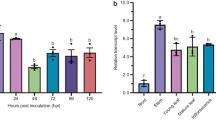
Abstract
Rice sheath blight, which is caused by Rhizoctonia solani, is a devastating disease in many areas of the world where rice is cultivated. The role of polygalacturonase (PG) in the infection process of R. solani was investigated in the present study by cloning and investigating the function of a new PG-encoding gene, which was designated RsPG2. Bioinformatics showed that RsPG2 consisted of a 1,633 bp open reading frame (ORF) with six introns; the deduced protein contained 436 amino acids with a predicted mass of 45.88 kDa after cleavage of the predicted 17-amino acid signal sequence. Culture supernatants obtained from Pichia pastoris producing recombinant RsPG2 degraded polygalacturonic acid in vitro, thus confirming that RsPG2 encodes a PG gene. Purified recombinant RsPG2 also degraded rice tissue and elicited obvious necrotic symptoms 48 h after inoculation. Real-time qRT-PCR indicated that the expression of RsPG2 was strongly induced during the infection of rice by R. solani. These data unequivocally demonstrate that RsPG2 plays an important role in R. solani infection and provide further insights for elucidating the function of pg genes in the virulence of R. solani.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhgari, A. B., & Motallebi, Z. M. R. (2012). Bean PG-inhibiting protein expressed in transgenic Brassica napus inhibits PG from its fungal pathogen Rhizoctonia solani. Plant Protection Science, 48, 1–9.
Arnold, K., Bordoli, L., Kopp, J., & Schwede, T. (2006). The SWISS-MODEL workspace: A web-based environment for protein structure homology modelling. Bioinformatics, 21, 195–201.
Baiswar, P., Bag, T .K., Basumatary, R., Chandra, S., & Ngachan, S. V. (2012). Molecular evidence reveals presence of Rhizoctonia solani AG1-IB on Tagetes patula in India. Australian Plant Disease Notes 7, 63–66.
Bendtsen, J. D., Nielsen, H., Heijne, G. V., & Brunak, S. (2004). Improved prediction of signal peptides: Signal P 3.0. Journal of Molecular Biology, 340, 783–795.
Benedetti, M., Andreani, F., Leggio, C., Galantini, L., Di Matteo, A., Favel, N. V., De Lorenzo, G., Cervone, F., Federici, L., & Sicilia, F. (2013). A single amino-acid substitution allows endo-polygalacturonase of Fusarium verticillioides to acquire recognition by PGIP2 from Phaseolus vulgaris. PloS One, 8, 1–11.
Cabanne, C., & Doneche, B. (2002). Polygalacturonase isozymes produced during infection of the grape berry by Botrytis cinerea. Journal of Grape Research, 41, 129–132.
Catharina, S., Vakhrushev, S. Y., Joshi, H. J., Kong, Y., Vester-Christensen, M. B., Schjoldager, K. T.-B. G., Lavrsen, K., Dabelsteen, S., Pedersen, N. B., Marcos-Silva, L., Gupta, R., Bennett, E. P., Mandel, U., Brunak, S., Wandall, H. H., Levery, S. B., & Clausen, H. (2013). Precision mapping of the human O-GalNAc glycoproteome through SimpleCell technology. EMBO Journal, 32, 1478–1488.
Chen, X. J., Zhang, H., Xu, J. Y., Tong, Y. H., & Ji, Z. L. (2006). Cell wall degrading enzymes produced by Rhizoctonia solani and their pathogenicity to rice plant (in Chinese). Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 22, 24–28.
Chen, X. J., Xu, Y., Tong, Y. H., Meng, L. J., Ji, Z. L., & Xu, J. Y. (2009). Pathogenic mechanism of phytotoxin produced by Rhizoctonia solani, the causal pathogen of rice sheath blight (in Chinese). Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 39, 439–443.
Chen, X. J., Wang, Y. D., Zuo, S. M., Tong, Y. H., Pan, X. B., & Xu, J. Y. (2010). Isolation, purification and characterization of polygalacturonase (PG) from Rhizoctonia solani, the pathogen of rice sheath blight (in Chinese). Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 40, 276–281.
Chen, X. J., Chen, Y., Zhang, L. N., Xu, B., Zhang, J. H., Chen, Z. X., Tong, Y. H., Zuo, S. M., & Xu, J. Y. (2016). Overexpression of OsPGIP1 enhances rice resistance to sheath blight. Plant Disease, 100, 388–395.
Combet, C., Blanchet, C., Geourjon, C., & Deleage, G. (2000). NPS@: Network protein sequence analysis. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 25, 147–150.
Contreras, E. J. C., Hours, R. A., Voget, C. E., & Mignone, C. F. (1999). Aspergillus kawachii produces an acidic pectin releasing enzyme activity. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 88, 48–52.
Cserzo, M., Eisenhaber, F., Eisenhaber, B., & Simon, I. (2002). On filtering false positive transmembrane protein predictions. Protein Engineering, 15, 745–752.
