Abstract
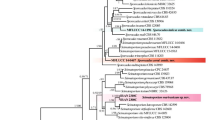
This study aims to identify and characterize species of Phaeoacremonium associated with Petri disease of table grapes in three regions in the Northeastern Brazil, to investigate the distribution of the species in these regions and to evaluate their pathogenicity and aggressiveness in excised green shoots of table grapes. Fungal identifications were made using a combination of morphology together with a phylogenetic analysis based on portions of the β-tubulin (TUB2) and actin (ACT) genes. Three species of Phaeoacremonium (Pm.) were identified: Pm. minimum, Pm. nordesticola sp. nov. and Pm. parasiticum. Phaeoacremonium minimum and Pm. parasiticum had previously been reported in grapevine. Phaeoacremonium minimum was the most prevalent species. All species of Phaeoacremonium were pathogenic on detached shoots of table grape, with Pm. minimum being the most aggressive.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araújo, J. L. P., & Ramalho, P. J. P. (2009). Custos de produção. In J. M. Soares & P. C. S. Leão (Eds.), A vitivinicultura no semi-árido brasileiro (pp. 727–736). Brasília: Embrapa Informação Tecnológica.
Ariyawansa, H. A., et al. (2015). Fungal diversity notes 111–252 – Taxonomic and phylogenetic contributions to fungal taxa. Fungal Diversity, 75, 27–274.
Aroca, A., García-Figueres, F., Bracamonte, L., Luque, J., & Raposo, R. (2006). A survey of trunk disease pathogens within rootstocks of grapevines in Spain. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 115, 195–202.
Aroca, A., & Raposo, R. (2009). Pathogenicity of Phaeoacremonium species on grapevines. Journal of Phytopathology, 157, 413–419.
Arzanlou, M., Groenewald, J. Z., Gams, W., Braun, U., Shin, H. D., & Crous, P. W. (2007). Phylogenetic and morphotaxonomic revision of Ramichloridium and allied genera. Studies in Mycology, 58, 57–93.
Arzanlou, M., Moshari, S., Salari, M., & Badali, H. (2013). Molecular characterization and pathogenicity of Phaeoacremonium spp. associated with esca disease of grapevines in northern Iran. Archives of Phytopathology and Plant Protection, 46, 375–388.
Auger, J., Perez, I., Esterio, M., Navia, V., Gubler, W. D., & Eskalen, A. (2005). Fungi associated with grapevine wood decay and young vine decline in Chile. Phytopathologia Mediterranea, 44, 89–90.
Berraf-Tebbal, A., Bouznad, Z., Santos, J. M., Coelho, M. A., Péros, J. P., & Phillips, A. J. L. (2011). Phaeoacremonium species associated with Eutypa dieback and esca of grapevines in Algeria. Phytopathologia Mediterranea, 50, S86–S97.
Camargo, U. A., Protas, J. F. S., & Mello, L. M. R. (2008). Grape growing and processing in Brazil. Acta Horticulturae, 785, 51–57.
Carbone, I., & Kohn, L. M. (1999). A method for designing primers sets for speciation studies in filamentous ascomycetes. Mycologia, 91, 553–556.
Cloete, M., Fourie, P. H., Damm, U., Crous, P. W., & Mostert, L. (2011). Fungi associated with die-back symptoms of apple and pear trees, a possible inoculum source of grapevine trunk disease pathogens. Phytopathologia Mediterranea, 50, S176–S190.
Correia, K. C., Câmara, M. P. S., Barbosa, M. A. G., Sales Jr., R., Agustí-Brisach, C., Gramaje, D., García-Jiménez, J., Abad-Campos, P., Armengol, J., & Michereff, S. J. (2013). Fungal trunk pathogens associated with table grape decline in northeastern Brazil. Phytopathologia Mediterranea, 52, 380–387.
Crous, P. W., & Gams, W. (2000). Phaeomoniella chlamydospora gen. Et comb. Nov., a causal organism of petri grapevine decline and esca. Phytopathologia Mediterranea, 39, 112–188.
Crous, P. W., Gams, W., Wingfield, M. J., & Van Wyk, P. S. (1996). Phaeoacremonium gen. Nov. associated with wilt and decline diseases of woody hosts and human infections. Mycologia, 88, 786–796.
Damm, U., Mostert, L., Crous, P. W., & Fourie, P. H. (2008). Novel Phaeoacremonium species associated with necrotic wood of Prunus trees. Persoonia, 20, 87–102.
Decoin, M. (2001). Grapevine products: News on withdrawals and restrictions. Phytoma, 543, 28–33.
