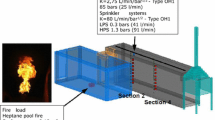
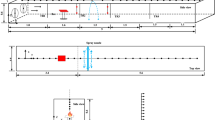
Abstract
This work focuses on interactions between a water mist and a smoke layer generated by a fire. It aims at highlighting and quantifying the mist impact on smoke stratification, investigating both thermal and optical effects. The study is based on large-scale experiments and numerical reconstruction with the computational code fire dynamics simulator (FDS v.6). The use of FDS allows understanding the complicated flow generated by the water mist and the fire, which yields specific gas temperature and opacity conditions within the medium composed of soot and water droplets in suspension. There are two main results. As expected, a de-stratification occurs as a consequence of mist application. A 1 m high smoke-free layer was observed in the present case before mist activation, which disappears due to the mist action. However, consecutive effects on optical and thermal properties are not identical. In the presented tests, water mist application homogenized the gas temperature downward the nozzle location to a value close to 50°C due to both mixing and cooling effects (while temperature was varying between ambient temperature near the floor and 150°C below the ceiling before mist activation). On the contrary opacity measurements revealed remaining discrepancies, in soot and droplet concentrations. Transmissivity decreases after mist activation, but significant variations are still seen in the smoke layer. As a consequence, characterization of the smoke layer with one single technique or the other (namely: opacity measurement or temperature measurement) would lead to different conclusions on the smoke homogeneity. It appears that both measurements should be involved simultaneously for a complete characterization of the environment.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jenft A, Collin A, Boulet P, Pianet G, Breton A, Muller A (2014) Experimental and numerical study of pool fire suppression using water mist. Fire Saf J 67:1–12
Collin A, Lechêne S, Boulet P, Parent G (2010) Water mist and radiation interactions—application to a water curtain used as a radiative shield. Numer Heat Transf A 57:537–553
Lechêne S, Acem Z, Parent G, Jeandel G, Boulet P (2011) Upward vs downward injection of droplets for the optimization of a radiative shield. Int J Heat Mass Tranf 54:1689–1697
Lechêne S, Acem Z, Parent G, Collin A, Boulet P (2012) Radiative shielding by water mist: comparison between downward, upward and impacting of droplets. J Phys 69:012027
Blanchard E, Boulet P, Fromy P, Desanghère S, Carlotti P, Vantelon JP, Garo JP (2014) Experimental and numerical study of the interaction between water mist and fire in an intermediate test tunnel. Fire Technol 50(3):565–587
Tang Z, Fang Z, Yuan JP, Merci B (2013), Experimental study of the downward displacement of fire-induced smoke by water sprays. Fire Saf J 55:35–49
Tang Z, Vierendeels J, Fang Z, Merci B (2013) Description and application of an analytical model to quantify downward smoke displacement caused by water spray. Fire Saf J 55:50–60
Blanchard E (2011) Modélisation de l’interaction entre brouillard d’eau et feu en tunnel. PhD Thesis, Université Henri Poincaré Nancy 1
Babrauskas V (2002) Heat release rates (Chap. 3). In: SFPE Handbook of fire protection engineering, 3rd edn. SFPE, New England, pp 3–37
McGrattan K, McDermott R, Hostikka S, Floyd J (2013) FDS (Version 6) user’s guide. Technical report, NIST
McGrattan K, McDermott R, Hostikka S, Floyd J (2013) FDS (Version 6) Technical reference guide: mathematical model, vol 1. Technical report, NIST
Solovjov VP, Webb B W (2001) An efficient method for modeling radiative transfer in multicomponent gas mixtures with soot. J Heat Transf 123:450
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morlon, R., Boulet, P., Parent, G. et al. Study of De-stratification and Optical Effects Observed During Smoke/Mist Interactions. Fire Technol 51, 1231–1248 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10694-014-0437-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10694-014-0437-y