Abstract
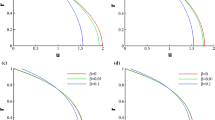
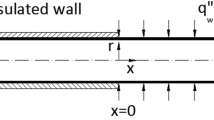
The classical Graetz problem, which is the problem of the hydrodynamically developed, thermally developing laminar flow of an incompressible fluid inside a tube neglecting axial conduction and viscous dissipation, is one of the fundamental problems of internal-flow studies. This study is an extension of the Graetz problem to include the rarefaction effect, viscous dissipation term and axial conduction with a constant wall temperature thermal boundary condition. The energy equation is solved to determine the temperature field analytically using general eigenfunction expansion with a fully developed velocity profile. To analyze the low-Peclet-number nature of the flow, the flow domain is extended from \(-\infty \) to \(+\infty \). To model the rarefaction effect, a second-order slip model is implemented. The temperature distribution, local Nusselt number, and local entropy generation are determined in terms of confluent hypergeometric functions. This kind of theoretical study is important for a fundamental understanding of the convective heat transfer characteristics of flows at the microscale and for the optimum design of thermal systems, which includes convective heat transfer at the microscale, especially operating at low Reynolds numbers.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Graetz L (1883) Uben die wärmeleitungsfähigkeit von flüssigkeiten (On the thermal conductivity of liquids, part 1). Ann Phys Chem 18:79–94
Graetz L (1885) Uben die wärmeleitungsfähigkeit von flüssigkeiten (On the thermal conductivity of liquids, part 2). Ann Phys Chem 25:337–357
Nusselt W (1910) Die abhängigkeit der wärmebergangszahl von der rohrlänge (The dependence of the heat transfer coefficient on the tube length). VDI Z 54:1154–1158
Shah RK, London AL (1978) Laminar flow forced convection in ducts: a source book for compact heat exchanger analytical data. Academic Press, New York, pp 78–138
Lahjomri J, Quabarra A, Alemany A (2002) Heat transfer by laminar hartmann flow in thermal entrance region with a step change in wall temperatures: the Graetz problem extended. Int J Heat Mass Transf 45:1127–1148
Lahjomri J, Zniber K, Quabarra A, Alemany A (2003) Heat transfer by laminar hartmanns flow in thermal entrance region with uniform wall heat ux: the Graetz problem extended. Energy Convers Manag 44:11–34
Dutta P, Horiuchi K, Yin HM (2006) Thermal characteristics of mixed electroosmotic and pressure-driven microflows. Comput Math Appl 52:651–670
Horiuchi K, Dutta P, Hossain A (2006) Joule-heating effects in mixed electroosmotic and pressure-driven microflows under constant wall heat flux. J Eng Math 54:159–180
Barron RF, Wang XM, Warrington RO, Ameel TA (1997) The Graetz problem extended to slip flow. Int J Heat Mass Transf 40:1817–1823
Ameel TA, Barron RF, Wang XM, Warrington RO (1997) Laminar forced convection in a circular tube with constant heat flux and slip flow. Microscale Thermophys Eng 1:303–320
Larrode FE, Housiadas C, Drossinos Y (2000) Slip-flow heat transfer in circular tubes. Int J Heat Mass Transf 43:2669–2680
Ameel TA, Barron RF, Wang XM, Warrington RO (2001) Heat transfer in microtubes with viscous dissipation. Int J Heat Mass Transf 44:2395–2403
Tunc G, Bayazitoglu Y (2002) Convection at the entrance of micropipes with sudden wall temperature change. In ASME IMECE 2002, November 17–22, New Orleans, Lousiana
Mikhailov MD, Cotta RM, Kakac S (2005) Steady state and periodic heat transfer in micro conduits. In: Kakac S, Vasiliev L, Bayazitoglu Y, Yener Y (eds) Microscale heat transfer-fundamentals and applications in biological systems and MEMS. Kluwer Academic Publisher, Dordrecht
