Abstract
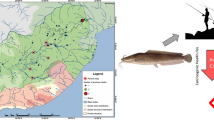
Fish is a significant source of essential nutrients, as well as toxic elements in the human diet. Concentration of 17 elements was determined in muscles of eels (Anguilla anguilla) collected from five fishing lakes in the territory of Latvia. The concentration of main elements determined in muscle tissues varied within the following ranges: for Pb, 0.019–0.047; Cd, 0.0051–0.011; Hg, 0.13–0.36; Cu, 0.76–0.92; Zn, 28–42; and As, 0.13–0.23 mg kg−1 wet weight. A positive correlation was revealed between the concentration of Hg in muscles and fish length in inland lakes. Concentration of metals in muscle tissues of eels from brackish coastal and inland lakes was without statistically significant difference. This research demonstrated that the elemental content of Cd and Pb in muscles of the examined fish was lower than the maximum allowed threshold set by the European Union legislation. Mercury content was over the threshold limit for all the analyzed eels if to compare with the Water Framework Directive Environmental Quality Standards. On other side, only 7 % of analyzed fish have indicated values that are over threshold limits for mercury established by the European Union food legislation. The current study contributes to the implementation of Water Framework Directive in Latvia by collection of information necessary for the further protection measures of waters. To our knowledge, this study provides the first data on multielemental bioaccumulation in muscle tissues of European eels collected from fishing lakes of Latvia.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Yousufa, M. H., El-Shahawi, M. S., & Al-Ghaisc, S. M. (2000). Trace metals in liver, skin, and muscle of Lethrinus lentjan fish species in relation to body length and sex. The Science of the Total Environment, 256(2–3), 87–94.
Bagenal, T. B., & Tesch, F. W. (1978). Age and Growth. In T. B. Bagenal (Ed.), Methods for assessment of fish production in fresh waters, IBP Handbook. London: Blackwell Scientific Publications.
Barak, N. A. E., & Mason, C. F. (1990). A survey of heavy metal levels in eels (Anguilla anguilla) from some rivers in East Anglia, England: the use of eels as pollution indicators. Internationale Revue der gesamten Hydrobiologie und Hydrographie, 75(6), 827–833.
Batty, J., Pain, D., & Caurant, F. (1996). Metal concentrations in Eels Anguilla anguilla from the Camargue Region of France. Biological Conservation, 76(1), 17–23.
Belpaire, C., & Goemans, G. (2007a). The European eel Anguilla anguilla, a rapporteur of the chemical status for the water framework directive? Vie et Milieu – Life and Environment, 57(4), 235–252.
Belpaire, C., & Goemans, G. (2007b). Eels contaminant cocktails pinpointing environmental contamination. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 64(7), 1423–1436.
Belpaire, C., Goemans, G., Geeraerts, C., Quataert, P., Parmentier, K., Hagel, P., & De Boer, J. (2009). Decreasing eel stocks: survival of the fattest? Ecology of Freshwater Fish, 18(2), 197–214.
Belpaire, C., Geeraerts, C., Evans, D., Ciccotti, E., & Poole, R. (2011). The European eel quality database: towards a pan-European monitoring of eel quality. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 183, 273–284.
Bordajandi, L. R., Gómez, G., Fernández, M. A., Abad, E., Rivera, J., & González, M. J. (2003). Study on PCBs, PCDD/Fs, organochlorine pesticides, heavy metals and arsenic content in freshwater fish species from the river Turia (Spain). chemosphere, 53, 163–171.
Boyden, C. R. (1977). Effect of size upon metal content of shellfish. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, 57, 675–714.
Briede, A. (1996). Phosphorus and heavy metals accumulation in reservoirs of Latvia. PhD diss. Riga: University of Latvia.
Bruslé, J. (1990). Effects of heavy metals on eels, Anguilla sp. Aquatic Living Resources, 3(2), 131–141.
Castonguay, M., Hodson, P. V., Couillard, C. M., Eckersley, M. J., Dutil, J. D., & Verreault, G. (1994). Why is recruitment of the American eel, Anguilla rostrata, declining in the St. Lawrence River and Gulf? Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 51(2), 479–488.
Cid, B. P., Boia, C., Pombo, L., & Rebelo, E. (2001). Determination of trace metals in fish species of the Ria de Aveiro (Portugal) by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Chemistry, 75, 93–100.
