Abstract
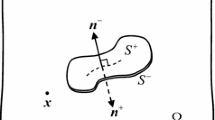
In this paper, we derive the exact closed-form fundamental solutions due to uniform extended displacement discontinuities over a triangular element in a piezoelectric half-space. Using the triangular elements to partition the penny-shaped crack, the triangular element fundamental solutions are verified by comparing with the existing analytical solution associated with the penny-shaped crack. The polarization saturation model is then applied to an elliptical crack in the piezoelectric half-space, and the resulting nonlinear fracture problem is solved by combing the triangular element fundamental solutions and the displacement discontinuity method. The electric yielding zone and the extended field intensity factors are obtained by an iterative approach. The effects of the applied mechanical load and electric displacement, the polarization saturation in the yielding zone, and the aspect ratio of the elliptical crack on the yielding zone size and field intensity factors are discussed through numerical examples.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhargava RR, Jangid K (2013) Strip-saturation model for piezoelectric plane weakened by two collinear cracks with coalesced interior zones. Appl Math Model 37:4093–4102
Chen WQ, Lim CW (2005) 3D point force solution for a permeable penny-shaped crack embedded in an infinite transversely isotropic piezoelectric medium. Int J Fract 131:231–246
Chen WQ, Shioya T, Ding HJ (1999) Integral equations for missed boundary value problem of a piezoelectric half-space and the application. Mech Res Commun 26:583–590
Chiang CR (2014a) Some half-space problems of cubic piezoelectric materials. Int J Solids Struct 51:1046–1051
Chiang CR (2014b) Subsurface crack problems in a cubic piezoelectric material. Eng Fract Mech 131:656–668
Crouch SL (1976) Solution of plane elasticity problems by the displacement discontinuity method. Int J Numer Methods Eng 10:301–343
Ding HJ, Chen B, Liang J (1997) On the green’s functions for two-phase transversely isotropic piezoelectric media. Int J Solids Structures 33:3041–3057
Dugdale DS (1960) Yielding of steel containing slits. J Mech Phys Solids 8:100–104
Dunn ML (1994) The effects of crack face boundary conditions on the fracture mechanics of piezoelectric solids. Eng Fract Mech 48:25–39
Fan CY, Zhao MH, Zhou YH (2009) Numerical solution of polarization saturation/dielectric breakdown model in 2D finite piezoelectric media. J Mech Phys Solids 57:1527– 1544
Fan CY, Guo ZH, Dang HY, Zhao MH (2014a) Extended displacement discontinuity method for nonlinear analysis of penny-shaped cracks in three-dimensional piezoelectric media. Eng Anal Bound Elem 38:8–16
Fan CY, Dang HY, Zhao MH (2014b) Nonlinear solution of the PS model for a semi-permeable crack in a 3D piezoelectric medium. Eng Anal Bound Elem 46:23–29
Gao HJ, Zhang TY, Tong P (1997) Local and global energy release rates for an electrically yielding crack in a piezoelectric ceramic. J Mech Phys Solids 45:491–510
Linder C (2012) An analysis of the exponential electric displacement saturation model in fracturing piezoelectric ceramics. Technische Mechanik 32:53–69
Linder C (2014) A complex variable solution based analysis of electric displacement saturation for a cracked piezoelectric material. J Appl Mech 81:091006
Linder C, Miehe C (2012) Effect of electric displacement saturation on the hysteretic behavior of ferroelectric ceramics and the initiation and propagation of cracks in piezoelectric ceramics. J Mech Phys Solids 60:882–903
Loboda V, Lapusta Y, Sheveleva A (2007) Electro-mechanical pre-fracture zones for an electrically permeable interface crack in a piezoelectric bimaterial. Int J Solids Struct 44:5538–5553
Pan E (1999) A BEM analysis of fracture mechanics in 2D anisotropic piezoelectric solids. Eng Anal Bound Elem 23:67–76
Pak YE (1992) Linear electro-elastic fracture mechanics of piezoelectric materials. Int J Fract 54:79–100