Dettman, J. R., Jacobson, D. J., & Taylor, J. W. (2003). A multilocus genealogical approach to phylogenetic species recognition in the model eukaryote Neurospora. Evolution, 57, 2703–2720.
Di Marco, S., Calzarano, F., Osti, F., & Mazzullo, A. (2004). Pathogenicity of fungi associated with a decay of kiwifruit. Australasian Plant Pathology, 33, 337–342.
Dupont, J., Laloui, W., Magnin, S., Larignon, P., & Roquebert, M. F. (2000). Phaeoacremonium viticola, a new species associated with esca disease of grapevine in France. Mycologia, 92, 499–504.
Dupont, J., Magnin, S., Césari, C., & Gatica, M. (2002). ITS and β-tubulin markers help delineate Phaeoacremonium species, and the occurrence of P. parasiticum in grapevine disease in Argentina. Mycological Research, 106, 1143–1150.
Essakhi, S., Mugnai, L., Crous, P. W., Groenewald, J. Z., & Surico, G. (2008). Molecular and phenotypic characterization of novel Phaeoacremonium species associated with petri disease and esca of grapevine. Persoonia, 21, 119–134.
FAO (2016). FAOSTAT. Resource database. http://faostat3.fao.org/home/E. Accessed on 24 October 2016.
Gava, R., Urben, A. F., & Garrido, L. R. (2010). Influence of culture media and temperature on mycelial growth of Phaeoacremonium angustius. Phytopathologia Mediterranea, 49, 110–111.
Glass, N. L., & Donaldson, G. C. (1995). Development of primer sets designed for use with the PCR to amplify conserved genes from filamentous infection due to Phaeoacremonium spp. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 41, 1332–1336.
Goh, T. K. (1999). Single-spore isolation using a handmade glass needle. Fungal Diversity, 2, 47–63.
Graham, A. B., Johnston, P. R., & Weir, B. S. (2009). Three new Phaeoacremonium species on grapevines in New Zealand. Australasian Plant Pathology, 38, 505–513.
Gramaje, D., Agustí-Brisach, C., Pérez-Sierra, A., Moralejo, E., Olmo, D., Mostert, L., Damm, U., & Armengol, J. (2012). Fungal trunk pathogens associated with wood decay of almond trees on Mallorca (Spain). Persoonia, 28, 1–13.
Gramaje, D., & Armengol, J. (2011). Fungal trunk pathogens in the grapevine propagation process: Potential inoculum sources, detection, identification, and management strategies. Plant Disease, 95, 1040–1055.
Gramaje, D., Armengol, J., Mohammadi, H., Banihashemi, Z., & Mostert, L. (2009). Novel Phaeoacremonium species associated with petri disease and esca of grapevines in Iran and Spain. Mycologia, 101, 920–929.
Gramaje, D., León, M., Pérez-Sierra, A., Burgess, T., & Armengol, J. (2014). New Phaeoacremonium species isolated from sandalwood trees in Western Australia. IMA Fungus, 5, 67–77.
Gramaje, D., Mostert, L., Groenewald, J. Z., & Crous, P. W. (2015). Phaeoacremonium: From esca disease to phaeohyphomycosis. Fungal Biology, 119, 759–783.
Groenewald, M., Kang, J.-C., Crous, P. W., & Gams, W. (2001). ITS and beta-tubulin phylogeny of Phaeoacremonium and Phaeomoniellaspecies. Mycological Research, 105, 651–657.
Halleen, F., Mostert, L., & Crous, P. W. (2007). Pathogenicity testing of lesser- known vascular fungi of grapevines. Australasian Plant Pathology, 36, 277–285.
Halliwell, R. S. (1966). Association of Cephalosporium with a decline of oak in Texas. Plant Disease Reporter, 50, 75–78.
Hausner, G., Eyjólfsdóttir, G., & Reid, J. (1992). Two additional species of the genus Togninia. Canadian Journal of Botany, 70, 724–734.
Hawksworth, D. L., Gibson, I. A. S., & Gams, W. (1976). Phialophora parasiticaassociated with disease conditions in various trees. Transactions of the British Mycological Society, 66, 427–431.
Kumar, S., Stecher, G., & Tamura, K. (2016). MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 33, 1870–1874.
Larignon, P., & Dubos, B. (1997). Fungi associated with esca disease in grapevine. European Journl of Plant Pathology, 103, 147–157.
Lazzarotto, J. J., & Fioravanço, J. C. (2013). Tendências e sazonalidades nas exportações e importações brasileiras de uva de mesa. Informações Econômicas, 43, 43–58.
Martín, L., Miera, L. E. S., & Martín, M. T. (2014). AFLP and RAPD characterization of Phaeoacremonium aleophilum associated with Vitis vinifera decline in Spain. Journal of Phytopathology, 162, 245–257.
