Abstract
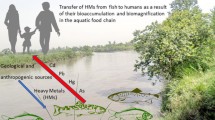
Concentrations of trace elements (Cd, Pb, As, V, Cr, Ni, Cu and Zn) were determined in superficial sediments and in muscle and hepatopancreas tissues of the red swamp crayfish Procambarus clarkii from Lake Preola and Gorghi Tondi Natural Reserve (SW Sicily). In particular, hepatopancreas showed a decidedly higher content of all analysed trace elements with respect to muscles (two- to threefold higher for Cd, Cu, As, Zn and V; four- to fivefold higher for Pb and Cr and seven times higher for Ni). However, no statistically reliable differential accumulation pattern emerged with regard to length and weight for trace elements (except for Cd for which significant positive correlations with length were recorded). Trace element concentrations found in crayfish tissues were in the range considered harmful to human health (except for Cd and Cr). Moreover, the As and Pb concentrations, either in sediment or crayfish tissues, are clearly related to intense agricultural activities, with extensive use of fertilizers and pesticides, that significantly affect the levels of these toxic metals in the study area.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd-Allah, M., & Abd-Allah, M. (2013). Effect of cooking on metal content of freshwater crayfish Procambarus clarkii. Chemistry and Ecology, 22, 329–334.
Alcorlo, P., Otero, M., Crehuet, M., Baltanas, A., & Montes, C. (2006). The use of the red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) as indicator of the bioavailability of heavy metals in environmental monitoring in the River Guadiamar (SW, Spain). Science of the Total Environment, 366, 380–399.
Alikhan, M. A., Bagatto, G., & Zia, S. (1990). The crayfish as a “biological indicator” of aquatic contamination by heavy metals. Water Research, 24, 1069–1076.
Allert, A. L., Fairchild, J. F., Di Stefano, R. J., Schmitt, C. J., Brumbaugh, W. G., & Besser, J. M. (2009). Ecological effects of lead mining on Ozark streams: in-situ toxicity to woodland crayfish (Orconectes hylas). Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 72, 1207–1219.
Anderson, M. B., Reddy, P., Preslan, J. E., Fingerman, M., Bollinger, J., Jolibois, L., et al. (1997). Metal accumulation in crayfish Procambarus clarkii exposed to petroleum-contaminated Bayou in Louisiana. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 37, 267–272.
Ansaldo, M., Nahabedian, D. E., Di Fonzo, C., & Wider, E. A. (2009). Effect of cadmium, lead and arsenic on the oviposition, hatching and embryonic survival of Biomphalaria glabrata. Science of the Total Environment, 497, 1923–1928.
Antòn, A., Serrano, T., Angulo, E., Ferrero, G., & Rallo, A. (2000). The use of two species of crayfish as environmental quality sentinels: the relationship between heavy metals content, cell and tissue biomarkers and physico-chemical characteristics of the environment. Science of the Total Environment, 247, 239–251.
Arumugtan, M., & Ravindranath, M. H. (1987). Copper toxicity in the crab, Scylla serrata, Cu levels in tissues and regulation after exposure to a Cu rich medium. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 39, 708–715.
Bagatto, G., & Alikham, M. A. (1987). Copper, cadmium, and nickel accumulation in crayfish population near copper-nickel smelters at Sudbury, Ontario, Canada. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 38, 540–545.
Bardeggia, M., & Alikhan, M. A. (1991). The relationship between copper and nickel levels in the diet, and their uptake and accumulation by Cambarus bartoni (Fabricius) (Decapoda, Crustacea). Water Research, 25, 1187–1192.
Bellante, A., Sprovieri, M., Buscaino, G., Salvagio Manta, D., Buffa, G., Di Stefano, V., et al. (2011). Stranded cetaceans as indicators of mercury pollution in the Mediterranean Sea. The Italian Journal of Zoology, 1, 1–10.
Bellante, A., Sprovieri, M., Buscaino, G., Buffa, G., Di Stefano, V., Salvagio Manta, D., et al. (2012). Distribution of Cd and As in organs and tissues of four marine mammals species stranded along the Italian coasts. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 14, 2382–2391.
Bohl, E. (1999). Motion of individual noble crayfish Astacus astacus in different biological situations: in-situ studies using radio telemetry. Freshwater Crayfish, 12, 677–687.
