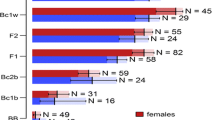
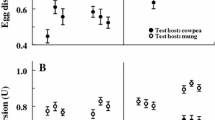
Abstract
Even though generalist insects are able to feed on many different host plants, local specialization may occur, which could lead to genetic differentiation. In this paper we assessed the level and extent of host plant specialization in the generalist herbivore Heliothis virescens Fabricius (Lepidoptera, Noctuidae). This generalist can grow and survive on many different plant species, belonging to more than 37 families. Previously, two laboratory strains were described that differ in their performance on cotton and chickpea. In this study we explored this phenomenon further. Specifically, we asked the following questions: (1) Do the two strains still differ in their performance on cotton and chickpea? Since we found that the most pronounced difference between the two strains was in their growth on fresh chickpea leaves, we then asked: (2) Does this variation in performance have a genetic basis? In our genetic analysis, we found that growth rates changed over time and that two linkage groups significantly affected the ability to grow on chickpea. One QTL was homologous to Bombyx mori chromosome 15, onto which genes for insecticide resistance and detoxicative enzymes have previously been mapped. (3) Is there a difference in oviposition preference between the two strains? Oviposition experiments revealed no preference in either strain when females were reared on the same artificial diet. However, we did find a maternal inheritance of oviposition preference: daughters collected as eggs from cotton oviposited significantly more eggs on cotton, and daughters collected as eggs from chickpea likewise laid more eggs on chickpea. Thus, Hopkins’ host selection principle seems to holds in this species, although imprinting seems to happen not at the larval but at the egg stage, which is a new finding. This study shows how genetic and nongenetic factors can interact to shape the patterns of local specialization in a generalist herbivore.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhtar Y, Isman MB (2003) Binary mixtures of feeding deterrents mitigate the decrease in feeding deterrent response to antifeedants following prolonged exposure in the cabbage looper, Trichoplusia ni (Lepidoptera : Noctuidae). Chemoecology 13:177–182
Anderson P, Sadek MM, Larsson M, Hansson BS, Thoming G (2013) Larval host plant experience modulates both mate finding and oviposition choice in a moth. Anim Behav 85:1169–1175
Barron AB (2001) The life and death of Hopkins’ host-selection principle. J Insect Behav 14:725–737
Belknap JK, Mitchell SR, Otoole LA, Helms ML, Crabbe JC (1996) Type I and Type II error rates for quantitative trait loci (QTL) mapping studies using recombinant inbred mouse strains. Behav Genet 26:149–160
Bernays EA (1999) Plasticity and the problem of choice in food selection. Ann Entomol Soc Am 92:944–951
Bernays EA (2001) Neural limitations in phytophagous insects: implications for diet breadth and evolution of host affiliation. Annu Rev Entomol 46:703–727
Bernays EA, Minkenberg O (1997) Insect herbivores: different reasons for being a generalist. Ecology 78:1157–1169
Blanco CA, Teran-Vargas AP, Lopez JD, Kauffman JV, Wei XK (2007) Densities of Heliothis virescens and Helicoverpa zea (Lepidoptera : Noctuidae) in three plant hosts. Fla Entomol 90:742–750
Blanco CA, Teran-Vargas AP, Abel CA, Portilla M, Rojas MG, Morales-Ramos JA, Snodgrass GL (2008) Plant host effect on the development of Heliothis virescens F. (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Environ Entomol 37:1538–1547
Blanco CA, Teran-Vargas AP, Lopez JD, Abel CA (2009) Incidence of Heliothis virescens on garbanzo varieties in Northwestern Mississippi. Southwest Entomol 34:61–67
Broman KW, Sen S (2009) A guide to QTL mapping with R/qtl, Vol. II. Springer, New York
Broman KW, Wu H, Sen S, Churchill GA (2003) R/qtl: QTL mapping in experimental crosses. Bioinformatics 19:889–890
Cahenzli F, Erhardt A (2013) Transgenerational acclimatization in an herbivore—host plant relationship. Proc R Soc B Biol Sci 280(1756):20122856
Caillaud MC, Via S (2012) Quantitative genetics of feeding behavior in two ecological races of the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum. Heredity 108:211–218
Chow JK, Akhtar Y, Isman MB (2005) The effects of larval experience with a complex plant latex on subsequent feeding and oviposition by the cabbage looper moth: Trichoplusia ni (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Chemoecology 15:129–133
Crispo E (2008) Modifying effects of phenotypic plasticity on interactions among natural selection, adaptation and gene flow. J Evol Biol 21:1460–1469
de Jong PW, Frandsen HO, Rasmussen L, Nielsen JK (2000) Genetics of resistance against defences of the host plant Barbarea vulgaris in a Danish flea beetle population. Proc R Soc B-Biol Sci 267:1663–1670
