Abstract
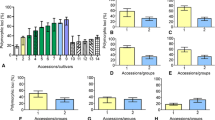
Rhizomania is the most damaging and widespread disease of the sugar beet crop and is caused by Beet necrotic yellow vein virus vectored by the fungus Polymyxa betae. The only disease management tool used is resistant varieties. In the last 30 years, “Rizor” and “Holly” (Rz1) resistances have been the most widely used. Despite the lack of information, a common origin for both types of resistance was hypothesized by some breeders. The aim of this study was to assess the phylogenetic relationship between Rizor and Rz1 by means of SNP analysis. Fifty leaf samples of each were genotyped with a fingerprinting panel of 192 SNPs, using the QuantStudio 12K Flex system coupled with Taqman OpenArray technology. Analysis of molecular variance and principal coordinate analysis confirmed that Rizor and Rz1 cannot be distinguished as separate sources of resistance.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amiri R, Moghaddam M, Mesbah M, Sadeghian SY, Ghannadha MR, Izadpanah K (2003) The inheritance of resistance to Beet necrotic yellow vein virus (BNYVV) in B. vulgaris subsp. maritima accession WB42: statistical comparisons with Holly1-4. Euphytica 132:363–373
Barzen E, Rainer S, Fuchs E, Borchardt DC, Salamini F (1997) Development of coupling-repulsion-phase SCAR markers diagnostic for the sugar beet Rz1 allele conferring resistance to rhizomania. Mol Breed 3:231–238
Biancardi E, Tamada T (2016) Rhizomania, Springer, Heidelberg, in press
Biancardi E, Lewellen RT, De Biaggi M, Erichsen AW, Stevanato P (2002) The origin of rhizomania resistance in sugar beet. Euphytica 127:383–397
Biancardi E, Panella LW, Lewellen RT (eds) (2012) Beta maritima: the origin of beets. Springer, Heidelberg
Bongiovanni GC, Lanzoni L (1964) La rizomania della bietola. Prog Agric 2:209–220
Canova A (1959) Appunti di patologia della barbabietola. Informatore Fitopatologico 9:390–396
De Biaggi M (1987) Methodes de selection—un cas concret. Proc IIRB 50:157–161
Doney DL, Whitney ED (1990) Genetic enhancement in Beta for disease resistance using wild relatives: a strong case for the value of genetic conservation. Econ Bot 44:445–451
Duffus JE, Whitney ED, Larsen RC, Liu HY Lewellen RT (1984) First report in Western hemisphere of rhizomania of sugar beet caused by Beet necrotic yellow vein virus. Plant Dis 68:251
Gentili P, Poggi G (1986) Ritmo, esperienze italiane contro rizomania e cercospora. Techn Publ 25, Maribo-Italia
Giorio G, Gallitelli MF, Carriero F (1997) Molecular markers linked to rhizomania resistance in sugar beet Beta vulgaris from two different sources map to the same linkage group. Plant Breed 116:401–408
Grimmer MK, Trybush S, Hanley S, Francis SA, Karp A, Asher MJC (2007) An anchored linkage map for sugar beet based on AFLP, SNP and RAPD markers and QTL mapping of a new source of resistance to Beet necrotic yellow vein virus. Theor Appl Genet 114:1151–1160
Lewellen RT, Biancardi E (1990) Breeding and performance of rhizomania resistant sugar beet. Proc IIRB 53:79–87
Lewellen RT, Skoyen IO, Erichsen AW (1987) Breeding sugarbeet for resistance to rhizomania: evaluation of host-plant reactions and selection for and inheritance of resistance. Proc IIRB 50:139–156
McGrann GRD, Grimmer MK, Mutasa-Göttgens ES, Stevens M (2009) Progress towards the understanding and control of sugar beet rhizomania disease. Mol Plant Pathol 10:129–141
Meulemans M, Janssens L, Horemans S (2003) Interactions between major genes and influence of the genetic background in the expression of rhizomania resistance. Proc IIRB-ASSBT 1:161–173
Munerati O, Zapparoli TV (1915) Di alcune anomalie della Beta vulgaris L. Atti Accad dei Lincei 25:1236–1239
Panella L, Lewellen RT (2007) Broadening the genetic base of sugar beet: introgression from wild relatives. Euphytica 154:383–400
Pavli OI, Stevanato P, Biancardi E, Skaracis GN (2011) Achievements and prospects in breeding for rhizomania resistance in sugar beet. Field Crop Res 122:165–172
Rush CM, Liu HY, Lewellen RT, Acosta-Leal R (2006) The continuing saga of rhizomania of sugar beets in the United States. Plant Dis 90:4–15
Scholten OE, Jansen RC, Keizer LCP, De Bock TSM, Lange W (1996) Major genes for resistance to Beet necrotic yellow vein virus (BNYVV) in Beta vulgaris. Euphytica 91:331–339
Scholten OE, De Bock TSM, Klein-Lankhorst RM, Lange W (1999) Inheritance of resistance to Beet necrotic yellow vein virus in Beta vulgaris, conferred by a second gene for resistance. Theor Appl Genet 99:740–746
Skaracis GN, Biancardi E (2000) Breeding for cercospora resistance in sugar beet. In: Cercospora beticola Sacc.: biology, agronomic influence and control measures in sugar beet. Adv Sugar Beet Res, vol 2. IIRB, Brussels, pp 177–195
Stevanato P, Broccanello C, Biscarini F, Del Corvo M, Panella L, Gaurav S, Stella A, Concheri G (2014) First application of QuantStudio platform for high throughput SNP marker assessment in sugar beet. Plant Mol Biol Rep 32:691–696
Tamada T, Baba T (1973) Beet necrotic yellow vein virus from rhizomania-affected sugar beet in Japan. Ann Phytopathol Soc Jpn 39:325–332
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Rizor, Rz1, and Rz2 written in roman letters refer to the genetic resistances. If written in italics, Rz1 and Rz2 mean the dominant genes carrying the resistance.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stevanato, P., De Biaggi, M., Broccanello, C. et al. Molecular genotyping of “Rizor” and “Holly” rhizomania resistances in sugar beet. Euphytica 206, 427–431 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-015-1503-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-015-1503-3