Abstract
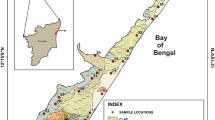
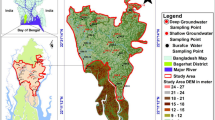
The impact of seawater intrusion was investigated using major hydrogeochemical ions to evaluate the origin of salinity in Sadras watershed located between Buckingham Canal and Bay of Bengal in the southeastern coast of India. From empirical data collected twice during pre- and post-monsoon seasons, it was found that groundwater was slightly acidic to mildly alkaline, and more than 44% of groundwater samples had EC > 3,000 μS/cm in both the seasons. Results of principle component analysis (PCA) showed that Na + , Cl − , Mg2 + , and SO\(_{4}^{\,\, 2-}\) concentrations had the highest loading factor and the samples affected by saline/seawater were separated from the cluster. Hydrochemical processes that accompany the saline/seawater were identified using ionic changes. It was observed during sampling periods that the mixing due to saline/seawater intrusion varied from 4.82–7.86%. Negative values of ionic change (e change) for Na + and K + decreased with the increasing fraction of seawater. Furthermore, salinity, sodium adsorption ratio, percentage of sodium Na (%), and exchangeable sodium percentage in well samples showed that groundwater was unsuitable for irrigation purposes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adepelumi, A. A., Ako, B. D., Ajayi, T. R., Afolabi, O., & Omotoso, E. J. (2009). Delineation of saltwater intrusion into the freshwater aquifer of Lekki Peninsula, Lagos, Nigeria. Environmental Geology, 56, 927–933.
American Public Health Association (APHA) (1985). Standard methods for the examination of water and waste (16th ed., p. 100). Washington, DC, USA: Am. Public Health Assoc.
Anderson, T. W. (1958). Introduction to multivariate statistical analysis. New York: Wiley.
Appelo, C. A. J., & Postma, D. (2005). Geochemistry, ground water and pollution (2nd ed.). Rotterdam: Balkema.
Arumugham, V. (1994). Site characterization for location of radioactive waste repository—A case study. Ph.D. Thesis, Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay, India.
Barrett, B., Heinson, G., Hatch, M., & Telfer, A. (2002). Geophysical methods in saline groundwater studies: Locating perched water tables and fresh-water lenses. Exploration Geophysics, 33, 115–121.
Beddows, P. A., Smart, P. L., Whitaker, F. F., & Smith, S. L. (2007). Decoupled fresh-saline groundwater circulation of a coastal carbonate aquifer: Spatial patterns of temperature and specific electrical conductivity. Journal of Hydrology, 346, 18–32.
Bobba, A. G. (2002). Numerical modeling of salt-water intrusion due to human activities and sea-level change in the Godavari Delta, India. Hydrological Sciences Journal-Journal Des Sciences Hydrologiques, 47, S67–S80.
Bottomley, D. J., Katz, A., Chan, L. H., Starinsky, A., Douglas, I. D., Clark, I. D., et al. (1999). The origin and evolution of Canadian Shield brines: Evaporation or freezing of seawater? New lithium isotope and geochemical evidence from the Slave craton. Chemical Geology, 155, 295–320.
Brown, C. H. (1998). Applied multivariate statistics in geohydrology and related sciences. Berlin: Springer.
Brown, E., Skougstad, M. W., & Fishmen, M. J. (1983). Method for collection and analyzing of water samples for dissolved minerals and gases (p. 75). Washington DC, USA: U.S. Govt. Printing Office.
Casanova, J., Négrel, P., Kloppmann, W., & Aranyossy, J. F. (2001). Origin of deep saline groundwaters in the Vienne granitoids (France). Constraints inferred from boron and strontium isotopes. Geofluids, 1, 91–102.
Cheng, A. H. D., & Ouazar, D. (2004). Coastal aquifer management-monitoring, modeling, and case studies (p. 280). USA: Lewis Publishers.
Diamantis, I. B., & Petalas, C. P. (1989). Seawater intrusion into coastal aquifers of Thrace and its impact on the environment. Toxicol Environmental Chemistry, 20–21, 291–305.