Dres M, Mallet J (2002) Host races in plant-feeding insects and their importance in sympatric speciation. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 357:471–492
Dukas R (2008) Evolutionary biology of insect learning. Annu Rev Entomol 53:145–160
Emelianov I, Mallet J, Baltensweiler W (1995) Genetic differentiation in Zeiraphera diniana (Lepidoptera, Tortricidae, the larch budmoth)—polymorphism, host races or sibling species. Heredity 75:416–424
Emelianov I, Simpson F, Narang P, Mallet J (2003) Host choice promotes reproductive isolation between host races of the larch budmoth Zeiraphera diniana. J Evol Biol 16:208–218
Etges WJ, de Oliveira CC, Noor MAF, Ritchie MG (2010) Genetics of incipient speciation in Drosophila mojavensis. III. Life-history divergence in allopatry and reproductive isolation. Evolution 64:3549–3569
Fitt GP (1989) The ecology of Heliothis species in relation to agroecosystems. Annu Rev Entomol 34:17–52
Fox CW, Waddell KJ, Mousseau TA (1995) Parental host plant affects offspring life histories in a seed beetle. Ecology 76:402–411
Funk WC, Murphy MA (2010) Testing evolutionary hypotheses for phenotypic divergence using landscape genetics. Mol Ecol 19:427–430
Futuyma DJ, Moreno G (1988) The evolution of ecological specialization. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 19:207–233
Groot AT, Estock ML, Horovitz JL, Hamilton J, Santangelo RG, Schal C, Gould F (2009) QTL analysis of sex pheromone blend differences between two closely related moths: insights into divergence in biosynthetic pathways. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 39:568–577
Groot AT, Classen A, Staudacher H, Schal C, Heckel DG (2010) Phenotypic plasticity in sexual communication signal of a noctuid moth. J Evol Biol 23:2731–2738
Groot AT, Classen A, Inglis O, Blanco CA, Lopez J, Vargas AT, Schal C, Heckel DG, Schofl G (2011) Genetic differentiation across North America in the generalist moth Heliothis virescens and the specialist H. subflexa. Mol Ecol 20:2676–2692
Hawthorne DJ, Via S (2001) Genetic linkage of ecological specialization and reproductive isolation in pea aphids. Nature 412:904–907
Heckel DG (1993) Comparative genetic linkage mapping in insects. Annu Rev Entomol 38:381–408
Heidel-Fischer HM, Vogel H, Heckel DG, Wheat CW (2010) Microevolutionary dynamics of a macroevolutionary key innovation in a Lepidopteran herbivore. BMC Evol Biol 10(1):60
Hendricks DE, Graham HM, Raulston JR (1973) Dispersal of sterile tobacco budworms from release points in Northeastern Mexico and Southern Texas. Environ Entomol 2:1085–1088
Henniges-Janssen K, Reineke A, Heckel DG, Groot AT (2011a) Complex inheritance of larval adaptation in Plutella xylostella to a novel host plant. Heredity 107:421–432
Henniges-Janssen K, Schofl G, Reineke A, Heckel DG, Groot AT (2011b) Oviposition of diamondback moth in the presence and absence of a novel host plant. Bull Entomol Res 101:99–105
Hilker M, Meiners T (2011) Plants and insect eggs: how do they affect each other? Phytochemistry 72:1612–1623
Hilker M, Rohfritsch O, Meiners T (2002) The plant’s response towards insect egg deposition. In: Hilker M, Meiners T (eds) Chemoecology of insect eggs and egg deposition. Blackwell Publishing Ltd., Berlin, pp 205–233
Hora KH, Roessingh P, Menken SBJ (2005) Inheritance and plasticity of adult host acceptance in Yponomeuta species: implications for host shifts in specialist herbivores. Entomol Exp Appl 115:271–281
Jaenike J (1983) Induction of host preference in Drosophila melanogaster. Oecologia 58:320–325
Jaenike J (1990) Host specialization in phytophagous insects. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 21:243–274
Janz N, Nylin S (1997) The role of female search behaviour in determining host plant range in plant feeding insects: a test of the information processing hypothesis. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 264:701–707
Janz N, Nylin S, Wahlberg N (2006) Diversity begets diversity: host expansions and the diversification of plant-feeding insects. BMC Evol Biol 6(1):4
Janz N, Soderlind L, Nylin S (2009) No effect of larval experience on adult host preferences in Polygonia c-album (Lepidoptera: Nymphalidae): on the persistence of Hopkins’ host selection principle. Ecol Entomol 34:50–57
Jones CD (2005) The genetics of adaptation in Drosophila sechellia. Genetica 123:137–145
Joyner K, Gould F (1985) Developmental consequences of cannibalism in Heliothis zea (Lepidoptera, Noctuidae). Ann Entomol Soc Am 78:24–28
Liu SM, Zhou S, Tian L, Guo EN, Luan YX, Zhang JZ, Li S (2011) Genome-wide identification and characterization of ATP-binding cassette transporters in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. BMC Genomics 12(1):491
Matsubayashi KW, Ohshima I, Nosil P (2010) Ecological speciation in phytophagous insects. Entomol Exp Appl 134:1–27
Maurya S, Singh UP, Singh DP, Singh KP, Srivastava JS (2005) Secondary metabolites of chickpea (Cicer arietinum) and their role in pathogenesis after infection by Sclerotium rolfsii. Z Pflanzenkr Pflanzenschutz 112:118–123
