Abstract
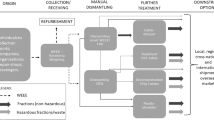
Waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE) consist of many different substances some of which contain hazardous components and valuable materials. The recovery of WEEE plays a key role on environmental sustainability because it minimizes the negative effects of hazardous materials and helps the efficient use of world’s limited resources. Recovery strategies enable companies to collect reusable components and to recycle the material content of WEEE by using operations like sorting, disassembly and bulk recycling. Usually companies associated with municipals collect WEEE from end-users and/or collection points. Then they sell these items to WEEE recycling facilities through bidding. For recycling facilities, it is important to generate the best operational level decisions to receive and handle WEEE. This study contributes to the fulfillment of this need by presenting a mixed integer linear programming model to determine the maximum bid price offer while determining the best operation planning strategies. In order to demonstrate the potential of the proposed model, a real life case study along with several scenarios is studied. The findings of the case study indicate that the model has the potential to enable the decision maker to come with stronger decisions related to both bidding process and operational strategies of the facility.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdessalem M, Hadj-Alouane AB, Riopel D (2012) Decision modelling of reverse logistics systems: selection of recovery operations for end-of-life products. Int J Logist Syst Manag 13:139–161. doi:10.1504/IJLSM.2012.048933
Amoyaw-Osei Y, Agyekum OO, Pwamang JA, Mueller E, Fasko R, Schluep M (2011) Ghana e-waste country assessment. Green Advocacy Ghana & Empa Switzerland, Ghana
Anghinolfi D, Paolucci M, Robba M, Taramasso AC (2013) A dynamic optimization model for solid waste recycling. Waste Manag 33:287–296. doi:10.1016/j.wasman.2012.10.006
Bing X, Bloemhof-Ruwaard J, Vorst JAJ (2014) Sustainable reverse logistics network design for household plastic waste. Flex Serv Manuf 26:119–142. doi:10.1007/s10696-012-9149-0
Brindley F, Angel J (2008) Tipping point: Australia’s E-waste Crisis. Total Environment Centre and Environment Victoria, Sydney, Australia
Cobbing M (2008) Toxic tech: not in our backyard: uncovering the hidden flows of e-waste. Greenpeace International, Amsterdam
Cucchiella F, D’Adamo I, Gastaldi M, Koh SCL (2014) Implementation of a real option in a sustainable supply chain: an empirical study of alkaline battery recycling. Int J Syst Sci 45:1268–1282. doi:10.1080/00207721.2012.761458
Cui J, Forssberg E (2003) Mechanical recycling of waste electric and electronic equipment: a review. J Hazard Mater 99:243–263
Cui J, Zhang L (2008) Metallurgical recovery of metals from electronic waste: a review. J Hazard Mater 158:228–256
Dalrymple I, Wright N, Kellner R, Bains N, Geraghty K, Goosey M, Lightfoot L (2007) An integrated approach to electronic waste (WEEE) recycling. Circuit World 33:52–58
DEFRA (2007) Trial to establish waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE) protocols. Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs, London
Dhouib D (2014) An extension of MACBETH method for a fuzzy environment to analyze alternatives in reverse logistics for automobile tire wastes. Omega 42:25–32. doi:10.1016/j.omega.2013.02.003
EPA (2009) Municipal solid waste in the United States: 2009 facts and figures. United States Environmental Protection Agency: EPA 530-R-510-012
EU (2002) Directive 2002/96/EC of the European parliament and of the council of 27 January 2003 on waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE)—joint declaration of the European parliament. The council and the commission relating to article 9. Off J L037:0024–0039
Guide VDR Jr (2000) Production planning and control for remanufacturing: industry practice and research needs. J Oper Manag 18:467–483. doi:10.1016/S0272-6963(00)00034-6
Gungor A, Gupta SM (1998) Disassembly sequence planning for products with defective parts in product recovery. Comput Ind Eng 35:161–164. doi:10.1016/S0360-8352(98)00047-3
Gungor A, Gupta SM (1999) Issues in environmentally conscious manufacturing and product recovery: a survey. Comput Ind Eng 36:811–853