Mohammadi, H. (2014). Phaeoacremonium spp. and Botryosphaeriaceae spp. associated with date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) decline in Iran. Journal of Phytopathology, 162, 575–581.
Mostert, L., Groenewald, J. A., Summerbell, R. C., Gams, W., & Crous, P. W. (2006a). Taxonomy and pathology on Togninia (Diaporthales) and its Phaeoacremonium anamorphs. Studies in Mycology, 54, 1–115.
Mostert, L., Groenewald, J. Z., Summerbell, R. C., Robert, V., Sutton, D. A., Padhye, A. A., & Crous, P. W. (2005). Species of Phaeoacremonium associated with infections in humans and environmental reservoirs in infected woody plants. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 43, 1752–1767.
Mostert, L., Halleen, F., Fourie, P. H., & Crous, P. W. (2006b). A review of Phaeoacremonium species involved in petri disease and esca of grapevines. Phytopathologia Mediterranea, 45, S12–S29.
Moyo, P., Mostert, L., Bester, M., & Halleen, F. (2016). Trunk disease fungi associated with Diospyros kaki in South Africa. Plant Disease. accepted. doi:10.1094/PDIS-02-16-0245-RE.
Mugnai, L., Graniti, A., & Surico, G. (1999). Esca (black measles) and brown wood streaking: Two old and elusive diseases of grapevines. Plant Disease, 83, 404–418.
Nigro, F., Boscia, D., Antelmi, I., & Ippolito, A. (2013). Fungal species associated with a severe decline of olive in southern Italy. Journal of Plant Pathology, 95, 668.
O’Donnell, K., & Cigelnik, E. (1997). Two divergent intragenomic rDNA ITS2 types within a monophyletic lineage of the fungus Fusarium are nonorthologous. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 7, 103–116.
Possingham, J. V. (2008). Developments in the production of table grapes, wine and raisins in the tropical regions of the world. Acta Horticulturae, 785, 45–50.
Raimondo, M. L., Lops, F., & Carlucci, A. (2014). Phaeoacremonium italicum sp nov., a new species associated with esca of grapevine in southern Italy. Mycologia, 106, 1119–1126.
Rayner, R. W. (1970). A mycological colour chart. Kew: Commonwealth Mycological Institute & British Mycological Society.
Romero-Rivas, L. C., Álvarez, L. A., Gramaje, D., & Armengol, J. (2009). First report of Phaeoacremonium parasiticum causing petri disease of grapevine in Perú. Plant Disease, 93, 200.
Rumbos, I. (1986). Phialophora parasitica, causal agent of cherry dieback. Journal of Phytopathology, 117, 283–287.
Sami, S., Mohammadi, H., & Heydarnejad, J. (2014). Phaeoacremonium species associated with necrotic wood of pome fruit trees in Iran. Journal of Plant Pathology, 96, 487–495.
Scheck, H. J., Vasquez, S. J., Fogle, D., & Gubler, W. D. (1998). Grape growers report losses to black-foot and grapevine decline. California Agriculturist, 52, 19–23.
Staden, R., Beal, K. F., & Bonfield, J. K. (1998). The Staden package, 1998. In S. Misener & S. A. Krawetz (Eds.), Bioinformatics methods and protocols (pp. 115–130). Humana Press: New York.
Stamatakis, A. (2014). RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics, 30, 1312–1313.
Úrbez-Torres, J. R., Haag, P., Bowen, P., & O’Gorman, D. T. (2014). Grapevine trunk diseases in British Columbia: Incidence and characterization of the fungal pathogens associated with esca and petri diseases of grapevine. Plant Disease, 98, 469–482.
Vaidya, G., Lohman, D. J., & Meier, R. (2011). SequenceMatrix: Concatenation software for the fast assembly of multi-gene datasets with character set and codon information. Cladistics, 27, 171–180.
Acknowledgements
This work was financed by Fundação de Amparo à Ciência e Tecnologia do Estado de Pernambuco - FACEPE (APQ 137-5.01/12) and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior – CAPES (Project 203/2009 - International Cooperation CAPES-Brazil/DGU-Spain). M. P. S. Câmara and S. J. Michereff are recipients of Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico - CNPq research fellowships. D. Gramaje was supported by the DOC-INIA program from the National Institute for Agronomic Research (INIA), co-funded by the European Social Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
da Silva, M.A., Correia, K.C., Barbosa, M.A.G. et al. Characterization of Phaeoacremonium isolates associated with Petri disease of table grape in Northeastern Brazil, with description of Phaeoacremonium nordesticola sp. nov.. Eur J Plant Pathol 149, 695–709 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-017-1219-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-017-1219-4