (Zea mays L.) growth and yield, soil nitrogen concentration, and soil water content for a long-term cropping experiment in Ontario, Canada. Can J Soil Sci 94:435–452
MacCarthy DS, Akponikpe PBI, Narh S, Tegbe R (2015) Modeling the effect of seasonal climate variability on the efficiency of mineral fertilization on maize in the coastal savannah of Ghana. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 102:45–64
McCallum BD, DePauw RM (2008) A review of wheat cultivars grown in the Canadian prairies. Can J Plant Sci 88:649–677
Norton JP (2008) Algebraic sensitivity analysis of environmental models. Environ Model Softw 23:963–972
Pathak TB, Jones JW, Fraisse CW, Wright DL, Hoogenboom G (2012) Uncertainty analysis and parameter estimation for the CSM-CROPGRO-Cotton model. Agron J 104:1356–1362
Qian B, De Jong R, Huffman T, Wang H, Yang JY (2015) Projecting yield changes of spring wheat under future climate scenarios on the Canadian Prairies. Theor Appl Climatol. doi:10.1007/s00704-015-1378-1
Saltelli A, Chan K, Scott M (2000) Sensitivity analysis. Probability and statistics series. Wiley, New York
Saltelli A, Ratto M, Andres T, Campolongo F, Cariboni J, Gatelli D, Saisana M, Tarantola S (2008) Global sensitivity analysis: the primer. Wiley Online Library, New York
Saltelli A, Annoni P, Azzini I, Campolongo F, Ratto M, Tarantola S (2010) Variance based sensitivity analysis of model output. Design and estimator for the total sensitivity index. Comput Phys Commun 181(2):259–270
Singh PK, Mishra AK, Imtiyaz M (1991) Moisture stress and the water use efficiency of mustard. Agric Water Manag 20:245–253
Sommer R, Mukalama J, Kihara J, Koala S, Winowiecki L, Bossio D (2015) Nitrogen dynamics and nitrous oxide emissions in a long-term trial on integrated soil fertility management in Western Kenya. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst. doi:10.1007/s10705-015-9693-6
Specka X, Nendel C, Wieland R (2015) Analysing the parameter sensitivity of the agro-ecosystem model MONICA for different crops. Eur J Agron 71:73–87
Subedi KD, Ma BL, Xue AG (2007) Planting date and nitrogen effects on grain yield and protein content of spring wheat. Crop Sci 47:36–44
Tan CS, Drury CF, Reynolds WD, Groenevelt PH, Dadfar H (2002) Water and nitrate loss through tiles under a clay loam soil in Ontario after 42 years of consistent fertilization and crop rotation. Agric Ecosyst Environ 93:121–130
Tarantola S, Saltelli A (2003) SAMO 2001: methodological advances and innovative applications of sensitivity analysis. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 79:121–122
Tsuji GY, Hoogenboom G, Thornton PK (1998) Understanding options for agricultural production. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht
Wang Z, Qi Z, Xue L, Bukovsky M, Helmers MJ (2015) Modeling the impacts of climate change on nitrogen losses and crop yield in a subsurface drained field. Clim Change. doi:10.1007/s10584-015-1342-1
Williams JR (1990) The erosion-productivity impact calculator (EPIC) model: a case history. USDA ARS, Washington, DC, pp 421–427
Yang JM, Liu JH, Dou S, Yang JY, Hoogenboom G (2011) Evaluation and optimization of best management practices of maize for soil in Jilin China using the DSSAT model. IV. Cultivar calibration and sensitivity analysis of maize yield parameters. Acta Pedol Sin 2:48
Yang JM, Yang JY, Dou S, Yang XM, Hoogenboom G (2013) Simulating the effect of long-term fertilization on maize yield and soil C/N dynamics in northeastern China using DSSAT and CENTURY-based soil model. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 95:287–303
Zhao G, Bryan BA, Song X (2014) Sensitivity and uncertainty analysis of the APSIM-wheat model: interactions between cultivar, environmental, and management parameters. Ecol Model 279:1–11
Acknowledgments
Senior author acknowledges the AAFC-MOE China program providing PhD scholarship (Grant no. 201403250068). Financial and technical support for this study from Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada and Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, W., Yang, J.Y., Zhou, W. et al. Sensitivity analysis of crop yields, soil water contents and nitrogen leaching to precipitation, management practices and soil hydraulic properties in semi-arid and humid regions of Canada using the DSSAT model. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 106, 201–215 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-016-9800-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-016-9800-3