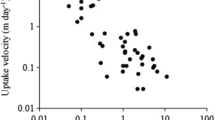
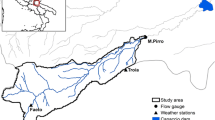
Abstract
As field data on in-stream nitrate retention is scarce at catchment scales, this study aimed at quantifying net retention of nitrate within the entire river network of a fourth-order stream. For this purpose, a practical mass balance approach combined with a Lagrangian sampling scheme was applied and seasonally repeated to estimate daily in-stream net retention of nitrate for a 17.4 km long, agriculturally influenced, segment of the Steinlach River in southwestern Germany. This river segment represents approximately 70 % of the length of the main stem and about 32 % of the streambed area of the entire river network. Sampling days in spring and summer were biogeochemically more active than in autumn and winter. Results obtained for the main stem of Steinlach River were subsequently extrapolated to the stream network in the catchment. It was demonstrated that, for baseflow conditions in spring and summer, in-stream nitrate retention could sum up to a relevant term of the catchment’s nitrogen balance if the entire stream network was considered.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aitkenhead, J. A., Hope, D., & Billett, M. F. (1999). The relationship between dissolved organic carbon in stream water and soil organic carbon pools at different spatial scales. Hydrological Processes, 13(8), 1289–1302.
Alexander, R., Smith, R., & Schwarz, G. (2000). Effect of stream channel size on the delivery of nitrogen to the Gulf of Mexico. Nature, 403, 758–761.
Battaglin, W. A., Kendall, C., Chang, C. C. Y., Silva, S. R., & Campbell, D. H. (2001). Chemical and isotopic evidence of nitrogen transformation in the Mississippi River, 1997–98. Hydrological Processes, 15, 1285–1300.
Birgand, F., Skaggs, R. W., Chescheir, G. M., & Gilliam, J. W. (2007). Nitrogen removal in streams of agricultural catchments—a literature review. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 37(5), 381–487.
Brookshire, E. N. J., Valett, H. M., Thomas, S. A., & Webster, J. R. (2005). Coupled cycling of dissolved organic nitrogen and carbon in a forest stream. Ecology, 86, 2487–2496.
Brown, J. B., Battaglin, W. A., & Zuellig, R. E. (2009). Lagrangian sampling for emerging contaminants through an urban stream corridor in Colorado. JAWRA Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 45, 68–82.
Burns, D. A. (1998). Retention of NO3 − in an upland stream environment: a mass balance approach. Biogeochemistry, 40, 73–96.
Camargo, J. A., Alonso, A., & Salamanca, A. (2005). Nitrate toxicity to aquatic animals: a review with new data for freshwater invertebrates. Chemosphere, 58(9), 1255–1267.
Claret, C., Marmonier, P., Boissier, J. M., Fontvieille, D., & Blanc, P. (1997). Nutrient transfer between parafluvial interstitial water and river water: influence of gravel bar heterogeneity. Freshwater Biology, 37, 657–670.
Deforet, T., Marmonier, P., Rieffel, D., Crini, N., Fritsch, C., Giraudoux, P., & Gilbert, D. (2008). The influence of size, hydrological characteristics and vegetation cover on nitrogen, phosphorus and organic carbon cycling in lowland river gravel bars (Doubs River, France). Fundamental and Applied Limnology, 171(2), 161–173.
Delong, M. D., & Brusven, M. A. (1991). Patterns of periphyton chlorophyll a in an agricultural nonpoint source impacted stream. Water Resources Bulletin, 28(4), 731–741.
European Environment Agency. (1999). Nutrients in European ecosystems. Environmental assessment report no. 4.http://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/ENVIASSRP04. Accessed 4 June 2015.
Haggerty, R., Martí, E., Argerich, A., von Schiller, D., & Grimm, N. B. (2009). Resazurin as a “smart” tracer for quantifying metabolically active transient storage in stream ecosystems. Journal of Geophysical Research, 114(G3), 1–14.
Hill, A. R. (1979). Denitrification in the nitrogen budget of a river ecosystem. Nature, 281, 291–292.
Kaushik, N. K., & Robinson, J. B. (1976). Preliminary observations on nitrogen transport during summer in a small spring-fed Ontario stream. Hydrobiologia, 49, 59–63.
Marzadri, A., Tonina, D., & Bellin, A. (2011). A semianalytical three-dimensional process-based model for hyporheic nitrogen dynamics in gravel bed rivers. Water Resources Research, 47(11), WR010583.
