Abstract
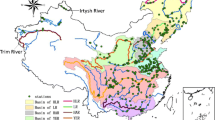
With economic development and the increase of energy consumption, surface water acidification has been a potential environmental concern in China. Here, we analyzed variations and trends in surface water pH of 73 sites from ten river basins in China from 2004 to 2014 with nonparametric Seasonal Kendall test method. Our analysis showed that the variations of surface water pH in China ranged from 6.5 to 9.0 in the past decade (2004–2014), which satisfied the water quality criteria in pH for protection of aquatic ecosystems in China (6.0–9.0) and USA (6.5–9.0). However, significant decreasing trends in surface water pH were found in 31 monitoring sites, which were mainly located in Haihe River, Taihu Lake and Yangtze River, while the pH value showed significant increasing trends in 22 sites, which mainly were located in Songhua River and Pearl River. Our results suggested the increased potential acidification of susceptible water bodies in China. Besides the control policy of sulfur dioxide (SO2) emissions, the emissions of nitrous oxides (NOx) should also be reduced to protect the aquatic systems in China.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Battarbee, R. W., Shilland, E. M., Kernan, M., Monteith, D. T., & Curtis, C. J. (2014). Recovery of acidified surface waters from acidification in the United Kingdom after twenty years of chemical and biological monitoring (1988–2008). Ecological Indicators, 37, 267–273. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2013.10.011.
Bouza-Deaño, R., Ternero-Rodríguez, M., & Fernández-Espinosa, A. J. (2008). Trend study and assessment of surface water quality in the Ebro River (Spain). Journal of Hydrology, 361(3–4), 227–239. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2008.07.048.
Burns, D. A., McHale, M. R., Driscoll, C. T., & Roy, K. M. (2006). Response of surface water chemistry to reduced levels of acid precipitation: comparison of trends in two regions of New York, USA. Hydrological Processes, 20(7), 1611–1627. doi:10.1002/hyp.5961.
Charles, D. F., Whitehead, D. R., Engstrom, D. R., Fry, B. D., Hites, R. A., Norton, S. A., et al. (1987). Paleolimnological evidence for recent acidification of Big Moose Lake, Adirondack Mountains, N.Y. (USA). Biogeochemistry, 3(1–3), 267–296. doi:10.1007/BF02185196.
Driscoll, C. T. L. G. B. B. A. J. B. T. J. C. C. S. E. C. K. F. L. G. E. S. J. L. W. K. (2001). Acidic deposition in the northeastern United States: sources and inputs, ecosystem effects, and management strategies: the effects of acidic deposition in the northeastern United States include the acidification of soil and water, which stresses terrestrial and aquatic biota. BioScience, 51(3).
Dou, M., Zuo, Q., Ma, J., & Li, G. (2016). Simulation and control of the linked systems of water quantity–water quality–socio-economics in the Huaihe River basin. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 61(4), 763–774. doi:10.1080/02626667.2014.959953.
Duan, L., Ma, X., Larssen, T., Mulder, J., & Hao, J. (2011). Response of surface water acidification in upper Yangtze River to SO2 emissions abatement in China. Environmental Science and Technology, 45(8), 3275–3281. doi:10.1021/es1038672.
EPA. (2012). pH. In Water: Monitoring and Assessment. United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). http://water.epa.gov/type/rsl/monitoring/vms54.cfm
Evans, C. D., Chadwick, T., Norris, D., Rowe, E. C., Heaton, T. H. E., Brown, P., et al. (2014). Persistent surface water acidification in an organic soil-dominated upland region subject to high atmospheric deposition: the North York Moors, UK. Ecological Indicators, 37, 304–316. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2012.02.018.
Evans, C. D., Cullen, J. M., Alewell, C., Kopacek, J., Marchetto, A., Moldan, F., et al. (2001). Recovery from acidification in European surface waters. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 5(3), 16.
Fang, Y. T., Wang, X. M., Zhu, F. F., Wu, Z. Y., Li, J., Zhong, L. J., et al. (2013). Three-decade changes in chemical composition of precipitation in Guangzhou city, southern China: has precipitation recovered from acidification following sulphur dioxide emission control? [Article]. Tellus Series B-Chemical and Physical Meteorology, 65, 15. doi:10.3402/tellusb.v65i0.20213.
Fischer, R. M. V. E. G. M. (2007). Monitoring of atmospheric deposition in European forests and an overview on its implication on forest condition. Applied Geochemistry, 22(6), 11.
Garmo, Ø., Skjelkvåle, B., de Wit, H., Colombo, L., Curtis, C., Fölster, J., et al. (2014). Trends in surface water chemistry in acidified areas in Europe and North America from 1990 to 2008. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 225(3), 1–14. doi:10.1007/s11270-014-1880-6.
Guerraiche, Z., Boudoukha, A., & Benkadja, R. (2015). Variation of the chemical composition of Grouz dam waters, Eastern Algeria. Desalination and Water Treatment, 57(11), 4878–4887. doi:10.1080/19443994.2014.995131.
