Abstract
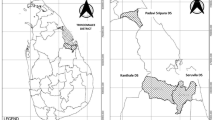
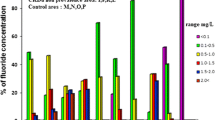
The Mahaweli is the largest river basin in Sri Lanka that provides water to the dry zone region through multipurpose irrigation schemes . Selenium, arsenic, cadmium, and other bioimportant trace elements in surface waters of the upper Mahaweli River were measured using ICP-MS. Trace element levels were then compared with water from two other rivers (Maha Oya, Kalu Ganga) and from six dry zone irrigation reservoirs. Results showed that the trace metal concentrations in the Mahaweli upper catchment were detected in the order of Fe > Cu > Zn > Se > Cr > Mn > As > Ni > Co > Mo. Remarkably high levels of Ca, Cr, Co, Ni, Cu, As, and Se were observed in the Mahaweli Basin compared to other study rivers. Considerably high levels of Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, As, and Se were found in upstream tributaries of the Mahaweli River. Such metals possibly originated from phosphate and organic fertilizers that are heavily applied for tea and vegetable cultivations within the drainage basin. Cadmium that is often attributed to the etiology of unknown chronic kidney diseases in certain parts of the dry zone is much lower than previously reported levels. Decrease in these metals in the lower part of the Mahaweli River could be due to adsorption of trace metals onto sediment and consequent deposition in reservoirs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aktar, M. W., Paramasivam, M., Ganguly, M., Purkait, S., & Sengupta, D. (2010). Assessment and occurrence of various heavy metals in surface water of Ganga river around Kolkata: A study for toxicity and ecological impact. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 160(1–4), 207–213.
Altschuler, Z. S. (1980). The geochemistry of trace elements in marine phosphorites: Part I. Characteristic abundances and enrichment. In: SEPM special publication No 29. The Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists (SEPM) (pp. 19–30).
Amarathunga, A. A. D., Weerasekara, K. A. W. S., Azmy, S. A. M., Sureshkumar, N., Wickramaarchchi, W. D. N., & Kazama, F. (2013). Behavior and loading of suspended sediment and nutrients from river basins in the hilly catena under intensive agriculture cropping: A case study in upper Kotmale Basin in Sri Lanka. Journal of Environmental Professionals Sri Lanka, 2(2), 13–31.
Athuraliya, T., Abeysekara, T., Kumarasiri, R., Abeysekara, C., Gooneratne, A., & Bandara, P. (2003). A baseline study on early renal diseases in a selected community of the North-Central Province of Sri Lanka. Research report, Faculty of Medicine, University of Peradeniya, Sri Lanka.
Athuraliya, N. T. C., Abeysekera, T., Amerasinghe, P. H., Kumarasiri, R., Bandara, P., Karunaratne, U., et al. (2011). Uncertain etiologies of proteinuric-chronic kidney disease in rural Sri Lanka. Kidney International, 80(11), 1212–1221.
Athuraliya, T., Abeysekera, D., Amerasinghe, P., Kumarasiri, P., & Dissanayake, V. (2009). Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in two tertiary care hospitals: High proportion of cases with uncertain aetiology. Ceylon Medical Journal, 54(1), 23–25.
Bandara, J. M. R. S., Senevirathna, D. M. A. N., Dasanayake, D. M. R. S. B., Herath, V., Bandara, J. M. R. P., Abeysekara, T., & Rajapaksha, K. H. (2008). Chronic renal failure among farm families in cascade irrigation systems in Sri Lanka associated with elevated dietary cadmium levels in rice and freshwater fish (Tilapia). Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 30(5), 465–478.
Bandara, J., Wijewardena, H., Bandara, Y., Jayasooriya, R., & Rajapaksha, H. (2011). Pollution of River Mahaweli and farmlands under irrigation by cadmium from agricultural inputs leading to a chronic renal failure epidemic among farmers in NCP, Sri Lanka. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 33(5), 439–453.