Bollinger, J. E., Bundy, K., Anderson, M. B., Millet, L., Preslan, J. E., & Lolibois, L. (1997). Bioaccumulation of chromium in red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkii). Journal of Hazardous Materials, 54, 1–13.
Bryan, G. W. (1968). Concentrations of zinc and copper in the tissues of decapod crustaceans. Journal of Marine Biology Assessment of the UK, 48, 303–321.
Buscaino, G., Filiciotto, F., Buffa, G., Di Stefano, V., Maccarrone, V., Buscaino, C., et al. (2012). The underwater acoustic activities of the red swamp crayfish Procambarus clarkii. The Journal of Acoustical Society of America, 132, 1792–1798.
Canivet, V., Chambon, P., & Gilbert, J. (2001). Toxicity and bioaccumulation of arsenic and chromium in epigean and hypogean freshwater macroinvertebrates. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 40, 345–354.
Canli, M., Stagg, R. M., & Rodger, G. (1997). The induction of metallothionein in tissues of the Norway lobster Nephrops norvegicus following exposure to Cd, Cu, and Zn: the relationships between metallothionein and the metals. Environmental Pollution, 96, 343–350.
Celi, M., Filiciotto, F., Parrinello, D., Buscaino, G., Damiano, M. A., Cuttitta, A., et al. (2012). Physiological and agonistic behavioural response of P. clarkii to an acoustic stimulus. Journal of Experimental Biology, 216, 709–718.
Chen, W., Krage, N., Wu, L. S., Pan, G. X., Khosrivafard, M., & Chang, A. C. (2008). Arsenic, Cadmium and Lead in California cropland soils; role of fertilizers. Journal of Environmental Quality, 37, 688–695.
Coombs, T. L., & George, S. C. (1978). Mechanisms of immobilization and detoxification of metals in marine organisms. In D. S. McLusky & A. J. Berry (Eds.), Physiology and behaviour of marine organisms (pp. 179–187). London: Pergamon Press.
Craig Moss, J., Hardaway, C. J., Richert, J. C., & Sneddon, J. (2010). Determination of cadmium, copper, iron, nickel, lead and zinc in crawfish (Procambarus clarkii) by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry: a study over the 2009 season in Southwest Louisiana. Microchemistry Journal, 95, 5–10.
Dall, W., & Moriarty, D. J. W. (1983). Functional aspects of nutrition and digestion. In D. E. Bliss & L. H. Mantel (Eds.), The biology of Crustacea 5 (pp. 215–261). New York: Academic.
Delmastro, G. B. (1992). Sull’acclimatazione del gambero della Louisiana Procambarus clarkii (Girard, 1852) nelle acque dolci italiane. Pianura Suppl. di Provincia Nuova 4, 5–10.
Devesa, V., Suner, M. A., Lai, V. W., Granchignho, S. C. R., Martinez, J. M., Velez, D., et al. (2002). Determination of arsenic species in a freshwater crustacean Procambarus clarkii. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 16, 123–132.
Devi, M., Thomas, D. A., Barber, J. T., & Fingerman, M. (1996). Accumulation and physiological and biochemical effects of cadmium in a simple aquatic food chain. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 33, 38–43.
Elia, A. C., Door, A. J., Mastrangelo, C., Prearo, M., & Abete, M. C. (2006). Glutathione and antioxidant enzymes in the hepatopancreas of crayfish Procambarus clarkii (Girard, 1852) of Lake Trasimeno (Italy). Bulletin Francais de la Peche et de la Pisciculture, 380, 1351–1361.
Faria, M., Huertas, D., Soto, D. X., Grimalt, J. O., Catalan, J., Riva, M. C., & Barata, C. (2010). Contaminant accumulation and multi-biomarker responses in field collected zebra mussels (Dreissena polymorpha) and crayfish (Procambarus clarkii), to evaluate toxicological effects of industrial hazardous dumps in Ebro river (NE Spain). Chemosphere, 78, 232–240.
FDA. (1993). Guidance document for chromium in shellfish. Washington: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, Office of Seafood (HFS-416).
Finerty, M. W., Madden, J. D., Feagley, S. E., & Grodner, R. M. (1990). Effect of environs and seasonality on metal residues in tissues of wild and pond-raised crayfish in southern Louisiana. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 19, 94–100.
Gherardi, F., Baldaccini, G. N., Ercolini, P., Barbaresi, S., De Luise, G., Mazzoni, D., & Mori, M. (1999). The situation in Italy. In F. Gherardi & D. M. Holdich (Eds.), Crayfish in Europe as alien species (pp. 107–128). Rotterdam: Balkema.
