Abstract
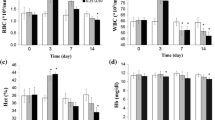
The effects of extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields on rainbow trout growth performance, innate immunity and biochemical parameters were studied. Rainbow trout (17–18 g) were exposed to electromagnetic fields (15 Hz) at 0.01, 0.1, 0.5, 5 and 50 µT, for 1 h daily over period of 60 days. Growth performance of fish improved in different treatment groups, especially at 0.1, 0.5, 5 and 50 µT. Immunological parameters, specifically hemagglutinating titer, total antiprotease and α1-antiprotease levels in treatment groups, were also enhanced. Total protein and globulin contents in the serum of fish exposed to 0.1, 0.5, 5 and 50 µT were significantly higher than those in the control group. No significant differences were found in serum enzyme activities, namely aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase of fish in all treatment groups. Conversely, alkaline phosphatase level decreased in fish exposed to 0.01 and 50 µT electromagnetic fields. Meanwhile, electromagnetic induction at 0.1, 0.5, 5 and 50 µT enhanced fish protection against Yersinia ruckeri. These results indicated that these specific electromagnetic fields had possible effects on growth performance, nonspecific immunity and disease resistance of rainbow trout.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allain CC, Poon LS, Chan CS, Richmond W, Fu PC (1974) Enzymatic determination of total serum cholesterol. Clin Chem 20:470–475
Cameron IL, Hunter KE, Winters WD (1985) Retardation of embryogenesis by extremely low frequency 60 Hz electromagnetic fields. Physiol Chem Phys Med NMR 17:135–138
Canseven AG, Coskun S, Seyhan N (2008) Effects of various extremely low frequency magnetic fields on the free radical processes, natural antioxidant system and respiratory burst system activities in the heart and liver tissues. Indian J Biochem Biophys 45:326–331
Cetin N, Bilgili A, Eraslan G (2006) Effects of pulsed magnetic field chronic exposure on some hematological parameters in mice. Revue Méd Vét 157:68–71
Cuesta A, Rodriguez A, Esteban MA, Meseguer J (2005) In vivo effects of propolis, a honeybee product, on gilthead seabream innate immune responses. Fish Shellfish Immunol 18:71–80
Cuesta A, Rodriguez A, Salinas I, Meseguer J, Esteban MA (2007) Early local and systemic innate immune responses in the teleost gilthead seabream after intraperitoneal injection of whole yeast cells. Fish Shellfish Immunol 22:242–251
Cuppen JJM, Wiegertjes GF, Lobee HWJ, Savelkoul HFJ, Elmusharaf MA, Beynen AC, Grooten HNA, Smink W (2007) Immune stimulation in fish and chicken through weak low frequency electromagnetic fields. Environmentalist. doi:10.1007/s10669-007-9055-2
Di Carlo AL, White NC, Litovitz TA (2000) Mechanical and electromagnetic induction of protection against oxidative stress. Bioelectrochemistry 53:87–95
Ellis AE (2001) Innate host defense mechanisms of fish against viruses and bacteria. Dev Comp Immunol 25:827–839
Fossati P, Prencipe L (1982) Serum triglycerides determined calorimetrically with an enzyme and produces hydrogen peroxide. Clin Chem 28:2077–2080
Frahm J, Lantow M, Lupke M, Weiss DG, Simkó M (2006) Alteration in cellular functions in mouse macrophages after exposure to 50 Hz magnetic fields. J Cell Biochem 99:168–177
Friedel R, Diederichs F, Lindena J (1979) Release and extracellular turnover of cellular enzymes. In: Schmidt E, Schmidt FW, Trautschold I, Friedel R (eds) Advances in clinical enzymology. Karger, Basel, pp 70–105
Gerardi G, De Ninno A, Prosdocimi M, Ferrari V, Barbaro F, Mazzariol S, Bernardini D, Talpo G (2008) Effects of electromagnetic fields of low frequency and low intensity on rat metabolism. Biomagn Res Technol 6:3
Gill AB, Bartlett M, Thomsen F (2012) Potential interactions between diadromous fishes of U.K. conservation importance and the electromagnetic fields and subsea noise from marine renewable energy developments. J Fish Biol 81:664–695
Gobba F, Bargellini A, Scaringi M, Bravo G, Borella P (2009) Extremely low frequency-magnetic fields (ELF-EMF) occupational exposure and natural killer activity in peripheral blood lymphocytes. Sci Total Environ 407:1218–1223
Goodman R (1991) Transcription and translation in cells exposed to extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields. J Electroanal Chem Interfacial Electrochem 320:335–355
Harakawa S, Inoue N, Hori T, Tochio K, Kariya T, Kunihito Takahashi K, Doge F, Martin ED, Saito A, Suzuki H, Nagasawa H (2005) Effects of exposure to a 50 Hz electric field on plasma levels of lactate, glucose, free fatty acids, triglycerides and creatine phosphokinase activity in hind-limb ischemic rats. J Vet Med Sci 67:969–974
Hashish AH, El-Missiry MA, Abdelkader HI, Abou-Saleh RH (2008) Assessment of biological changes of continuous whole body exposure to static magnetic field and extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields in mice. Ecotox Environ Safe 71:895–902
Heidarieh M, Mirvaghefi AR, Akbari M, Farahmand H, Sheikhzadeh N, Shahbazfar AA, Behgar M (2012) Effect of dietary Ergosan on growth performance, digestive enzymes, intestinal histology, hematological parameters and body composition of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Fish Physiol Biochem 38:1169–1174