Jeong HE, Jeong JT (2006) Extended Graetz problem including streamwise conduction and viscous dissipation in microchannels. Int J Heat Mass Transf 49:2151–2157
Aydin O, Avcı M (2006) Analysis of micro-Graetz problem in a microtube. Nanoscale Microscale Thermophys Eng 10(4):345–358
Çetin B, Yuncu H, Kakaç S (2006) Gaseous flow in microconduits with viscous dissipation. Int J Transp Phenom 8:297–315
Haji-Sheikh A, Beck JV, Amos DE (2008) Axial heat conductioin effects in the entrance region of parallel plate ducts. Int J Heat Mass Transf 51:5811–5822
Çetin B, Yazıcıog̃lu AG, Kakaç S (2009) Slip-flow heat transfer in microtubes with axial conduction and viscous dissipation—an extended Graetz problem. Int J Therm Sci 48:1673–1678
Yaman M, Khudiyev T, Ozgur E, Kanik M, Aktas O, Ozgur EO, Deniz H, Korkut E, Bayindir M (2011) Arrays of indefinitely long uniform nanowires and nanotubes. Nat Mater 10(7):494–501
Karniadakis GE, Beskok A, Aluru N (2005) Microflows and nanoflows: fundamentals and simulations. Springer, New York, pp 51–74, 167–172
Çetin B (2013) Effect of thermal creep on heat transfer for a 2D microchannel flow: an analytical approach. ASME J Heat Transf 135(101007):1–8
Weng HC, Chen C-K (2008) A challenge in Navier–Stokes based continuum modeling: Maxwell–Burnett slip law. Phys Fluids 20:106101
Deen WM (1998) Analysis of transport phenomena. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 391–392
Ash RL, Heinbockel JH (1970) Note on heat transfer in laminar fully developed pipe flow with axial conduction. Math Phys 21:266–269
Hsu CJ (1971) An exact analysis of low Peclet number thermal entry region heat transfer in transversely non-uniform velocity field. AIChE J 17:732–740
Davis EJ (1971) Exact solutions for a class of heat and mass transfer problems. Can J Chem Eng 51:562–572
Taitel V, Tamir A (1972) Application of the integral method to flows with axial conduction. Int J Heat Mass Transf 15:733–740
Taitel V, Bentwich M, Tamir A (1973) Effects of upstream and downstream boundary conditions on heat(mass) transfer with axial diffussion. Int J Heat Mass Transf 16:359–369
Papoutsakis E, Ramkrishna D, Lim HC (1980) The extended Graetz problem with dirichlet wall boundary condition. Appl Sci Res 36:13–34
Papoutsakis E, Ramkrishna D, Lim HC (1980) The extended Graetz problem with prescribed wall flux. AIChE J 26:779–787
Acrivos A (1980) The extended Graetz problem at low Peclet numbers. Appl Sci Res 36:35–40
Vick B, Ozisik MN, Bayazitoglu Y (1980) Method of analysis of low Peclet number thermal entry region problems with axial conduction. Lett Heat Mass Transf 7:235–248
Vick B, Ozisik MN (1981) An exact analysis of low Peclet number heat transfer in laminar flow with axial conduction. Lett Heat Mass Transf 8:1–10
Lahjomri J, Qubarra A (1999) Analytical solution of the Graetz problem with axial conduction. J Heat Transf 121:1078–1083
Çetin B, Yazıcıog̃lu AG, Kakaç S (2008) Fluid flow in microtubes with axial conduction including rarefaction and viscous dissipation. Int Comm Heat Mass Transf 35:535–544
Bejan A (1996) Entropy generation minimization: the method of thermodynamic optimization of finite-size systems and finite-time processes. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 71–74
Eckert EGR, Jr Drake RM (1972) Analysis of heat and mass transfer. McGraw-Hill, New York
Kays WM, Crawford M, Weigand B (2005) Convective heat and mass transfer. McGraw Hill, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Çetin, B., Zeinali, S. Analysis of heat transfer and entropy generation for a low-Peclet-number microtube flow using a second-order slip model: an extended-Graetz problem. J Eng Math 89, 13–25 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10665-014-9704-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10665-014-9704-7