Moreau J, Rahme J, Benrey B, Thiery D (2008) Larval host plant origin modifies the adult oviposition preference of the female European grapevine moth Lobesia botrana. Naturwissenschaften 95:317–324
Oppenheim SJ, Gould F, Hopper KR (2012) The genetic architecture of a complex ecological trait: host plant use in the specialist moth, Heliothis subflexa. Evolution 66:3336–3351
Pashley DP (1986) Host-associated genetic differentiation in fall armyworm (Lepidoptera, Noctuidae)—a sibling species complex. Ann Entomol Soc Am 79:898–904
Price TD, Qvarnstrom A, Irwin DE (2003) The role of phenotypic plasticity in driving genetic evolution. Proc R Soc Lond Ser B Biol Sci 270:1433–1440
Raulston JR, Wolf WW, Lingren PD, Sparks AN (1982) Migration as a factor in Heliothis management. International Proceedings workshop on Heliothis management. Patancheru, India, pp 61–73
Raulston JR, Pair SD, Pedraza Martinez FA, Westbrook J, Sparks AN, Sanchez Valdez VM (1986) Ecological studies indicating the migration of Heliothis zea, Spodoptera frugiperda, and Heliothis virescens from Northeastern Mexico and Texas. Insect flight: dispersal and migration. Springer, Berlin, pp 204–220
Reese JC (1978) Chronic effects of plant allelochemicals on insect nutritional physiology. Entomol Exp Appl 24:625–631
Scriber JM, Larsen ML, Allen GR, Walker PW, Zalucki MP (2008) Interactions between Papilionidae and ancient Australian angiosperms: evolutionary specialization or ecological monophagy? Entomol Exp Appl 128:230–239
Sezer M, Butlin RK (1998) The genetic basis of oviposition preference differences between sympatric host races of the brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens). Proc R Soc B-Biol Sci 265:2399–2405
Sheck AL, Gould F (1993) The genetic basis of host range in Heliothis virescens—larval survival and growth. Entomol Exp Appl 69:157–172
Sheck AL, Gould F (1995) Genetic analysis of differences in oviposition preferences of Heliothis virescens and Heliothis subflexa (Lepidoptera, Noctuidae). Environ Entomol 24:341–347
Sheck AL, Gould F (1996) The genetic basis of differences in growth and behavior of specialist and generalist herbivore species: selection on hybrids of Heliothis virescens and Heliothis subflexa (Lepidoptera). Evolution 50:831–841
Sheck AL, Groot AT, Ward CM, Gemeno C, Wang J, Brownie C, Schal C, Gould F (2006) Genetics of sex pheromone blend differences between Heliothis virescens and Heliothis subflexa: a chromosome mapping approach. J Evol Biol 19:600–617
Simmonds MSJ, Stevenson PC (2001) Effects of isoflavonoids from Cicer on larvae of Heliocoverpa armigera. J Chem Ecol 27:965–977
Thomas Y, Bethenod MT, Pelozuelo L, Frerot B, Bourguet D (2003) Genetic isolation between two sympatric host-plant races of the European corn borer, Ostrinia nubilalis Hubner. I. sex pheromone, moth emergence timing, and parasitism. Evolution 57:261–273
Thoming G, Larsson MC, Hansson BS, Anderson P (2013) Comparison of plant preference hierarchies of male and female moths and the impact of larval rearing hosts. Ecology 94:1744–1752
Thompson JN (1988) Evolutionary genetics of oviposition preference in swallowtail butterflies. Evolution 42:1223–1234
Thompson JN, Pellmyr O (1991) Evolution of oviposition behavior and host preference in Lepidoptera. Annu Rev Entomol 36:65–89
Waldvogel M, Gould F (1990) Variation in oviposition preference of Heliothis virescens. Evolution 44:1326–1337
Wheat CW, Vogel H, Wittstock U, Braby MF, Underwood D, Mitchell-Olds T (2007) The genetic basis of a plant-insect coevolutionary key innovation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:20427–20431
Wittstock U, Agerbirk N, Stauber EJ, Olsen CE, Hippler M, Mitchell-Olds T, Gershenson J, Vogel H (2004) Successful herbivore attack due to metabolic diversion of a plant chemical defense. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:4859–4864
Yu QY, Lu C, Li WL, Xiang ZH, Zhang Z (2009) Annotation and expression of carboxylesterases in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. BMC Genomics 10:553
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Carlos Blanco from the USDA for providing us with individuals from the MON and ARS strains, Susanne Donnerhacke and Antje Schmaltz for their help with the creation of the AFLP markers and the chromosome mapping, and Regina Seibt for the rearing of the two strains. We also thank Domenica Schnabelrauch for sequencing the selected AFLP markers. This research was partly funded by the National Science Foundation (award IOS-1052238), the W. M. Keck Center for Behavioral Biology, and the Max-Planck-Gesellschaft.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karpinski, A., Haenniger, S., Schöfl, G. et al. Host plant specialization in the generalist moth Heliothis virescens and the role of egg imprinting. Evol Ecol 28, 1075–1093 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10682-014-9723-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10682-014-9723-x