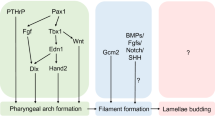
Abstract
This study aimed to better understand the hydromineral regulatory response of the anadromous river pufferfish, Takifugu obscurus, to salinity changes through real-time RT-PCR. After abrupt transfer from 30 or 5 psu to 5 or 30 psu, respectively, we analyzed the mRNA expression of Na+/K+ ATPase, prolactin receptor, and aquaporin from osmoregulatory organs of the river pufferfish such as gills, kidney, and intestine. Na+/K+ ATPase showed notable changes in the gills and kidney when salinity was increased. In the gills, the expression level of Na+/K+ ATPase suddenly increased within a day after abrupt transfer from 5 to 30 psu and then slightly declined within 2 days after exposure. In the kidney, Na+/K+ ATPase has shown consistently high mRNA expression after the increase in salinity. Expression levels of the prolactin receptor gene increased when environmental salinity decreased. In the intestine, gene expression of the prolactin receptor remained high, even when salinity decreased. To the contrary, there was a steady increase or decrease in mRNA expression in the kidney in response to salinity decrease or increase, respectively. As for aquaporins, aquaporin 1 was mainly expressed in the intestine and kidney, and aquaporin 3 was mainly expressed in the gills and intestine. In the gills, increased expression of aquaporin 3 was found after transfer to lower salinity and in the intestine and kidney, a decrease in salinity followed by an abrupt decrease in aquaporin 1 and aquaporin 3. Contrastingly, the expression of these genes increased in the intestine after transfer to 30 psu. Osmoregulatory genes were expressed in diverse organs, apparently to overcome an influx or exhaust of water or ions. A superior adaptation ability of the river pufferfish to a wide range of salinities is most reasonably due to active osmoregulatory processes mediated by the genes monitored here.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agre P (2006) The aquaporin water channels. Proc Am Thorac Soc 3:5–13
An KW, Min BH, Park IS, Heo YS, Choi YK, Jo PG (2008) Expression of prolactin receptor mRNA and blood physiological responses to salinity changes in the black porgy Acanthopagrus schlegelii. Kor J Aquac 21:63–69
Aoki M, Kaneko T, Katoh F, Hasegawa S, Tsutsui N, Aida K (2003) Intestinal water absorption through aquaporin 1 expressed in the apical membrane of mucosal epithelial cells in seawater-adapted Japanese eel. J Exp Biol 206:3495–3505
Bentley P (2002) Endocrines and osmoregulation: a comparative account in vertebrates. Springer, Berlin, p 300
Binart N, Bachelot A, Bouilly J (2010) Impact of prolactin receptor isoforms on reproduction. Trends Endocrinol Metab 21:362
Borgnia M, Nielsen S, Engel A, Agre P (1999) Cellular and molecular biology of the aquaporin water channels. Annu Rev Biochem 68:425–458
Braun EJ, Dantzler WH (1987) Mechanisms of hormone actions on renal function. In: Pang KTP, Schreibman MP (eds) Vertebrate endocrinology: fundamentals and biomedical implications, vol 2. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 189–210
Burnett KG, Bain LJ, Baldwin WS, Callard GV, Cohen S, Di Giulio RT, Evans DH, Gomez-Chiarri M, Hahn ME, Hoover CA, Karchner SI, Katoh F, MacLatchy DL, Marshall WS, Meyer JN, Nacci DE, Oleksiak MF, Rees BB, Singer TD, Stegeman JJ, Towle DW, Van Veld PA, Vogelbein WK, Whitehead A, Winn RN, Crawford DL (2007) Fundulus as the premier teleost model in environmental biology: opportunities for new insights using genomics. Comp Biochem Physiol 2D:257–286
Bystriansky JS, Richards JG, Schulte PM, Ballantyne JS (2006) Reciprocal expression of gill Na+/K+-ATPase alpha-subunit isoforms alpha 1a and alpha 1b during seawater acclimation of three salmonid fishes that vary in their salinity tolerance. J Exp Biol 209:1848–1858
Choi C, An K (2008) Cloning and expression of Na+/K+-ATPase and osmotic stress transcription factor 1 mRNA in black porgy, Acanthopagrus schlegeli during osmotic stress. Comp Biochem Physiol 149B:91–100
Clarke WC, Bern HA (1980) Comparative endocrinology of prolactin. In: Li CH (ed) Hormonal proteins and peptides, vol. VIII. Academic Press, New York, pp 105–197