Henttonen, P., & Huner, J. V. (1999). The introduction of alien species in Europe: a historical introduction. In F. Gherardi & D. M. Holdich (Eds.), Crayfish in Europe as alien species (Crustacean issues, Vol. 11, pp. 13–22). Rotterdam: A.A. Balkema.
Hothem, R. L., Bergen, D. R., Bauer, M. L., Crayon, J. J., & Meckstroth, A. M. (2007). Mercury and trace elements in crayfish from Northern California. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 79, 628–632.
Jeckel, W. H., Roth, R. R., & Ricci, L. (1996). Patterns of trace-metal distribution in tissues of Pleoticus muelleri (Crustacea: Decapoda: Solenoceridae). Marine Biology, 125, 297–306.
Jiao, W., Chen, W., Chang, A., & Page, A. (2012). Environmental risks of trace elements associated with long term phosphate fertilizers applications: a review. Environmental Pollution, 168, 44–53.
Jorhem, L., Engman, J., Sundström, B., & Thim, A. M. (1994). Trace elements in crayfish: regional differences and changes induced by cooking. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 26, 137–142.
Kouba, A., Buric, M., & Kozak, P. (2000). Bioaccumulation and effects of heavy metals in crayfish: a review. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 211, 5–16.
Krauskopf, K. B. (1979). Introduction to geochemistry (International series in the earth and planetary science). Tokyo: Mc Grow-Hill.
Luo, C., Yang, R., Wang, Y., Li, J., Zhang, G., & Li, X. (2012). Influence of agricultural practice on trace metals in soils and vegetation in the water conservation area along the East River (Dongjiang River), South China. Science of the Total Environment, 431, 26–32.
Mackevičienė, G. (2002). Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in noble crayfish (Astacus astacus) tissues under aquaculture conditions. Ecologia (Vilnius), 2, 79–82.
Madden, J. D., Grodner, R. M., Feagley, S. E., Finerty, M. W., & Andrews, L. S. (1991). Minerals and xenobiotic residues in the edible tissues of wild and pond-raised Louisiana crayfish. Journal of Food Safety, 12, 1–15.
Madigosky, S. R., Alvarez-Hernandez, X., & Glass, J. (1991). Lead, cadmium, and aluminum accumulation in the red swamp crayfish Procambarus clarkii collected from roadside drainage ditches in Louisiana. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 20, 253–258.
McLaughlin, M. J., Maier, N. A., Freeman, K., Tiller, G., Williams, C. M. J., & Smart, M. K. (1995). Effect of potassic and phosphatic fertilizer type, phosphatic fertilizer Cd content and additions of zinc on cadmium uptake by commercial potato crops. Fertilizer Research, 40, 63–70.
McNeely, R. N., Neimais, V. P., & Dwyer, L. (1979). Water quality sourcebook: a guide to water quality parameters. Ottawa: Environmental Canada Publications.
Medina, F., Hernandea, F., & Pastor, A. (1986). Determination of trace elements in fish tissues by standard addition method. Atomic Absorption News Letter, 14, 49.
Merz, W. (1982). Clinical and public health significance of chromium. In A. S. Prasad (Ed.), Clinical, biochemical, and nutritional aspects of trace elements (pp. 315–323). NewYork: Alan. R. Liss.
Olafson, R. W., Sim, R. G., & Boto, K. G. (1979). Isolation and chemical characterization of the heavy metal binding protein metallothionein from marine invertebrates. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, 62B, 407–416.
Overnell, J. (1982). Copper metabolism in crabs and metallothionein in vitro effects of copper 2+ on soluble hepatopancreas metal binding components in the crab Cancer pagurus containing varying amounts of cadmium. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, 73B, 555–564.
Overnell, J., & Trewhella, E. (1979). Evidence for the natural occurrence of (cadmium, copper)-metallothionein in the crab Cancer pagurus. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, 64C, 69–76.
Pekey, M., Karakas, D., Ayberk, S., Tolun, L., & Bekoglu, M. (2004). Ecological risk assessment using trace elements from surface sediments of Izmit Bay (North-eastern Marmara Sea) Turkey. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 48, 946–953.