Bandara, J. M. R. S., Wijewardena, H. V. P., Liyanege, J., Upul, M. A., & Bandara, J. M. U. A. (2010). Chronic renal failure in Sri Lanka caused by elevated dietary cadmium: Trojan horse of the green revolution. Toxicology Letters, 198(1), 33–39.
Benke, M. B., Indraratne, S. P., Hao, X., Chang, C., & Goh, T. B. (2008). Trace element changes in soil after long-term cattle manure applications. Journal of Environmental Quality, 37(3), 798–807.
Benson, N. U., Anake, W. U., & Etesin, U. M. (2014). Trace metals levels in inorganic fertilizers commercially available in Nigeria. Journal of Scientific Research and Reports, 3(4), 610–6120.
Bolan, N., Adriano, D., & Mahimairaja, S. (2004). Distribution and bioavailability of trace elements in livestock and poultry manure by-products. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 34(3), 291–338.
Bolan, N. S., Szogi, A., Chuasavathi, T., Seshadri, B., Rothrock, M., & Panneerselvam, P. (2010). Uses and management of poultry litter. World’s Poultry Science Journal, 66(04), 673–698.
Bowen, H. J. M. (1979). Environmental chemistry of the elements. London: Academic Press.
Bowman, C. A., Bobrowsky, P. T., & Selinus, O. (2003). Medical geology: New relevance in the earth sciences. Episodes, 26(4), 270–278.
Breuste, J., & Dissanayake, L. (Eds.). (2013). Socioeconomic and environmental change of Sri Lanka’s Central Highlands. Forschen im Gebirge Christoph Stadel zum 75. Geburtstag. Verlag der Österreichischen Akademie der Wissenschaften.
Chandrajith, R., Nanayakkara, S., Itai, K., Aturaliya, T. N. C., Dissanayake, C. B., Abeysekera, T., et al. (2011). Chronic kidney diseases of uncertain etiology (CKDue) in Sri Lanka: Geographic distribution and environmental implications. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 33(3), 267–278.
Chandrajith, R., Seneviratna, S., Wickramaarachchi, K., Attanayake, T., Aturaliya, T. N. C., & Dissanayake, C. B. (2010). Natural radionuclides and trace elements in rice field soils in relation to fertilizer application: Study of a chronic kidney disease area in Sri Lanka. Environmental Earth Sciences, 60(1), 193–201.
Dissanayake, C. B., & Chandrajith, R. (2007). Medical geology in tropical countries with special reference to Sri Lanka. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 29(2), 155–162.
Dissanayake, C. B., & Chandrajith, R. (2009a). Introduction to medical geology: Focus on tropical environments. Heidelberg: Springer.
Dissanayake, C. B., & Chandrajith, R. (2009b). Phosphate mineral fertilizers, trace metals and human health. Journal of the National Science Foundation of Sri Lanka, 37(3), 153–165.
Dissanayake, C. B., & Weerasooriya, S. V. R. (1986). The environmental chemistry of Mahaweli river, Sri Lanka. International journal of environmental studies, 28(2–3), 207–223.
Dissanayake, C., Niwas, J., & Weerasooriya, S. (1987). Heavy metal pollution of the mid-canal of Kandy: An environmental case study from Sri Lanka. Environmental Research, 42(1), 24–35.
Fraga, C. G. (2005). Relevance, essentiality and toxicity of trace elements in human health. Molecular Aspects of Medicine, 26(4), 235–244.
Hewawasam, T. (2010). Effect of land use in the upper Mahaweli catchment area on erosion, landslides and siltation in hydropower reservoirs of Sri Lanka. Journal of the National Science Foundation of Sri Lanka, 38(1), 3–14.
Hewawasam, T., von Blanckenburg, F., Schaller, M., & Kubik, P. (2003). Increase of human over natural erosion rates in tropical highlands constrained by cosmogenic nuclides. Geology, 31(7), 597–600.
Isam, B., Ghada, H., & Nasri, K. (2003). Trace metal content of commercial fertilizers marketed in Lebanon. In: W. L. Hall, W. P. Robarge (Eds.), Environmental impact of fertilizer on soil and water. ACS symposium series (Vol. 872, pp. 90–99). American Chemical Society. doi:10.1021/bk-2004-0872.ch007.