Johansson O (2009) Disturbance of the immune system by electromagnetic fields—a potentially underlying cause for cellular damage and tissue repair reduction which could lead to disease and impairment. Pathophysiology 16:157–177
Justo OR, Pérez VH, Alvarez DC, Alegre RM (2006) Growth of Escherichia coli under extremely low-frequency electromagnetic fields. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 134:155–163
Magnadottir B (2006) Innate immunity of fish (overview). Fish Shellfish Immunol 20:137–151
Maniu CL, Hritcu L (2010) Low frequency low intensity pulse electromagnetic field in vivo influence on immune capacity in rat. Secţiunea Geneticã şi Biologie Molecularã, TOM 171–175
Markov M, Gabi N, Carlton H, Jan C (2006) Interactions between electromagnetic fields and immune system: possible mechanism for pain control. In: Ayrapetyan SN, Markov M (eds) Bioelectromagnetics current concepts. Springer, Netherlands, pp 213–225
Maus S, Macmillan S, McLean S, Hamilton B, Thomson A, Nair M, Rollins C (2010) The US/UK world magnetic model for 2010–2015 (report). National Geophysical Data Center. http://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/geomag/WMM/data/WMM2010/WMM2010
Miyakoshi J (2006) Biological responses to extremely low-frequency electromagnetic fields. J Dermatol Sci Suppl 2:S23–S30
Moore A, Riley WD (2009) Magnetic particles associated with the lateral line of the European eel Anguilla anguilla. J Fish Biol 74:1629–1634
Murray JC, Farndale RW (1985) Modulation of collagen production in cultured fibroblasts by a low-frequency, pulsed magnetic field. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Gen Subj 838:98–105
Newaj-Fyzul A, Adesiyun AA, Mutani A, Ramsubhag A, Brunt J, Austin B (2007) Bacillus subtilis AB1 controls Aeromonas infection in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss, Walbaum). J Appl Microbiol 103:1699–1706
Nootash S, Sheikhzadeh N, Baradaran B, Khani Oushani A, Maleki Moghadam MR, Nofouzi K, Monfaredan A, Aghebati L, Zare F, Shabanzadeh S (2013) Green tea (Camellia sinensis) administration induces expression of immune relevant genes and biochemical parameters in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Fish Shellfish Immunol 35:1916–1923
Piera V, Rodriquez A, Cobos A, Torrente M, Cobos P (1992) Influence of continuous electromagnetic fields on the stage, weight and stature of chick embryo. Acta Ana Base 145:302–306
Rao V, Chakrabarti R (2005) Stimulation of immunity in Indian major carp Catla catla with herbal feed ingredients. Fish Shellfish Immunol 18:327–334
Richardson NE, McCleave JD, Albert EN (1976) Effect of extremely low frequency electric and magnetic fields on locomotor activity rhythms of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) and American eels (Anguilla rostrata). Environ Pollut 10:65–76
Rodemann HP, Bayreuther K, Pfleiderer G (1989) The differentiation of normal and transformed human fibroblasts in vitro is influenced by electromagnetic fields. Exp Cell Res 182:610–621
Schüz J, Ahlbom A (2008) Exposure to electromagnetic fields and the risk of childhood leukaemia: a review. Radiat Prot Dosim 132:202–211
Sheikhzadeh N, Tayefi-Nasrabadi H, Khani Oushani A, Najafi Enferadi MH (2012) Effects of Haematococcus pluvialis supplementation on antioxidant system and metabolism in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Fish Physiol Biochem 38:413–419
Simkó M, Mattsson MO (2004) Extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields as effectors of cellular responses in vitro: possible immune cell activation. J Cell Biochem 93:83–92
Simkó M, Droste S, Kriehuber R, Weiss DG (2001) Stimulation of phagocytosis in murine macrophages by 50 Hz electromagnetic fields. Eur J Cell Biol 80:562–566
Singh S, Kaur M, Khanduja KL, Mittal PK (1999) Exposure to 50 Hz electromagnetic field induces changes in the antioxidant defense system and inhibits lipid peroxidation in mice. Electro- Magnetobiol 18:7–14
Skauli KS, Reitan JB, Walther BT (2000) Hatching in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos exposed to a 50 Hz magnetic field. Bioelectromagnetics 21:407–410
Vriens AM, Bretschneider F (1979) The electrosensitivity of the lateral line of the European eel, Anguilla anguilla. J Physiol Paris 75:341–342
Zwirska-Korczala K, Jochem J, Adamczyk-Sowa M, Sowa P, Polaniak R, Birkner E, Latocha M, Pilc K, Suchanek R (2005) Effect of extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields on cell proliferation, antioxidative enzyme activities and lipid peroxidation in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes-an in vitro study. J Physiol Pharmacol 56:101–108
Acknowledgments
The researchers would like to thank Dr. Baradaran for his convenient comments during this project. The first author is grateful to Research affairs of University of Tabriz, Iran, for supporting financially.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nofouzi, K., Sheikhzadeh, N., Mohamad-Zadeh Jassur, D. et al. Influence of extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields on growth performance, innate immune response, biochemical parameters and disease resistance in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss . Fish Physiol Biochem 41, 721–731 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-015-0041-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-015-0041-1