Rainbow, P. S. (1998). Phylogeny of trace metals accumulation in crustaceans. In W. J. Langstone & M. Bebianno (Eds.), Metal metabolism in aquatic environment (pp. 285–319). London: Chapman and Hall.
Rainbow, P. S. (2002). Trace metal concentrations in aquatic invertebrates: why and so what? Environmental Pollution, 120, 497–507.
Rainbow, P. S., & Scott, A. G. (1979). Two heavy metal-binding proteins in the mid gut gland of the crab Carcinus maenas. Marine Biology, 55, 143–150.
Raven, K. P., & Loeppert, R. H. (1997). Heavy metals in the environment: trace element composition of fertilizers and soil amendments. Journal of Environmental Quality, 26, 551–557.
Rigler, F. H., & Downing, J. A. (1984). The calculation of secondary production. In J. A. Downing & F. H. Rigler (Eds.), A manual on methods for the assessment of secondary productivity in fresh waters. IBP Handbook (2nd ed., Vol. 17, pp. 19–58). Oxford: Blackwell.
Rincón-León, F., Zurera-Cosano, G., & Pozo-Lora, R. (1988). Lead and cadmium concentrations in red crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) in the Guadalquivir River marshes (Spain). Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 17, 251–256.
Rodriguez-Martin, J. A., Arias, M. L., Grau, J. M., & Corbi, J. M. (2006). Heavy metals contents in agricultural top soils in the Ebro Basin (Spain): application of the multivariate geoestatistical methods to study spatial variations. Environmental Pollution, 144, 1001–1012.
Rowe, C. L., Hopkins, W. A., Zehnder, C., & Congdon, J. D. (2001). Metabolic costs incurred by crayfish (Procambarus acutus) in a trace element-polluted habitat: further evidence of similar responses among diverse taxonomic groups. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology. C, 129, 275–283.
Sánchez-López, F. J., Gil, M. D., Martínez, J. L., Aquilera, P. A., & Garrido, P. A. (2004). Assessment of metal contamination in Doñana National Park (Spain) using crayfish (Procambarus clarkii). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 93, 17–29.
Scalici, M., Chiesa, S., Scuderi, S., Celauro, D., & Gibertini, G. (2010). Population structure and dynamics of Procambarus clarkii (Girard, 1852) in a Mediterranean brackish wetland (Central Italy). Biology Invasions, 12, 1415–1425.
Schilderman, P. A. E., Moonen, E. J. C., Maas, L. M., Welle, I., & Kleinjans, J. C. S. (1999). Use of Crayfish in biomonitoring studies of environmental pollution of the River Meuse. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 44, 241–252.
Schmitt, J. C., Brumbaugh, W. G., Linder, G. L., & Hinck, J. E. (2006). A screening-level assessment of lead, cadmium and zinc in fish and crayfish from Northeast Oklahoma, USA. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 28, 445–471.
Schütze, S., Stein, H., & Born, O. (1999). Radio telemetry observations on migration and activity patterns of restocked noble crayfish Astacus astacus (L.) in the small river Sempt, Northeast of Munich, Germany. Freshwater Crayfish, 12, 688–695.
Suarez-Serrano, A., Alcaraz, C., Ibanez, C., Trobajo, R., & Barata, C. (2010). Procambarus clarkii as a bioindicator of heavy metals pollution sources in the lower Ebro river and Delta. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 73, 280–286.
Timmermans, K. R. (1993). Accumulation and effects of trace metals in freshwater invertebrates. In R. Dallinger & P. S. Rainbow (Eds.), Ecotoxicology of metals in invertebrates (pp. 133–148). Boca Raton: Lewis.
Tinner, W., Van Leeuwen, J. F. N., Colombaroli, D., Vescovi, E., Van der Knaap, W. O., & Henne, P. D. (2009). Holocene environmental and climate changes at Gorgo Basso, a coastal lake in south western Sicily, Italy. Quaternary Science Reviews, 28, 1498–1510.
Viikinkoski, T., Henttonen, P., Matinvesi, J., Könönen, H., & Suntioinen, S. (1995). The physiological condition and edibility of noble crayfish (Astacus astacus (L) in warm waste waters of a steel works in northwest Finland. Freshwater Crayfish, 10, 304–321.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bellante, A., Maccarone, V., Buscaino, G. et al. Trace element concentrations in red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) and surface sediments in Lake Preola and Gorghi Tondi natural reserve, SW Sicily. Environ Monit Assess 187, 404 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4613-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4613-4