De Lorenzo, G., D’Ovidio, R., & Cervone, F. (2001). The role of PG-inhibiting proteins (PGIPs) in defense against pathogenic fungi. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 39, 313–335.
Diaz, A. A., Tomba, E., Lennarson, R., Richard, R., Baqajewicz, M. J., & Harrison, R. G. (2009). Prediction of protein solubility in Escherichia coli using logistic regression. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 105, 374–383.
Dong, Z. Y., & Wang, Z. Z. (2015). Isolation and heterologous expression of a PG produced by Fusarium oxysporum f. Sp. cubense race 1 and 4. International Journal of Molecular Science, 16, 7595–7607.
Eken, C., & Demirci, E. (2003). Identification and pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia solani and binucleate Rhizoctonia anastomosis groups isolated from forage legumes in Erzurum Turkey. Phytoparasitica, 31, 76–80.
Federici, L., Caprari, C., Mattei, B., Savino, C., Di Matteo, A., De Lorenzo, G., Cervone, F., & Tsernoglou, D. (2001). Structural requirements of endopolygalacturonase form interaction with PGIP (polygalacturonase-inhibiting protein). Proceedings of the National Academy of Science of the United States of America, 98, 13425–13430.
Ferrari, S., Galletti, R., Pontiggia, D., Manfredini, C., Lionetti, V., Bellincampi, D., Cervone, F., & De Lorenzo, G. (2008). Transgenic expression of a fungal endo-PG increases plant disease resistance to pathogens and reduces auxin sensitivity. Plant Physiology, 146, 669–681.
Ferrari, S., Sella, L., Janni, M., De, L. G., & Favaron, F. (2012). Transgenic expression of PG-inhibiting protein in Arabidopsis and wheat increase resistance to the flower pathogen Fusarium graminearum. Plant Biology 14. Supplemental, 1, 31–38.
Gainvors, A., Nedjaoum, N., Gognies, S., Muzart, M., Nedjma, M., & Belarbi, A. (2000). Purification and characterization of acidic endo-polygalacturonase encoded by the PGL1-1 gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 183, 131–135.
Gasteiger, E., Hoogland, C., Gattiker, A., Duvaud, S., Wilkins, R., Appel, R. D., & Bairoch, A. (2005). Protein identification and analysis tools on the ExPASY server. (In J. M. Walker (Ed.) The proteomics protocols handbook (pp. 571–607). Totowa, New Jersey: Humana Press).
Hassan Dar, G. H., Beig, M. A., Ahanger, F. A., & Ganai, N. A. (2011). Management of root rot caused by Rhizoctonia solani and Fusarium oxysporum in blue pine (Pinus wallichiana) through use of fungal antagonists. Asian Journal of Plant Pathology, 5, 1–13.
Hwang, B. H., Bae, H. H., Lim, H. S., Kin, K. B., Kim, S. J., Im, M. H., Park, B. S., Kim, D. S., & Kim, J. K. (2010). Overexpression of polygalacturonase-inhibiting protein 2 (PGIP2) of Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis) increased resistance to the bacterial pathogen Pectobacterium carotovorum Ssp. carotovorum. Plant Cell Tissue and Organ Culture, 103, 293–305.
Joubert, D. A., Slaughter, A. R., Kemp, G., Becker, J. V., Krooshof, G. H., Bergmann, C., Benen, J., Pretorius, I. S., & Vivier, M. A. (2006). The grapevine polygalacturonase-inhibiting protein (VvPGIP1) reduces Botrytis cinerea susceptibility in transgenic tobacco and differentially inhibits fungal polygalacturonases. Transgenic Research, 15, 687–702.
Kant, S., Vohra, A., & Gupta, R. (2013). Purification and physicochemical properties of polygalacturonase from Aspergillus niger MTCC 3323. Protein Expression and Purification, 7, 11–16.
Kumar, G. M., Mamidala, P., & Podile, A. R. (2009). Regulation of PG-inhibitory proteins in plants is highly dependent on stress and light responsive elements. Plant Omics, 2, 238–249.
Lemanczyk, G., & Kwasna, H. (2013). Effects of sharp eyespot (Rhizoctonia cerealis) on yield and grain quality of winter wheat. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 135, 187–200.
Markovic, O., & Janecek, S. (2001). Pectin degrading glycoside hydrolases of family 28: Sequence-structural features, specificities and evolution. Protein Engineering., 14, 615–631.
Martins, E. D. S., Leite, R. S., da Silva, R., & Gomes, E. (2013). Purification and properties of polygalacturonase produced by thermophilic fungus Thermoascus aurantiacus CBMAI-756 on solid-state fermentation. Enzyme Research, 2, 1–7.
Misawa, T., & Kuninaga, S. (2013). First report of white leaf rot on Chinese chives caused by Rhizoctonia solani AG-2-1. Journal of General Plant Pathology, 79, 280–283.
Niture, S. K. (2008). Comparative biochemical and structural characterizations of fungal polygalacturonases. Biologia, 63, 1–19.
