Abstract
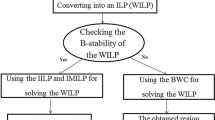
The current research concerns multiobjective linear programming problems with interval objective functions coefficients. It is known that the most credible solutions to these problems are necessarily efficient ones. To solve the problems, this paper attempts to propose a new model with interesting properties by considering the minimax regret criterion. The most important property of the new model is attaining a necessarily efficient solution as an optimal one whenever the set of necessarily efficient solutions is nonempty. In order to obtain an optimal solution of the new model, an algorithm is suggested. To show the performance of the proposed algorithm, numerical examples are given. Finally, some special cases are considered and their characteristic features are highlighted.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ben-Tal, A., El Ghaoui, L., & Nemirovski, A. (2009). Robust optimization. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Bitran, G. R. (1980). Linear multiple objective problems with interval coefficients. Management Science, 26, 694–706.
Dong, C., Huang, G., Cai, Y., & Xu, Y. (2011). An interval-parameter minimax regret programming approach for power management systems planning under uncertainty. Applied Energy, 88(8), 2835–2845.
Ehrgott, M. (2005). Multicriteria optimization (2nd ed.). Berlin: Springer.
Ehrgott, M., Puerto, J., & Rodríguez-Chía, A. (2007). Primal-dual simplex method for multiobjective linear programming. Journal of Optimization Theory, 134(3), 483–497.
Goberna, M. A., & López, M. A. (2002). Linear semi-infinite programming theory: An updated survey. European Journal of Operational Research, 143(2), 390–405.
Hladík, M. (2008). Computing the tolerances in multiobjective linear programming. Optimization Methods and Software, 23(5), 731–739.
Hladík, M. (2010). On necessary efficient solutions in interval multiobjective linear programming. In C. H. Antunes, D. R. Insua, & L. C. Dias (Eds.), CD-ROM Proceedings of the 25th mini-EURO conference uncertainty and robustness in planning and decision making URPDM 2010, April 15–17 (pp. 1–10). Portugal: Coimbra.
Hladík, M. (2012). Complexity of necessary efficiency in interval linear programming and multiobjective linear programming. Optimization Letters, 6(5), 893–899.
Hladík, M. (2012). Interval linear programming: A survey. In Z. A. Mann (Ed.), Linear programming—new frontiers in theory and applications (pp. 85–120). New York: Nova Science Publishers.
Hladík, M. (2013). Weak and strong solvability of interval linear systems of equations and inequalities. Linear Algebra and its Applications, 438(11), 4156–4165.
Hladík, M. (2014). How to determine basis stability in interval linear programming. Optimization Letters, 8(1), 375–389.
Inuiguchi, M., & Kume, Y. (1991). Goal programming problems with interval coefficients and target intervals. European Journal of Operational Research, 52(3), 345–360.
Inuiguchi, M., & Sakawa, M. (1995). Minimax regret solution to linear programming problems with an interval objective function. European Journal of Operational Research, 86(3), 526–536.
Inuiguchi, M., & Sakawa, M. (1996). Possible and necessary efficiency in possibilistic multiobjective linear programming problems and possible efficiency test. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 78(2), 231–241.
Ishibuchi, H., & Tanaka, H. (1990). Multiobjective programming in optimization of the interval objective function. European Journal of Operational Research, 48(2), 219–225.
López, M., & Still, G. (2007). Semi-infinite programming. European Journal of Operational Research, 180(2), 491–518.
Loulou, R., & Kanudia, A. (1999). Minimax regret strategies for greenhouse gas abatement: Methodology and application. Operations Research Letters, 25(5), 219–230.
Mausser, H. E., & Laguna, M. (1998). A new mixed integer formulation for the maximum regret problem. International Transactions in Operational Research, 5(5), 389–403.
Moore, R. E., Kearfott, R. B., & Cloud, M. J. (2009). Introduction to interval analysis. Philadelphia, PA: SIAM.
Oliveira, C., & Antunes, C. H. (2007). Multiple objective linear programming models with interval coefficients—an illustrated overview. European Journal of Operational Research, 181(3), 1434–1463.
Oliveira, C., & Antunes, C. H. (2009). An interactive method of tackling uncertainty in interval multiple objective linear programming. Journal of Mathematical Sciences, 161(6), 854–866.
Rivaz, S., & Yaghoobi, M. (2013). Minimax regret solution to multiobjective linear programming problems with interval objective functions coefficients. Central European Journal of Operations Research, 21(3), 625–649.
Urli, B., & Nadeau, R. (1992). An interactive method to multiobjective linear programming problems with interval coefficients. INFOR, 30(2), 127–137.
Wu, H. C. (2009). The Karush–Kuhn–Tucker optimality conditions in multiobjective programming problems with interval-valued objective functions. European Journal of Operational Research, 196(1), 49–60.
Acknowledgments
Milan Hladík was supported by the Czech Science Foundation Grant P402-13-10660S.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rivaz, S., Yaghoobi, M.A. & Hladík, M. Using modified maximum regret for finding a necessarily efficient solution in an interval MOLP problem. Fuzzy Optim Decis Making 15, 237–253 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10700-015-9226-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10700-015-9226-4
Keywords
- Multiobjective linear programming
- Interval programming
- Minimax regret criterion
- Necessarily efficient solutions