Güngör A, Gupta SM (2002) Disassembly line in product recovery. Int J Prod Res 40:2569–2589. doi:10.1080/00207540210135622
Guo S, Aydin G, Souza GC (2013) Dismantle or remanufacture? Eur J Oper Res 233:580–583. doi:10.1016/j.ejor.2013.09.042
He W, Li G, Ma X, Wang H, Huang J, Xu M, Huang C (2006) WEEE recovery strategies and the WEEE treatment status in China. J Hazard Mater 136:502–512
Huscroft JR, Hazen BT, Hall D, Skipper JB, Hanna JB (2013) Reverse logistics: past research, current management issues, and future directions. Int J Logist Manag 24:304–327. doi:10.1108/IJLM-04-2012-0024
Ilgin MA, Gupta SM (2010) Environmentally conscious manufacturing and product recovery (ECMPRO): a review of the state of the art. J Environ Manage 91:563–591
Ilgin MA, Gupta SM (2012) Remanufacturing modeling and analysis. CRC Press, Florida
Kalayci C, Polat O, Gupta SM (2014) A hybrid genetic algorithm for sequence-dependent disassembly line balancing problem. Ann Oper Res. doi:10.1007/s10479-014-1641-3
Kang H-Y, Schoenung JM (2005) Electronic waste recycling: a review of U.S. infrastructure and technology options. Resour Conserv Recycl 45:368–400
Kannan G, Sasikumar P, Devika K (2010) A genetic algorithm approach for solving a closed loop supply chain model: a case of battery recycling. Appl Math Model 34:655–670. doi:10.1016/j.apm.2009.06.021
Kapetanopoulou P, Tagaras G (2009) An empirical investigation of value-added product recovery activities in SMEs using multiple case studies of OEMs and independent remanufacturers. Flex Serv Manuf 21:92–113. doi:10.1007/s10696-010-9063-2
Karakayali I, Emir-Farinas H, Akcali E (2007) An analysis of decentralized collection and processing of end-of-life products. J Oper Manag 25:1161–1183. doi:10.1016/j.jom.2007.01.017
Krikke HR, van Harten A, Schuur PC (1998) On a medium-term product recovery and disposal strategy for durable assembly products. Int J Prod Res 36:111–140. doi:10.1080/002075498193967
Krikke HR, van Harten A, Schuur PC (1999) Business case Roteb: recovery strategies for monitors. Comput Ind Eng 36:739–757
Minciardi R, Paolucci M, Robba M, Sacile R (2008) Multi-objective optimization of solid waste flows: environmentally sustainable strategies for municipalities. Waste Manag 28:2202–2212. doi:10.1016/j.wasman.2007.10.003
Moore KE, Gungor A, Gupta SM (1998) A Petri net approach to disassembly process planning. Comput Ind Eng 35:165–168
Pati RK, Vrat P, Kumar P (2008) A goal programming model for paper recycling system. Omega 36:405–417
Ploog M, Spengler T (2002) Integrated planning of electronic scrap disassembly and bulk recycling. IEEE Int Symp Electron Environ. doi:10.1109/isee.2002.1003277
Quariguasi Frota Neto J, Walther G, Bloemhof J, van Nunen JAEE, Spengler T (2009) A methodology for assessing eco-efficiency in logistics networks. Eur J Oper Res 193:670–682. doi:10.1016/j.ejor.2007.06.056
Quariguasi Frota Neto J, Walther G, Bloemhof J, van Nunen JAEE, Spengler T (2010) From closed-loop to sustainable supply chains: the WEEE case. Int J Prod Res 48:4463–4481. doi:10.1080/00207540902906151
Rahimifard S, Abu Bakar MS, Williams DJ (2009) Recycling process planning for the end-of-life management of waste from electrical and electronic equipment. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 58:5–8
Rahman S, Subramanian N (2012) Factors for implementing end-of-life computer recycling operations in reverse supply chains. Int J Prod Econ 140:239–248. doi:10.1016/j.ijpe.2011.07.019
Renteria A, Alvarez E (2012) Optimizing the recycling process of electronic appliances: new trends and applications. In: Golinska P, Romano CA (eds) Environmental issues in supply chain management. Springer, Berlin, pp 91–105. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-23562-7_6
Renteria A, Alvarez E, Perez J, del Pozo D (2010) A methodology to optimize the recycling process of WEEE: case of television sets and monitors. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 54:789–800
Rios PJ, Stuart JA (2004) Scheduling selective disassembly for plastics recovery in an Electronics Recycling Center. IEEE Trans Electron Packag Manuf 27:187–197
Robinson BH (2009) E-waste: an assessment of global production and environmental impacts. Sci Total Environ 408:183–191