Cutler CP, Cramb G (2002) Branchial expression of an aquaporin 3 (AQP-3) homologue is downregulated in the European eel Anguilla anguilla following seawater acclimation. J Exp Biol 205:2643–2651
Cutler CP, Martinez AS, Cramb G (2007) The role of aquaporin 3 in teleost fish. Comp Biochem Physiol 148A:82–91
Dahms HU, Hagiwara A, Lee JS (2011) Ecotoxicology, ecophysiology, and mechanistic studies with rotifers. Aquat Toxicol 101:1–12
Deane EE, Woo NY (2006) Tissue distribution, effects of salinity acclimation, and ontogeny of aquaporin 3 in the marine teleost, silver sea bream (Sparus sarba). Mar Biotechnol 8:663–671
Eddy FB, Bath RN (1979) Ionic regulation in rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) adapted to fresh water and diluted sea water. J Exp Biol 83:181–192
Evans D, Claiborne J (1993) Osmotic and ionic regulation. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 315–341
Giffard-Mena I, Boulo V, Aujoulat F, Fowden H, Castille R, Charmantier G, Cramb G (2007) Aquaporin molecular characterization in the sea-bass (Dicentrarchus labrax): the effect of salinity on AQP1 and AQP3 expression. Comp Biochem Physiol 148A:430–444
Giffard-Mena I, Lorin-Nebel C, Charmantier G, Castille R, Boulo V (2008) Adaptation of the sea-bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) to fresh water: role of aquaporins and Na+/K+-ATPases. Comp Biochem Physiol 150A:332–338
Gonen T, Walz T (2006) The structure of aquaporins. Q Rev Biophys 39:361–396
Grosell M (2006) Intestinal anion exchange in marine fish osmoregulation. J Exp Biol 209:2813–2827
Hwang PP, Fang MJ, Tsai JC, Huang CJ, Chen ST (1998) Expression of mRNA and protein of Na+/-K+-ATPase α subunit in gills of tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus). Fish Physiol Biochem 18:363–373
Kang CK, Tsai SC, Lee TH, Hwang PP (2008) Differential expression of branchial Na+/K(+)-ATPase of two medaka species, Oryzias latipes and Oryzias dancena, with different salinity tolerances acclimated to fresh water, brackish water and seawater. Comp Biochem Physiol 151A:566–575
Kato A, Doi H, Nakada T, Sakai H, Hirose S (2005) Takifugu obscurus is a euryhaline fugu species very close to Takifugu rubripes and suitable for studying osmoregulation. BMC Physiol 5:18
Kelly SP, Chow INK, Woo NYS (1999) Haloplasticity of black seabream (Mylio macrocephalus): hypersaline to freshwater acclimation. J Exp Zool 283:226–241
Kim JH, Kim SJ, Min GS, Han KN (2008) Nutritional condition determined using RNA/DNA ratios of the river pufferfish Takifugu obscurus under different salinities. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 372:243–252
Kim JH, Dahms HU, Rhee JS, Lee YM, Lee J, Han KN, Lee JS (2010a) Expression profiles of seven glutathione S-transferase (GST) genes in cadmium-exposed river pufferfish (Takifugu obscurus). Comp Biochem Physiol 151C:99–106
Kim JH, Rhee JS, Dahms HU, Lee J, Han KN, Lee JS (2010b) Effect of cadmium exposure on expression of antioxidant gene transcripts in the river pufferfish, Takifugu obscurus (Tetraodontiformes). Comp Biochem Physiol 152C:473–479
Knepper MA (1997) Molecular physiology of urinary concentrating mechanism: regulation of aquaporin water channels by vasopressin. Am J Physiol 272:F3–F12
Lee KM, Kaneko T, Katoh F, Aida K (2006) Prolactin gene expression and gill chloride cell activity in fugu Takifugu rubripes exposed to a hypoosmotic environment. Gen Comp Endocrinol 149:285–293
Liang P, Jones CA, Bisgrove BW, Song L, Glenn ST, Yost HJ, Gross KW (2004) Genomic characterization and expression analysis of the first nonmammalian renin gene from zebrafish and pufferfish. Physiol Genomics 16:314–322
Lignot JH, Cutler CP, Hazon N, Cramb G (2002a) Immunolocalisation of aquaporin 3 in the gill and the gastrointestinal tract of the European eel Anguilla anguilla (L.). J Exp Biol 205:2653–2663
Lignot JH, Cutler C, Hazon N, Cramb G (2002b) Water transport and aquaporins in the European eel (Anguilla anguilla). Symposia of the Society for Exp Biol, pp 59
Lin CH, Tsai RS, Lee TH (2004) Expression and distribution of Na, K-ATPase in gill and kidney of the spotted green pufferfish, Tetraodon nigroviridis, in response to salinity challenge. Comp Biochem Physiol 138A:287–295