Mulholland, P. J. (2004). The importance of in-stream uptake for regulating stream concentrations and outputs of N and P from a forested watershed: evidence from long-term chemistry records for Walker Branch Watershed. Biogeochemistry, 70, 403–426.
Mulholland, P. J., Helton, A. M., Poole, G. C., Hall, R. O., Jr., Hamilton, S. K., Peterson, B. J., et al. (2008). Stream denitrification across biomes and its response to anthropogenic nitrate loading. Nature, 452, 202–205.
Osenbrück, K., Wöhling, T., Lemke, D., Rohrbach, N., Schwientek, M., Leven, C., Castillo Alvarez, C., Taubald, H., & Cirpka, O. A. (2013). Assessing hyporheic exchange and associated travel times by hydraulic, chemical, and isotopic monitoring at the Steinlach Test Site, Germany. Environmental Earth Sciences, 69(2), 359–372.
Pauwels, H., Foucher, J. C., & Kloppmann, W. (2000). Denitrification and mixing in a schist aquifer: influence on water chemistry and isotopes. Chemical Geology, 168(3–4), 307–324.
Peterson, B. J., Wollheim, W. M., Mulholland, P. J., Webster, J. R., Meyer, J. L., Tank, J. L., et al. (2001). Control of nitrogen export from watersheds by headwater streams. Science, 292(5514), 86–90.
Petzoldt, T., & Uhlmann, D. (2006). Nitrogen emissions into freshwater ecosystems: is there a need for nitrate elimination in all wastewater treatment plants? Acta Hydrochimica et Hydrobiologica, 34(4), 305–324.
Rothwell, J. J., Dise, N. B., Taylor, K. G., Allott, T. E. H., Scholefield, P., Davies, H., & Neal, C. (2010). Predicting river water quality across North West England using catchment characteristics. Journal of Hydrology, 395(3–4), 153–162.
Saunders, D. L., & Kalff, J. (2001). Nitrogen retention in wetlands, lakes and rivers. Hydrobiologia, 443, 205–212.
Schwientek, M., Guillet, G., Rügner, H., Kuch, B., & Grathwohl, P. (2016). A high-precision sampling scheme to assess persistence and transport characteristics of micropollutants in rivers. Science of the Total Environment, 540, 444–454.
Smith, R. L., Böhlke, J. K., Repert, D. A., & Hart, C. P. (2009). Nitrification and denitrification in a midwestern stream containing high nitrate: in situ assessment using tracers in dome-shaped incubation chambers. Biogeochemistry, 96(1–3), 189–208.
Tamelander, T., Reigstad, M., Olli, K., Slagstad, D., & Wassmann, P. (2013). New production regulates export stoichiometry in the ocean. Plos One, 8(1), e54027.
Triska, F. J., & Oremland, R. S. (1981). Denitrification associated with periphyton communities. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 42(4), 745–748.
van Grinsven, H. J. M., ten Berge, H. F. M., Dalgaard, T., Fraters, B., Durand, P., Hart, A., et al. (2012). Management, regulation and environmental impacts of nitrogen fertilization in northwestern Europe under the Nitrates Directive; a benchmark study. Biogeosciences, 9(12), 5143–5160.
Vincent, W. F., & Downes, M. T. (1980). Variation in nutrient removal from a stream by watercress. Aquatic Botany, 9, 221–235.
Wagenschein, D., & Rode, M. (2008). Modelling the impact of river morphology on nitrogen retention—a case study of the Weisse Elster River (Germany). Ecological Modelling, 211(1–2), 224–232.
Writer, J. H., Antweiler, R. C., Ferrer, I., Ryan, J. N., & Thurman, E. M. (2013). In-stream attenuation of neuro-active pharmaceuticals and their metabolites. Environmental Science and Technology, 47(17), 9781–9790.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank J. H. Fleckenstein for helpful comments on earlier versions of the manuscript. This work was supported by a grant from the Ministry of Science, Research and Arts of Baden-Württemberg (AZ Zu 33–721.3-2) and the Helmholtz Center for Environmental Research, Leipzig (UFZ). The study was also supported by the EU FP7 Collaborative Project GLOBAQUA (Grant Agreement no 603629).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schwientek, M., Selle, B. Quantifying in-stream retention of nitrate at catchment scales using a practical mass balance approach. Environ Monit Assess 188, 111 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5097-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5097-6