Jayasumana, C., Gajanayake, R., & Siribaddana, S. (2014). Importance of Arsenic and pesticides in epidemic chronic kidney disease in Sri Lanka. BMC Nephrology, 15(1), 124.
Jayatilake, N., Mendis, S., Maheepala, P., & Mehta, F. R. (2013). Chronic kidney disease of uncertain aetiology: Prevalence and causative factors in a developing country. BMC Nephrology, 14(1), 1–13.
Kar, D., Sur, P., Mandai, S. K., Saha, T., & Kole, R. K. (2008). Assessment of heavy metal pollution in surface water. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 5(1), 119–124.
Khan, K., Lu, Y., Khan, H., Zakir, S., Khan, S., Khan, A. A., et al. (2013). Health risks associated with heavy metals in the drinking water of Swat, northern Pakistan. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 25(10), 2003–2013.
Lokeshwari, H., & Chandrappa, G. T. (2006). Impact of heavy metal contamination of Bellandur Lake on soil and cultivated vegetation. Current Science, 91(5), 622–627.
McBride, M. B., & Spiers, G. (2001). Trace element content of selected fertilizers and dairy manures as determined by ICP–MS. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 32(1–2), 139–156.
Nriagu, J. O. (1988). A silent epidemic of environmental metal poisoning? Environmental Pollution, 50(1), 139–161.
Nriagu, J. O. (1990). Global metal pollution: Poisoning the biosphere? Environment: Science and Policy for Sustainable Development, 32(7), 7–33.
Perera, B. M. A. O., & Jayasuriya, M. C. N. (2008). The dairy industry in Sri Lanka: Current status and future directions for a greater role in national development. Journal of National Science Foundation Sri Lanka, 36, 115–126.
Premarathna, H., Hettiarachchi, G., & Indraratne, S. (2011). Trace metal concentration in crops and soils collected from intensively cultivated areas of Sri Lanka. Sri Lanka: Pedologist, 230–240.
Reza, R., & Singh, G. (2010). Heavy metal contamination and its indexing approach for river water. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 7(4), 785–792.
Shortle, J. S., Abler, D. G., & Ribaudo, M. (2001). Agriculture and water quality: The issues. Environmental Policies for Agricultural Pollution Control, 1–18.
Skaggs, R., Breve, M., & Gilliam, J. (1994). Hydrologic and water quality impacts of agricultural drainage. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 24(1), 1–32.
Stocking, M. (1993). Soil erosion in the Upper Mahaweli Catchment, Sri Lanka. Oxon: HR Wallingford Ltd.
Van Kauwenbergh, S. J. (1997). Cadmium and other minor elements in world resources of phosphate rock. In Proceedings-Fertiliser Society (United Kingdom). The Fertilizer Society, York, UK.
Vinceti, M., Crespi, C. M., Bonvicini, F., Malagoli, C., Ferrante, M., Marmiroli, S., & Stranges, S. (2013). The need for a reassessment of the safe upper limit of selenium in drinking water. Science of the Total Environment, 443, 633–642.
Weeraratna, C. (2009). Fertilizer use in Sri Lanka with special reference to Chronic Kidney Disease of unidentified etiology (CKDu). Paper presented at the Symposium on “Chronic Kidney Disease of uncertain origin (CKDu): A scientific basis for future action”, Galadari Hotel, Colombo, 10 December 2013.
WHO. (1996). Water quality assessments: A guide to the use of biota, sediments and water in environmental monitoring. London: World Health Organization-E&FN Spon.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Research Council (NRC), Sri Lanka research Grant (NRC 12-102) offered to RC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Diyabalanage, S., Abekoon, S., Watanabe, I. et al. Has irrigated water from Mahaweli River contributed to the kidney disease of uncertain etiology in the dry zone of Sri Lanka?. Environ Geochem Health 38, 679–690 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-015-9749-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-015-9749-1