Domenico, P. A., & Schwartz, F. W. (1990). Physical and chemical hydrogeology. New York: Wiley.
Ergil, M. E. (2000). The salination problem of the Guzelyurt aquifer, Cyprus. Water Research, 34(4), 1201–1214.
Fidelibus, M. D. (2003). Environmental tracing in coastal aquifers: Old problems and new solutions. In Coastal aquifer intrusion technology: Mediterranean countries (Vol. 2, pp. 79–111). Madrid: Publ. IGME.
Franco, R., Biella, G., Tosi, L., Teatini, P., Lozej, A., Chiozzotto, B., et al. (2009). Monitoring the saltwater intrusion by time lapse electrical resistivity tomography: The Chioggia test site (Venice Lagoon, Italy). Journal of Applied Geophysics, 69(3–4), 117–130.
Gibbs, R. J. (1970). Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science, 170, 1088–1090.
Gurumoorthy, C., Sasidhar, P., Arunugham, V., & Nathur, R. K. (2004). Sub-surface investigations on deep saline ground water of charnokite rock formation, Kalpakkam, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 91, 211–22.
Hem, J. D. (1989). Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water. U.S.G.S. Water-supply paper (Vol. 2254). Washington DC: US Government Printing Office.
Jalali, M. (2007). Salinization of ground water in arid and semi-arid zones: An example from Tajarak, western Iran. Environmental Geology, 52, 1133–1149.
Karanath, K. R. (1987). Quality of ground water. In: K. R. Karnath (Ed.), Ground water assessment development and management (pp. 217–275). New Delhi: Tata McGraw Hill.
Kim, K. Y., Chon, C. M., & Park, K. H. (2007). A simple method for locating fresh water–salt water interface using pressure data. Ground Water, 45(6), 723–728.
Kim, K. Y., Park, Y. S., Kim, G. P., & Park, K. H. (2009). Dynamic freshwater–saline water interaction in the coastal zone of Jeju Island, South Korea. Hydrogeological Journal, 17, 617–629.
Lambrakis, N. J. (1998). The impact of human activities in the Malia coastal area (Crete) on groundwater quality. Environmental Geology, 36(1–2), 87–92.
Mandel, S., & Shiftan, Z. L. (1980). Ground water resources investigation and development. New York: Academic Press.
Mhamdi, A., Gouasmia, M., Gasmi, M., Bouri, S., & Dhia, H. B. (2006). Evaluation of the water quality by the geoelectrical method: Example of the El Mida plain-North Gabes (southern Tunisia). Comptes Rendus Geoscience, 338(16), 1228–1239.
Mondal, N. C., Singh, V. S., Saxena, V. K., & Prasad, R. K. (2008). Improvement of ground water quality due to fresh water ingress in Potharlanka Island, Krishna delta, India. Environmental Geology, 55(3), 595–603.
Mondal, N. C., Singh, V. P., Singh, S., & Singh, V. S. (2010a). Hydrochemical characteristic of coastal aquifer from Tuticorin, Tamil Nadu, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. doi:10.1007/s10661-010-1549-6.
Mondal, N. C., Singh, V. S., Puranik, S. C., & Singh, V. P. (2010b). Trace element concentration in groundwater of Pesarlanka Island, Krishna Delta, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 163(1–4), 215–227.
Morrison, D. F. (1964). Multivariate statistical methods. New York: McGraw Hill.
Murad, A. A., & Krishnamurthy, R. V. (2004). Factors controlling groundwater quality in Eastern United Arab Emirates: A chemical and isotopic approach. Journal of Hydrology, 286(1–4), 227–235.
Nasab, A. A., Boufadel, M. C., Li, H., & Weaver, J. W. (2010). Saltwater flushing by freshwater in a laboratory beach. Journal of Hydrology, 386(1–4), 1–12.
Oteri, A. U. (1988). Electric log interpretation for the evaluation of salt water intrusion in the eastern Niger Delta. Hydrological Science Journal, 33(2), 19–30.
