Abstract
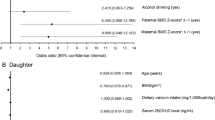
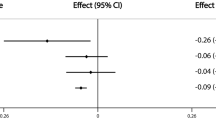
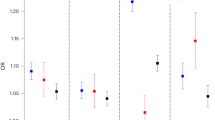
Osteoporosis is a major public health concern and its prevalence can be predicted based on forearm bone mineral density (BMD). This study is to investigate the familial aggregation of forearm BMD in a population-based, cross-sectional study in Anhui, China. Information on sociodemographic and environmental variables was obtained from 1,636 subjects from 409 nuclear families (including mother, father, and their first two children) by a standardized questionnaire. The forearm BMD was measured by peripheral dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (pDXA). Using generalized additive models with a sequential adjustment for covariates, it was clearly indicated that the forearm BMD of the mother, the father, and the first sibling each had a significant and independent relation to the forearm BMD of the second sibling. Furthermore, using multiple logistic regression, the second sibling had an odds ratio (OR) of 5.3 (95%CI: 2.0–14.5) of having an extremely low (bottom 10th percentile) proximal forearm BMD and an OR of 4.3 (95%CI: 1.6–12.0) of having an extremely low distal forearm BMD when the parental mean forearm BMD was low and the first sibling’s forearm BMD was low. Our findings showing strong familial aggregation of both proximal and distal forearm BMD values suggest that genetic factors play a significant role in determining both traits.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BMD:
-
Bone mineral density
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
- PDXA:
-
Peripheral dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry
References
Kanis JA, Melton LJ 3rd, Christiansen C, Johnston CC, Khaltaev N. The diagnosis of osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res 1994;9:1137–41.
Melton LJ 3rd, Atkinson EJ, O’Connor MK, O’Fallon WM,Riggs BL. Bone density and fracture risk in men. J Bone Miner Res 1998;13:1915–23.
Hui SL, Slemenda CW,Johnston CC Jr. Baseline measurement of bone mass predicts fracture in white women. Ann Intern Med 1989;111:355–61.
Ross PD, Davis JW, Epstein RS,Wasnich RD. Pre-existing fractures and bone mass predict vertebral fracture incidence in women. Ann Intern Med 1991;114:919–23.
Cummings SR, Black DM, Nevitt MC, Browner W, Cauley J, Ensrud K, et al. Bone density at various sites for prediction of hip fractures. The study of osteoporotic fractures research group. Lancet 1993;341:72–5.
Gilfillan CP, Silberberg S, Scrivenor P, Griffiths RC, McCloud PI, Burger HG. Determinants of forearm mineral density and its correlation with fracture history in women. Maturitas 1994;20:199–208.
Gardsell P, Johnell O,Nilsson BE. Predicting fractures in women by using forearm bone densitometry. Calcif Tissue Int 1989;44:235–42.
Cummings SR, Nevitt MC, Browner WS, Stone K, Fox KM, Ensrud KE, et al. Risk factors for hip fracture in white women. Study of osteoporotic fractures research group. N Engl J Med 1995;332:767–73.
Smith DM, Nance WE, Kang KW, Christian JC,Johnston CC Jr. Genetic factors in determining bone mass. J Clin Invest 1973;52:2800–8.
Seeman E, Hopper JL, Young NR, Formica C, Goss P,Tsalamandris C. Do genetic factors explain associations between muscle strength, lean mass, and bone density? A twin study. Am J Physiol 1996;270:E320–7.
Liu PY, Qin YJ, Zhou Q, Recker RR,Deng HW. Complex segregation analyses of bone mineral density in Chinese. Ann Hum Genet 2004;68:154–64.
Feng Y, Hsu YH, Terwedow H, Chen C, Xu X, Niu T, et al. Familial aggregation of bone mineral density and bone mineral content in a Chinese population. Osteoporos Int 2005;16:1917–23.
Leboff MS, Fuleihan GE, Angell JE, Chung S,Curtis K. Dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry of the forearm: reproducibility and correlation with single-photon absorptiometry. J Bone Miner Res 1992;7:841–46.
Xu X, Niu T, Chen C, Kuo AY,Rosen CJ. Forearm bone mineral density in Chinease women: a community-based study. J Clinical densitom 1998;1:149–56.
Livshits G, Deng HW, Nguyen TV, Yakovenko K, Recker RR,Eisman JA. Genetics of bone mineral density: evidence for a major pleiotropic effect from an intercontinental study. J Bone Miner Res 2004;19:914–23.
Danielson ME, Cauley JA, Baker CE, Newman AB, Dorman JS, Towers JD, et al. Familial resemblance of bone mineral density (BMD) and calcaneal ultrasound attenuation: the BMD in mothers and daughters study. J Bone Miner Res 1999;14:102–10.
Soroko SB, Barrett-Connor E, Edelstein SL,Kritz-Silverstein D. Family history of osteoporosis and bone mineral density at the axial skeleton: the Rancho Bernardo Study. J Bone Miner Res 1994;9:761–9.
Dequeker J, Nijs J, Verstraeten A, Geusens P,Gevers G. Genetic determinants of bone mineral content at the spine and radius: a twin study. Bone 1987;8:207–9.
Jouanny P, Guillemin F, Kuntz C, Jeandel C,Pourel J. Environmental and genetic factors affecting bone mass. Similarity of bone density among members of healthy families. Arthritis Rheum 1995;38:61–7.
Slemenda CW, Christian JC, Williams CJ, Norton JA,Johnston CC Jr. Genetic determinants of bone mass in adult women: a reevaluation of the twin model and the potential importance of gene interaction on heritability estimates. J Bone Miner Res 1991;6:561–7.
Acknowledgments
We wish to acknowledge the assistance and cooperation of the faculty and staff of the Harvard School of Public health, the Anqing Medical University, Anqing Public Health Bureau and Anqing Hospital. Drs. Changzhong Chen and Binyan Wang were supported in part by Fogarty International Center Training Grant TW00828.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, X., Niu, T., Chen, C. et al. Familial aggregation of forearm bone mineral density in Chinese. Eur J Epidemiol 22, 335–341 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-007-9117-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-007-9117-2