Phongtinnaboot W, Rungamornrat J, Chintanapakdee C (2013) Modeling of cracks in 3D piezoelectric finite media by weakly singular SGBEM. Eng Anal Bound Elem 35:319–329
Qin TY, Yu YS, Noda NA (2007) Finite-part integral and boundary element method to solve three-dimensional crack problems in piezoelectric materials. Int J Solids Struct 44:4770–4783
Ru CQ (1999) Effect of electrical polarization saturation on stress intensity factors in a piezoelectric ceramic. Int J Solids Struct 36:869–883
Ru CQ, Mao X (1999) Conducting cracks in a piezoelectric ceramic of limited electric polarization. J Mech Phys Solids 47:2125–2146
Shang FL, Kuna M, Abendroth M (2003) Finite element analyses of three-dimensional crack problems in piezoelectric structures. Eng Fract Mech 70:143–160
Sosa HA (1992) On the fracture mechanics of piezoelectric solids. Int J Solids Struct 29:2613–2622
Sosa H, Khutoryansky N (1996) New developments concerning piezoelectric materials with defects. Int J Solids Struct 33:3399–3414
Suo Z, Kuo CM, Barnett DM, Willis JR (1992) Fracture mechanics for piezoelectric ceramics. J Mech Phys Solids 40:739–765
Wang BL, Mai YQ (2003) Crack tip field in piezoelectric/piezomagnetic media. Eur J Mech A Solid 22:591–602
Wang ZK, Huang SH (1995) Fields near elliptical crack tip in piezoelectric ceramics. Eng Fract Mech 51:447–456
Zhang TY, Zhao MH, Tong P (2002) Fracture of piezoelectric ceramics. Adv Appl Mech 38:147–298
Zhao MH, Liu YJ, Cheng CJ (1994) Boundary-integral equations and the boundary-element method for three-dimensional fracture mechanics. Eng Anal Bound Elem 13:333–338
Zhao MH, Shen YP, Liu YJ, Liu GN (1999) Crack analysis in semi-infinite transversely isotropic piezoelectric solid. II. Penny-shaped crack near the surface. Theor Appl Fract Mech 32:233–240
Zhao MH, Shen YP, Liu YJ, Liu GN (1997a) Isolated crack in three-dimensional piezoelectric solid. I. Solution by Hankel transform. Theor Appl Fract Mech 26:129–139
Zhao MH, Shen YP, Liu YJ, Liu GN (1997b) Isolated crack in three-dimensional piezoelectric solid—II: stress intensity factors for circular crack. Theor Appl Fract Mech 26:141–149
Zhao MH, Zhang QY, Pan E, Fan CY (2014) Fundamental solutions and numerical modeling of an elliptical crack with polarization saturation in a transversely isotropic piezoelectric medium. Eng Fract Mech 131:627–642
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 11172273, 11272290), the Construction Project of Key Laboratory in Henan Colleges, and Henan Bairen Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendices
Appendix 1
The coefficients \(L_{f} ,\;L_{h} ,\;L_{fk}^{i} ,\;L_{hk}^{ij} ,\;L_{fk\alpha }^{i}\) and \(\;L_{hk\alpha }^{ij} (i, j=1, 2, 3, k=1, 2, 3, \alpha =1, 2)\) in Eqs. (3a), (3b), (3c) and (3d) are listed below:
where \(s_{i}\) are the eigenvalues, \(c_{ij}, e_{ij}, \varepsilon _{ij}\) are the elastic constants, PE constants and dielectric constants; \(A_{i }(A_{ij}), B_{i }(B_{ij}), D_{i }(D_{ij}), \omega _{i1}, \vartheta _{i1}\) and \(\vartheta _{i2}\) are the material-related constants listed in Ding et al. (1997). Furthermore, the subscripts f and h indicate the parameters associated with full- and half-spaces respectively.
Appendix 2
The coefficients in Eqs. (6a), (6b), (6c) and (6d) are listed below (for \(k=1-5\) and \(i=1-3\)):
where the subscript f on the left-hand side of Eq. (27) indicates the full-space parameters, and
We point out that by replacing \(\bar{{z}}_{i}\) in \(M_{fk}^{i}\) by \(z_{ij} (i,j=1,2,3\)), one obtains the expressions for \(M_{hk}^{ij}\) where the subscript h denotes the parameters of the half-space. We further point out that the parameters \(\bar{{z}}_{i}\) and \(z_{ij}\) are defined in Eq. (4).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Zhao, M., Pan, E. et al. Analysis of a nonlinear crack in a piezoelectric half-space via displacement discontinuity method. Int J Fract 194, 107–122 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10704-015-0040-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10704-015-0040-3