Papatheodorou, G., Lambrakis, N., & Panagopoulos, G. (2007). Application of multivariate statistical procedures to the hydrochemical study of a coastal aquifer: An example from Crete, Greece. Hydrological Processes, 21, 1482–1495.
Park, S. C., Yun, S. T., Chae, G. T., Yoo, I. S., Shin, K. S., Heo, C. H., et al. (2005). Regional hydrochemical study on salinization of coastal aquifers, western coastal area of South Korea. Journal of Hydrology, 313, 182–194.
Pujari, P. R., & Soni, A. K. (2009). Sea water intrusion studies near Kovaya limestone mine, Saurashtra coast, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 154(1–4), 93–109.
Qahman, K., & Larabi, A. (2006). Evaluation and numerical modeling of seawater intrusion in the Gaza aquifer (Palestine). Hydrogeological Journal, 14, 713–728.
Rabinove, C. L., Longford, R. H., & Brookhart, J. W. (1958). Saline water resources of North Dakota (p. 364). US Geographical Survey Water Supply, Paper 1418.
Radharkishna, I., & Chowdary, M. V. R. (1998). Simulation of chloride migration rates in Paleo Pennar delta region, coastal Andhra Pradesh, India. Environmental Geology, 36(1–2), 109–117.
Rajmohan, N., Elango, L., Ramachandran, S. & Natarajan, M. (2000). Major ion correlation in ground water of Kancheepuram Region, South India. Indian Journal of Environmental Protection, 20(3), 188–193.
Ramesh, R. (2003). Ground water quality along the east coast of India. In Recent trends in hydrogeochemistry (pp. 139–146). New Delhi: Publishing Company.
Rao, N. S., Nirmala, I. S., & Suryanarayana, K. (2005). Groundwater quality in a coastal area: A case study from Andhra Pradesh, India. Environmental Geology, 48(4–5), 543–550.
Sarwade, D. V., Nandakumar, M. V., Kesari, M. P., Mondal, N. C., Singh, V. S. & Singh, B. (2007). Evaluation of seawater ingress into an Indian Attoll. Environmental Geology, 52(2), 1475–1483.
Satpathy, C. C., Mathur, P. K. & Nair, K. V. K. (1987). Contribution of Edayur-Sadras estuarine system to the hydrographic characteristics of Kalpakkam coastal waters. Journal of the Marine Biological Association, 29(1–2), 344–350.
Saxena, V. K., Singh, V. S., Mondal, N. C., & Jain, S. C. (2003). Use of chemical parameters to delineation fresh ground water resources in Potharlanka Island, India. Environmental Geology, 44(5), 516–521.
Saxena, V. K., Mondal, N. C., & Singh, V. S. (2004). Identification of seawater ingress using Sr and B in Krishna delta. Current Science, 86(4), 586–590.
Saxena, V. K., Mondal, N. C., Singh, V. S., & Kumar, D. (2005). Identification of water-bearing fractures in hard rock terrain by electrical conductivity logs, India. Environmental Geology, 48(8), 1084–1095.
Senthilkumar, G., Ramanathan, A. L., Nainwal, H. C., & Chidambaram, S. (2008). Evaluation of the hydro geochemistry of groundwater using factor analysis in the Cuddalore coastal region, Tamil Nadu, India. Indian Journal of Marine Sciences, 37(2), 181–185.
Shainberg, I., & Oster, J. D. (1976). Quality of irrigation water. IIIC publication no. 2.
Sharma, S. (1996) Applied Multivariate Techniques (pp. 90–143) . New York: Wiley.
Sherif, M. & Kacimov, A. (2007). Seawater intrusion in the coastal aquifer of Wadi Ham, UAE: A new focus on groundwater seawater interactions. In Proceedings of symposium HS 1001 at IUGG 2007, Perugia (pp. 315–325). Wallingford, UK: IAHS Publ. 312, IAHS.
Singh, U. K., Das, R. K., & Hodlur, G. K. (2004a). Significance of Dar-Zarruck parameters in the exploration of quality affected coastal aquifer systems. Environmental Geology, 45, 696–702.