Deelder, C. L. (1970). Synopsis of biological data of the eel Anguilla anguilla, Linnaeus, 1758. Rome: FAO Fisheries Synopsis.
Dekker, W. (2003). Status of the European eel stock and fisheries. In K. Aida, K. Tsukamoto, & K. Yamauchi (Eds.), Eel biology. Tokyo: Springer Verlag.
Durrieu, G., Maury Brachet, R., Girardin, M., Rochard, E., & Boudou, A. (2005). Contamination by heavy metals (Cd, Zn, Cu, and Hg) of eight fish species in the Gironde Estuary (France). Estuaries, 28(4), 581–591.
Eipurs, I. (1984). Mūsu saldūdeņu zivis [our freshwater fish]. Rīga: Zinātne.
Eira, C., Torres, J., Miquel, J., Vaqueiro, J., Soares, A. M. V. M., & Vingada, J. (2009). Trace element concentrations in Proteocephalus macrocephalus (Cestoda) and Anguillicola crassus (Nematoda) in comparison to their fish host, Anguilla anguilla in Ria de Aveiro, Portugal. The Science of the Total Environment, 407, 991–998.
European Commission. (2006). Commission Regulation (EC) 1881/2006 of 19 December 2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs. Official Journal of the European Commission, L364, 0005–0024.
European Commission. (2008). Commission Regulation (EC) 629/2008 of 2 July 2008 amending Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs. Official Journal of the European Union, L173, 0006–0009.
European Union Water Framework Directive. (2000). Directive of the European parliament and of the council 2000/60/EC establishing a framework for community action in the field of water policy. Official Journal of the European Union, L327, 0001–0073.
Farkas, A., Salánki, J., & Varanka, I. (2000). Heavy metal concentrations in fish of Lake Balaton. Lakes and Reservoirs: Research and Management, 5, 271–279.
Haenen, O. L. M., Lehmann, J., Engelsma, M. Y., Stürenberg, F. J., Roozenburg, I., Kerkhoff, S., et al. (2010). The health status of European silver eels, Anguilla anguilla, in the Dutch River Rhine Watershed and Lake Ijsselmeer. Aquaculture, 309, 15–24.
Hakanson, L. (1984). Metals in fish and sediment from the River Kolbacksan water system, Sweden. Archiv für Hydrobiologie, 101, 373–400.
ICES/EIFAC (2004). Report of the ICES/EIFAC Working Group on Eels, 7–11 October 2003, Sukarrieta, Spain. ICES CM 2004/ACFM, 09.
Kavacs, G. (1998). Latvijas daba [The Nature of Latvia. Encyclopedia]. Rīga: Preses nams.
Kļaviņš, M., Rodinov, V., & Vereskūns, G. (1998a). Metals and organochlorine compounds in fish from Latvian Lakes. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 60, 538–545.
Kļaviņš, M., Briede, A., Parele, E., Rodinov, V., & Kļaviņa, I. (1998b). Metal accumulation in sediments and benthic invertebrates in Lakes of Latvia. Chemosphere, 26, 2043–3053.
Kļaviņš, M., Rodinovs, V., & Kokorīte, I. (2002). Chemistry of surface waters in Latvia. Riga: LU.
Lawal, I., & Bichi, A. H. (2014). Length-weight relationship and condition factor of 11 commercial fish species of Daberam, Reservoir, Katsina State. Entomology and Applied Science Letters, 1(3), 32–35.
Le, Q. D., Shirai, K., Nguyen, D. C., Miyazaki, N., & Arai, T. (2009). Heavy metals in a tropical eel Anguilla marmorata from the central part of Vietnam. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 204, 69–78.
Lelek, A. (1987). Threatened Fishes of Europe. In J. Holcik (Ed.), The freshwater fishes of Europe. Aula Verlag: Wiesbaden.
Linde, A. R., Arribas, P., Sanchez-Galan, S., & Garcia-Vazquez, E. (1996). Eel (Anguilla anguilla) and brown trout (Salmo trutta) target species to assess the biological impact of trace metal pollution in freshwater ecosystems. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 31, 297–302.