Haines, T., & Baker, J. (1986). Evidence of fish population responses to acidification in the Eastern United States. Water, air, and soil pollution, 31(3–4), 605–629. doi:10.1007/BF00284216.
Hao, J., Ye, X., Duan, L., & Zhou, Z. (2001). Calculating critical loads of sulfur deposition for 100 surface waters in China using the magic model. [Article]. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 131(1–4 Part 3), 1157–1162.
Helsel, D. R & Hirsch, R.M. (1992). Statistical Methods in Water Resources: U.S. Geological Survey Techniques of Water Resources Investigations Book 4, Chapter A3. http://water.usgs.gov/pubs/twri/twri4a3/
Hirsch, R. M., & Slack, J. R. (1984). A nonparametric trend test for seasonal data with serial dependence. Water Resources Research, 20(6), 727–732. doi:10.1029/WR020i006p00727.
Hirsch, R. M., Slack, J. R., & Smith, R. A. (1982). Techniques of trend analysis for monthly water quality data. Water Resources Research, 18(1), 107–121. doi:10.1029/WR018i001p00107.
Hu, Y., Wu, P., Zhao, Y., Zhang, Z., & Xu, B. (2013). Water quality of cropland drainage ditches in the Yellow River irrigation regions of Ningxia and Inner Mongolia, China. [Article]. Shengtaixue Zazh, 32(7), 1730–1738.
Jiang, Y.-J., He, W., Liu, W.-X., Qin, N., Ouyang, H.-L., Wang, Q.-M., et al. (2014). The seasonal and spatial variations of phytoplankton community and their correlation with environmental factors in a large eutrophic Chinese lake (Lake Chaohu). Ecological Indicators, 40, 58–67. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2014.01.006.
Kahl, J. S., & Center for the Environment, P. S. U. U. S. A. S. J. R. S. R. F. J. D. W. C. A. J. P. K. K. N. S. (2004). Have U.S. surface waters responded to the 1990 Clean Air Act amendments? Environmental Science & Technology, 38(24), 484A–490A.
Kvaeven, B., Ulstein, M., Skjelkvåle, B., Raddum, G., & Hovind, H. (2001). ICP Waters—an international programme for surface water monitoring. Water, air, and soil pollution, 130(1–4), 775–780. doi:10.1023/A:1013802122401.
Li, H. B., Hou, G. X., Dakui, F., Xiao, B. D., Song, L. R., & Liu, Y. D. (2007). Prediction and elucidation of the population dynamics of Microcystis spp. in Lake Dianchi (China) by means of artificial neural networks. [Article]. Ecological Informatics, 2(2), 184–192. doi:10.1016/j.ecoinf.2007.03.007.
Lynch, J. A., Bowersox, V. C., & Grimm, J. W. (2000). Acid rain reduced in Eastern United States. Environmental Science & Technology, 34(6), 940–949. doi:10.1021/es9901258.
Malcolm, I. A., Bacon, P. J., Middlemas, S. J., Fryer, R. J., Shilland, E. M., & Collen, P. (2014). Relationships between hydrochemistry and the presence of juvenile brown trout (Salmo trutta) in headwater streams recovering from acidification. Ecological Indicators, 37(Part B), 351–364. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2012.02.029.
Matsubara, H., Morimoto, S., Sase, H., Ohizumi, T., Sumida, H., Nakata, M., et al. (2009). Long-term declining trends in river water pH in Central Japan. Water, air, and soil pollution, 200(1–4), 253–265. doi:10.1007/s11270-008-9909-3.
Matzner, E. M. D. (1995). Soil changes induced by air pollutant deposition and their implication for forests in Central Europe. Water, air, and soil pollution, 85(1), 63–76.
Menz, F. C., & Seip, H. M. (2004). Acid rain in Europe and the United States: an update. Environmental Science & Policy, 7(4), 253–265. doi:10.1016/j.envsci.2004.05.005.
Minella, M., De Laurentiis, E., Buhvestova, O., Haldna, M., Kangur, K., Maurino, V., et al. (2013). Modelling lake-water photochemistry: three-decade assessment of the steady-state concentration of photoreactive transients (.OH, CO3(−.) and (3)CDOM( *)) in the surface water of polymictic Lake Peipsi (Estonia/Russia). Chemosphere, 90(10), 2589–2596. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.10.103.
Murphy, J. F., Winterbottom, J. H., Orton, S., Simpson, G. L., Shilland, E. M., & Hildrew, A. G. (2014). Evidence of recovery from acidification in the macroinvertebrate assemblages of UK fresh waters: a 20-year time series. Ecological Indicators, 37, 330–340. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2012.07.009.
Nordberg, G. (2003). Cadmium and human health: a perspective based on recent studies in China. The Journal of Trace Elements in Experimental Medicine, 16(4), 307–319. doi:10.1002/jtra.10039.