Ruiz-Torres AJ, Ablanedo-Rosas JH, Mukhopadhyay S (2013) Supplier allocation model for textile recycling operations. Int J Logist Syst Manag 15:108–124
Schweiger K, Sahamie R (2013) A hybrid Tabu Search approach for the design of a paper recycling network. Transp Res Part E Logist Transp Rev 50:98–119. doi:10.1016/j.tre.2012.10.006
Shih L-H, Lee S-C (2007) Optimizing disassembly and recycling process for EOL LCD-type products: a Heuristic method. IEEE Trans Electron Packag Manuf 30:213–220
Simic V, Dimitrijevic B (2012a) Modelling production processes in a vehicle recycling plant. Waste Manage Res 30:940–948. doi:10.1177/0734242X12454695
Simic V, Dimitrijevic B (2012b) Production planning for vehicle recycling factories in the EU legislative and global business environments. Resour Conserv Recycl 60:78–88. doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2011.11.012
Simic V, Dimitrijevic B (2013) Risk explicit interval linear programming model for long-term planning of vehicle recycling in the EU legislative context under uncertainty. Resour Conserv Recycl 73:197–210. doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2013.02.012
Sodhi MS, Reimer B (2001) Models for recycling electronics end-of-life products. OR Spectrum 23:97–115. doi:10.1007/PL00013347
Sodhi MS, Young J, Knight WA (1999) Modelling material separation processes in bulk recycling. Int J Prod Res 37:2239–2252. doi:10.1080/002075499190743
Spengler T, Ploog M, Schröter M (2003) Integrated planning of acquisition, disassembly and bulk recycling: a case study on electronic scrap recovery. OR Spectrum 25:413–442. doi:10.1007/s00291-003-0119-5
Stindt D, Sahamie R (2014) Review of research on closed loop supply chain management in the process industry. Flex Serv Manuf 26:268–293. doi:10.1007/s10696-012-9137-4
Stuart JA, Christina V (2003) New metrics and scheduling rules for disassembly and bulk recycling. IEEE Trans Electron Packag Manuf 26:133–140
Teunter RH (2006) Determining optimal disassembly and recovery strategies. Omega 34:533–537
Thierry M, Salomon M, Nunen JV, Wassenhove LV (1995) Strategic issues in product recovery management. Calif Manag Rev 37:114–135
UNEP (2006) Call for global action on E-waste. United Nations Environment Programme, Nairobi
Walther G, Steinborn J, Spengler T, Luger T, Herrmann C (2010) Implementation of the WEEE-directive—economic effects and improvement potentials for reuse and recycling in Germany. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 47:461–474. doi:10.1007/s00170-009-2243-0
Webster S, Mitra S (2007) Competitive strategy in remanufacturing and the impact of take-back laws. J Oper Manag 25:1123–1140. doi:10.1016/j.jom.2007.01.014
Widmer R, Oswald-Krapf H, Sinha-Khetriwal D, Schnellmann M, Böni H (2005) Global perspectives on e-waste. Environ Impact Assess Rev 25:436–458
Williams JAS (2006) A review of electronics demanufacturing processes. Resour Conserv Recycl 47:195–208
Williams JAS, Wongweragiat S, Qu X, McGlinch JB, Bonawi-tan W, Choi JK, Schiff J (2007) An automotive bulk recycling planning model. Eur J Oper Res 177:969–981
Wu CC, Chang NB (2003) Global strategy for optimizing textile dyeing manufacturing process via GA-based grey nonlinear integer programming. Comput Chem Eng 27:833–854. doi:10.1016/S0098-1354(02)00270-3
Ziout A, Azab A, Atwan M (2014) A holistic approach for decision on selection of end-of-life products recovery options. J Clean Prod 65:497–516. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2013.10.001
Acknowledgments
The authors are indebted to the anonymous referees and the Editor for several suggestions, which substantially improved the paper. This research is partially funded by the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK) under the Grant Number 111M428. The authors wish to acknowledge this valuable support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Capraz, O., Polat, O. & Gungor, A. Planning of waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE) recycling facilities: MILP modelling and case study investigation. Flex Serv Manuf J 27, 479–508 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10696-015-9217-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10696-015-9217-3