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Manzon LA (2002) The role of prolactin in fish osmoregulation: a review. Gen Comp Endocrinol 125:291–310
Marshall WS, Grosell M (2006) Ion transport, osmoregulation and acid-base balance. In: Evans DH, Claiborne JB (eds) The physiology of fishes, 3rd edn. Taylor and Francis, London, pp 177–230
Martinez AS, Cutler CP, Wilson GD, Phillips C, Hazon N, Cramb G (2005) Regulation of expression of two aquaporin homologs in the intestine of the European eel: effects of seawater acclimation and cortisol treatment. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 288:R1733–R1743
McCormick S (1995) Hormonal control of gill Na+, K+-ATPase and chloride cell function. Academic Press, New-York, pp 285–315
McCormick S (2001) Endocrine control of osmoregulation in teleost fish. Am Zool 41:781–794
Nielsen C, Madsen S, Bjornsson B (1999) Changes in branchial and intestinal osmoregulatory mechanisms and growth hormone levels during smolting in hatchery-reared and wild brown trout. J Fish Biol 54:799–818
Nielsen S, Frokiaer J, Marples D, Kwon TH, Agre P, Knepper MA (2002) Aquaporins in the kidney: from molecules to medicine. Physiol Rev 82:205–244
Pierce AL, Fox BK, Davis LK, Visitacion N, Kitahashi T, Hirano T, Grau EG (2007) Prolactin receptor, growth hormone receptor, and putative somatolactin receptor in Mozambique tilapia: tissue specific expression and differential regulation by salinity and fasting. Gen Comp Endocrinol 154:31–40
Sakamoto T, McCormick SD (2006) Prolactin and growth hormone in fish osmoregulation. Gen Comp Endocrinol 147:24–30
Shi Y, Zhang G, Zhu Y, Liu J (2010) Effects of photoperiod, temperature, and salinity on growth and survival of obscure puffer Takifugu obscurus larvae. Aquaculture 309:103–108
Smith HW (1930) The absorption and excretion of water and salts by marine teleost. Am J Physiol 93:480–505
Tang CH, Lee TH (2011) Morphological and ion-transporting plasticity of branchial mitochondrion-rich cells in the euryhaline spotted green pufferfish, Tetraodon nigroviridis. Zool Stud 50:31–42
Tomy S, Chang YM, Chen YH, Cao JC, Wang TP, Chang CF (2009) Salinity effects on the expression of osmoregulatory genes in the euryhaline black porgy Acanthopagrus schlegeli. Gen Comp Endocrinol 161:123–132
Tse WK, Au DW, Wong CK (2006) Characterization of ion channel and transporter mRNA expressions in isolated gill chloride and pavement cells of seawater acclimated eels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 346:1181–1190
Wang PJ, Lin CH, Hwang LY, Huang CL, Lee TH, Hwang PP (2009) Differential responses in gills of euryhaline tilapia, Oreochromis mossambicus, to various hyperosmotic shocks. Comp Biochem Physiol 152A:544–551
Watanabe S, Kaneko T, Aida K (2005) Aquaporin-3 expressed in the basolateral membrane of gill chloride cells in Mozambique tilapia Oreochromis mossambicus adapted to freshwater and seawater. J Exp Biol 208:2673–2682
Wedemeyer G (1997) Effects of rearing conditions on the health and physiological quality of fish in intensive culture. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 35–72
Yan M, Li Z, Xiong B (2005) Preliminary results on osmolality responses of pufferfish Takifugu obscurus to sudden salinity change. J Appl Ichthyol 21:156–159
Yang Z, Chen Y (2006) Salinity tolerance of embryos of obscure puffer Takifugu obscurus. Aquaculture 253:393–397
Acknowledgments
This research was a part of the project titled “Development of Korea Operational Oceanographic System (KOOS)” and “Long-term change of structure and function in marine ecosystems of Korea” funded by the Ministry of Land, Transport and Maritime Affairs (MLTM), Korea. This work was supported by the Inha grant program (2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Su-Young Jeong and Jin-Hyoung Kim have equally contributed to this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeong, SY., Kim, JH., Lee, WO. et al. Salinity changes in the anadromous river pufferfish, Takifugu obscurus, mediate gene regulation. Fish Physiol Biochem 40, 205–219 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-013-9837-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-013-9837-z