Singh, V. S., Sarwade, D. V., Mondal, N. C., Nanadakumar, M. V., & Singh, B. (2009). Evaluation of groundwater resources in a tiny Andrott Island, Union Territory of Lakshadweep, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 158(1–4), 145–154.
Singh, V. S., & Saxena, V. K. (2004). Assessment of utilization ground water resources in a coastal shallow aquifer. In Proceeding of the 2nd Asia pacific association of hydrology & water resources conference (Vol. 2, pp. 347–364). Singapore.
Singh, V. S., Saxena, V. K., Prakash, B. A., Mondal, N. C., & Jain, S. C. (2004b). Augmentation of ground water resources in saline ingress coastal deltaic area (p. 61). NGRI-Tech. Report. No. NGRI-2004-GW-422.
Somay, M. A., & Gemici, U. (2009). Assessment of the salinization process at the coastal area with hydrogeochemical tools and geographical information systems (GIS): Selçuk plain, Izmir, Turkey. Water Air Soil Pollution, 201, 55–74.
Subba Rao, N. (2006). Seasonal variation of groundwater quality in a part of Guntur district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environmental Geology, 49, 413–429.
Sukhija, B. S., Varma, V. N., Nagabhushanam, P., & Reddy, D. V. (1996). Differentiation of paleomarine and modern seawater intruded salinities in coastal ground waters (of Karaikal and Tanjavur, India) based on inorganic chemistry, organic biomarker fingerprints and radiocarbon dating. Journal of Hydrology, 174, 173–201.
Taniguchi, M., Ishitobi, T., Burnett, W. C., & Wattayakorn, G. (2007). Evaluating ground water–sea water interactions via resistivity and seepage meters. Ground Water, 45(6), 729–735.
Telford, W. M., Geldart, L. P., & Sheriff, R. E. (1990). Applied geophysics (2nd ed.). New York: Cambridge University Press.
Tellam, J. H. (1995). Hydrochemistry of the saline ground waters of the lower Mersey Basin Permo-Triassic sandstone aquifer, UK. Journal Hydrology, 165, 45–84.
Thorne, D. W., & Petersonm, H. B. (1954). Irrigated soils. London: Constable and Company.
Tijani, M. N. (1994). Hydrogeochemical assessment of groundwater in Moro Area, Kwara State, Nigeria. Environmental Geology, 24(3), 194–202.
Todd, D. K. (1959). Ground water hydrology (pp. 277–294). New York: Wiley.
Todd, D. K. (1980). Groundwater hydrology (2nd ed.). New York: Wiley.
Wilcox, L. V. (1955). Classification and use of irrigation waters (p. 19). U.S. Dept. Agri., Circular, No. 969.
World Health Organization (WHO) (1984). Guideline of drinking quality (pp. 333–335). Washington, DC, USA: World Health Organization.
Yaouti, F. E., Mandour, A. E., Khattach, D., Benavente, J., & Kaufmann, O. (2009). Salinization processes in the unconfined aquifer of Bou-Areg (NE Morocco): A geostatistical, geochemical, and tomographic study. Applied Geochemistry, 24, 16–31.
Zekri, S. (2008). Using economic incentives and regulations to reduce seawater intrusion in the Batinah coastal area of Oman. Agricultural Water Management, 95(3), 243–252.
Zhang, Q., Volker, R. E., & Lockington, D. A. (2004). Numerical investigation of seawater intrusion at Gooburrum, Bundaberg, Queensland, Australia. Hydrogeological Journal, 12, 674–687.
Zhou, X., Chen, M., Ju, X., Ning, X., & Wang, J. (2000). Numerical simulation of sea water intrusion near Beihai, China. Environmental Geology, 40(1–2), 223–233.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mondal, N.C., Singh, V.S., Saxena, V.K. et al. Assessment of seawater impact using major hydrochemical ions: a case study from Sadras, Tamilnadu, India. Environ Monit Assess 177, 315–335 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1636-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1636-8