Oeser, B., Heidrich, P. M., Muller, U., Tudzynski, P., & Tenberge, K. B. (2002). Polygalacturonase is a pathogenicity factor in the Claviceps purpurea/rye interaction. Fungal Genetics and Biology, 36, 176–186.
Pan, X., Li, K., Ma, R., Shi, P. G., Huang, H. Q., Yang, P. L., Meng, K., & Yao, B. (2015). Biochemical characterization of three distinct polygalacturonase from Neosartorya fischeri P1. Food Chemistry, 188, 569–575.
Rivera, M. C., Wright, E. R., Asciutto, K., & Gasoni, L. (2003). Occurrence of damping-off and wilt of Violax x witterockiana caused by Rhizoctonia solani in Argentina. Australasian Plant Pathology, 32, 561–562.
Rosa, D. D., Ohto, C. T., Basseto, M. A., Furtadoa, E. L., & Souzaa, N. L. D. (2008). First report of Rhizoctonia solani AG4 HG-II attacking Gazunia rigens plants in Brazil. Australasian Plant Disease Notes, 3, 1–2.
van Santen, Y., Benen, J. A. E., Schroter, K. H., Kalk, K. H., Armand, S., Visser, J., & Dijkstra, B. W. (1999). 1.68-Å crystal structure of endopolygalacturonase II from Aspergillus niger and identification of active site residues by site-directed mutagenesis. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 274, 30474–30480.
Sella, L., Castiglioni, C., Roberti, S., D’Ovidio, R., & Favaron, F. (2004). An endo-polygalacturonase (PG) of Fusarium moniliforme escaping inhibition by plant polygalacturonase-inhibiting proteins (PGIPs) provides new insight into the PG-PGIP interaction. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 240, 117–124.
Shieh, M. T., Brown, R. L., Whitehead, M. P., Cary, J. W., Cotty, P. J., Cleveland, T. E., & Dean, R. A. (1997). Molecular genetic evidence for the involvement of a specific PG, P2c, in the invasion and spread of Aspergillus flavus in cotton bolls. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 63, 3549–3552.
Taylor, R. J., & Secor, G. A. (1988). An improved diffusion assay for quantifying the polygalacturonase content of Erwinia culture filtrates. Phytopathology, 78, 1101–1103.
Xu, J. Y., Zhang, H. D., Zhang, H., Tong, Y. H., Xu, Y., Chen, X. J., & Ji, Z. L. (2004). Toxin produced by Rhizoctonia solani and its relationship with pathogenicity of the fungus (in Chinese). Journal of Yangzhou University (Agricultural and Life Science Edition), 25, 61–64.
Yang, J., Luo, H. Y., Li, J., Wang, K., Cheng, H. P., Bai, Y. G., Yuan, T. Z., Fan, Y. L., & Yao, B. (2011). Cloning, expression and characterization of an acidic endo-polygalacturonase from Bispora sp. MEY-1 and its potential application in juice clarification. Process Biochemistry, 46, 272–277.
Yang, Y. Q., Yang, M., Li, M. H., & Zhou, E. X. (2012). Cloning and functional analysis of an endo-PG-encoding gene Rrspg1 of Rhizoctonia solani, the causal agent of rice sheath blight. Canadian Journal of Plant Pathology, 34, 436–447.
Zhang, H., Chen, X. J., Tong, Y. H., Ji, Z. L., & Xu, J. Y. (2005). Damage of cell wall degrading enzymes produced by Rhizoctonia solani to rice tissue and cells (in Chinese). Journal of Yangzhou University (Agricultural and Life Science Edition), 26, 83–86.
Zuo, S. M., Yin, Y. J., Pan, C. H., Chen, Z. X., Zhang, Y. F., Gu, S. L., Zhu, L. H., & Pan, X. B. (2013). Fine mapping of qSB-11 LE, the QTL that confers partial resistance to rice sheath blight. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 126, 1257–1272.
Zuo, S. M., Chen, X. J., Chen, H. Q., Xu, Y., Zhang, J. H., Chen, Y., Chen, Z. X., Tong, Y. H., Xu, J. Y., & Pan, X. B. (2014). Defense response and physiological difference of rice cultivars with different sheath blight resistance levels to the toxin produced by Rhizoctonia solani (in Chinese). Chinese Journal of Rice Sciences, 28, 551–558.
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by the Science and Technology Project of Jiangsu Province (BE2015342), the National Transgenic Key Project (2014ZX0800103B), the key project of Jiangsu Natural Science Foundation for Colleges (14KJA210003), the Open Project of the Key Laboratory of Plant Functional Genomics, Jiangsu Province (K13004), the key plan of Yangzhou agriculture (YZ2015028) and a project funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 64 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Lili, L., Zhang, Y. et al. Functional analysis of polygalacturonase gene RsPG2 from Rhizoctonia solani, the pathogen of rice sheath blight. Eur J Plant Pathol 149, 491–502 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-017-1198-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-017-1198-5