Linde, A. R., Sanchez-Galan, S., & Garcia-Vazquez, E. (2004). Heavy metal contamination of European eel (Anguilla anguilla) and brown trout (Salmo trutta) caught in wild ecosystems in Spain. Journal of Food Protection, 67(10), 2332–2336.
Lizama, M. A. P., & Ambrosio, A. M. (2002). Condition factor in nine species of fish of the Characidae family in the upper Parana River Floodplain, Brazil. Brazilian Journal of Biology, 62(1), 113–124.
Maes, G. E., Raeymaekers, J. A. M., Pampoulie, C., Seynaeve, A., Goemans, G., Belpaire, C., et al. (2005). The catadromous European eel Anguilla anguilla (L.) as a model for freshwater evolutionary ecotoxicology: relationship between heavy metal bioaccumulation, condition and genetic variability. Aquatic Toxicology, 73, 99–114.
Maes, J., Belpaire, C., & Goemans, G. (2008). spatial variations and temporal trends between 1994 and 2005 in polychlorinated biphenyls, organochlorine pesticides and heavy metals in European eel (Anguilla anguilla L.) in Flanders, Belgium. Environmental Pollution, 153, 223–237.
Noël, L., Chekri, R., Millour, S., Merlo, M., Leblanc, J. C., & Guérin, T. (2013). Distribution and relationships of As, Cd, Pb and Hg in freshwater fish from five French fishing areas. Chemosphere, 90, 1900–1910.
Pierron, F., Baudrimont, M., Bossy, A., Bourdineaud, J. P., Brèthes, D., Elie, P., & Massabuau, J. C. (2007). Impairment of lipid storage by cadmium in the European eel (Anguilla anguilla). Aquatic Toxicology, 81(3), 304–311.
Poikāne, R. (2008). The role of suspended particulate matter and sediment in the dynamics of metals in the Gulf of Riga. PhD diss. Riga: University of Latvia.
Republic of Latvia (2001). Regulations regarding Commercial Fishing in Inland Waters, 2 January. Regulation No. 3.
Ringuet, S., Muto, F., & Raymakers, C. (2002). Eels: their harvest and trade in Europe and Asia. Traffic Bulletin, 19(2), 2–27.
Robinet, T., & Feunteun, E. (2002). Sublethal effects of exposure to chemical compounds: a cause for the decline in Atlantic eels? Ecotoxicology, 11, 265–277.
Seinfeld, J. H., & Pandis, S. N. (2006). Atmospheric chemistry and physics: from air pollution to climate change. New Jersey: Wiley-InterScience.
Sinha, V., & Jones, J. (1975). The European freshwater eel. Liverpool: Liverpool University Press.
Storelli, M. M., Barone, G., Garofalo, R., & Marcotrigiano, G. O. (2007). Metals and organochlorine compounds in eel (Anguilla anguilla) from the Lesina Lagoon, Adriatic Sea (Italy). Food Chemistry, 100, 1337–1341.
Tsukamoto, K., Nakai, I., & Tesch, W. (1998). Do all freshwater eels migrate? Nature, 396, 635–636.
Ureña, R., Peri, S., del Ramo, J., & Torreblanca, A. (2007). Metal and metallothionein content in tissues from wild and farmed Anguilla anguilla at commercial size. Environment International, 33, 532–539.
Usero, J., Iquierdo, C., Morillo, J., & Gracia, I. (2003). Heavy metals in fish (Solea vulgaris, Anguilla anguilla and Liza aurata) from salt marshes on the southern Atlantic Coast of Spain. Environment International, 29, 949–956.
Vircavs, M., Taure, I., Njastad, O., & Steinnes, E. (1995). An evaluation of the environmental state of Lake Liepāja (Latvia) using elemental distributions in sediments. Chemical Geology, 124, 135–141.
Windon, H. L. (1988). A guide to interpretation of metal concentrations in estuarine sediments. In S. J. Schropp (Ed.), Coastal zone management section (pp. 22–23). Florida: Tallahassee.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grant “Establishing a research group for the study of chemical and biological pollution of fish in inland waters” grant No. 2013/0016/1DP/1.1.1.2.0/13/APIA/VIAA/055
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rudovica, V., Bartkevics, V. Chemical elements in the muscle tissues of European eel (Anguilla anguilla) from selected lakes in Latvia. Environ Monit Assess 187, 608 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4832-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4832-8