Oni, S. K., Futter, M. N., Bishop, K., Köhler, S. J., Ottosson-Löfvenius, M., & Laudon, H. (2013). Long-term patterns in dissolved organic carbon, major elements and trace metals in boreal headwater catchments: trends, mechanisms and heterogeneity. Biogeosciences, 10(4), 2315–2330. doi:10.5194/bg-10-2315–2013.
Oulehle, F., Chuman, T., Majer, V., & Hruška, J. (2013). Chemical recovery of acidified Bohemian lakes between 1984 and 2012: the role of acid deposition and bark beetle induced forest disturbance. Biogeochemistry, 116(1–3), 83–101. doi:10.1007/s10533-013-9865-x.
Ouyang, X.-J., Zhou, G.-Y., Huang, Z.-L., Liu, J.-X., Zhang, D.-Q., & Li, J. (2008). Effect of simulated acid rain on potential carbon and nitrogen mineralization in forest soils1. Pedosphere, 18(4), 503–514. doi:10.1016/S1002-0160(08)60041-7.
R Core Team. R. (2014). A language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing. http://www.R-project.org/.
Skjelkvale, B. L., Wright, R. F., & Henriksen, A. (1998). Norwegian lakes show widespread recovery from acidification; results from national surveys of lakewater chemistry 1986–1997. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 2(4), 555–562.
Stoddard, J. L., Jeffries, D. S., Lukewille, A., Clair, T. A., Dillon, P. J., Driscoll, C. T., et al. (1999). Regional trends in aquatic recovery from acidification in North America and Europe. Nature, 401(6753), 575–578. doi:10.1038/44114.
Tabari, H., Marofi, S., & Ahmadi, M. (2011). Long-term variations of water quality parameters in the Maroon River, Iran. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 177(1–4), 273–287. doi:10.1007/s10661-010-1633-y.
Tanaka, T., Sato, T., Watanabe, K., Wang, Y., Yang, D., Inoue, H., et al. (2013). Irrigation system and land use effect on surface water quality in river, at lake Dianchi, Yunnan, China. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 25(6), 1107–1116. doi:10.1016/s1001-0742(12)60206-x.
Tang, D. (2006). Acid rain in China. Rapid industrialization has put citizens and ecosystems at risk. Environmental Science and Technology, 40(2), 418–425.
US-EPA [United States Environmental Protection Agency] (2009). National Recommend Water Quality Criteria. Office of Water, Office of Science and Technology. Available via: http://water.epa.gov/scitech/ swguidance/ standards/current/upload/nrwqc-2009.pdf
Wällstedt, T., Edberg, F., & Borg, H. (2009). Long-term water chemical trends in two Swedish lakes after termination of liming. Science of the Total Environment, 407(11), 3554–3562. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.01.031.
Watt, W. D., Scott, C. D., & White, W. J. (1983). Evidence of acidification of some Nova Scotian Rivers and its impact on Atlantic Salmon, Salmo solar. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 40(4), 462–473. doi:10.1139/f83-065.
Wright, R., Dale, T., Gjessing, E., Hendrey, G., Henriksen, A., Johannessen, M., et al. (1976). Impact of acid precipitation on freshwater ecosystems in Norway. Water, air, and soil pollution, 6(2–4), 483–499. doi:10.1007/BF00182887.
Xu, G., Kang, R., Luo, Y., & Duan, L. (2013). Current status of surface water acidification in Northeast China. [Article]. Huanjing Kexue, 34(5), 1695–1699.
Yamada, T., Inoue, T., Fukuhara, H., Nakahara, O., Izuta, T., Suda, R., et al. (2007). Long-term trends in surface water quality of five lakes in Japan. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution: Focus, 7(1), 259–266. doi:10.1007/s11267-006-9076-8.
Ye, H. F., Guo, S. H., Li, F. M., & Li, G. (2013). Water quality evaluation in Tidal River reaches of Liaohe River Estuary, China using a revised QUAL2K model. [Article]. Chinese Geographical Science, 23(3), 301–311. doi:10.1007/s11769-013-0586-9.
Zhang, J.-E., Ouyang, Y., & Ling, D.-J. (2007). Impacts of simulated acid rain on cation leaching from the Latosol in south China. Chemosphere, 67(11), 2131–2137. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.12.095.
Zhang, X. M., Chai, F. H., Wang, S. L., Sun, X. Z., & Han, M. (2010). Acid rain research status in China. Research of Environmental Sciences, 23(5), 527–532. doi:10.13198/j.res.2010.05.3.zhangxm.005.
Zhang, Y., Gao, X., & Zhang, H. (2012). Association study between water quality of Chaohu Lake and resources input in agriculture of basin. [Article]. Huanjing Kexue, 33(9), 3009–3013.
Acknowledgments
We thank the editor and two anonymous referees whose comments and suggestions greatly improved the quality of the article. This research was funded by the National Water Pollution Control and Treatment Science and Technology Major Project (2012ZX07501003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiao, Y., Feng, J., Liu, X. et al. Surface water pH variations and trends in China from 2004 to 2014. Environ Monit Assess 188, 443 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5454-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5454-5