Abstract
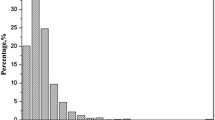
Based on 1625 data collected from the published literature, the geochemistry of tin (Sn) in Chinese coals, including the abundance, distribution, modes of occurrence, genetic types and combustion behavior, was discussed to make a better understanding. Our statistic showed the average Sn of Chinese coal was 3.38 mg/kg, almost two times higher than the world. Among all the samples collected, Guangxi coals occupied an extremely high Sn enrichment (10.46 mg/kg), making sharp contrast to Xinjiang coals (0.49 mg/kg). Two modes of occurrence of Sn in Chinese coals were found, including sulfide-bounded Sn and clay-bounded Sn. In some coalfields, such as Liupanshui, Huayingshan and Haerwusu, a response between REEs distribution and Sn content was found which may caused by the transportation of Sn including clay minerals between coal seams. According to the responses reflecting on REEs patterns of each coalfield, several genetic types of Sn in coalfields were discussed. The enrichment of Sn in Guangxi coals probably caused by Sn-rich source rocks and multiple-stage hydrothermal fluids. The enriched Sn in western Guizhou coals was probably caused by volcanic ashes and sulfide-fixing mechanism. The depletion of Sn in Shengli coalfield, Inner Mongolia, may attribute to hardly terrigenous input and fluids erosion. As a relative easily volatilized element, the Sn-containing combustion by-products tended to be absorbed on the fine particles of fly ash. In 2012, the emission flux of Sn by Chinese coal combustion was estimated to be 0.90 × 109 g.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amouroux, D., Tessier, E., & Donard, O. F. (2000). Volatilization of organotin compounds from estuarine and coastal environments. Environmental Science and Technology, 34(6), 988–995.
Bai, X., & Li, W. (2001). Coal characteristics and governed factors for coal properties of Datong Jurassic 10–11 # coal. Coal Conversion, 4, 004. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Becker, J. S. (2005). Trace and ultratrace analysis in liquids by atomic spectrometry. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 24(3), 243–254.
Berman, E. (1980). Toxic metals and their analysis. London: John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Besser, R., Krämer, G., Thümler, R., Bohl, J., Gutmann, L., & Hopf, H. (1987). Acute trimethyltin limbic-cerebellar syndrome. Neurology, 37(6), 945.
Bouška, V., & Pešek, J. (1999). Quality parameters of lignite of the North Bohemian Basin in the Czech Republic in comparison with the world average lignite. International Journal Of Coal Geology, 40(2), 211–235.
Breen, C., Molloy, K., & Quill, K. (1992). Moessbauer spectroscopic and thermogravimetric studies of tin–clay complexes. Clay Minerals, 27, 445.
Byrd, J. T., & Andreae, M. O. (1982). Tin and methyltin species in seawater: Concentrations and fluxes. Science, 218(4572), 565–569.
Byrd, J. T., & Andreae, M. O. (1986a). Concentrations and fluxes of tin in aerosols and rain. Atmospheric Environment (1967), 20(5), 931–939.
Byrd, J. T., & Andreae, M. O. (1986b). Geochemistry of tin in rivers and estuaries. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 50(5), 835–845.
Castillo, S., de la Rosa, J. D., de la Campa, A. M. S., González-Castanedo, Y., & Fernández-Camacho, R. (2013). Heavy metal deposition fluxes affecting an Atlantic coastal area in the southwest of Spain. Atmospheric Environment, 77, 509–517.
Champ, M. A. (2000). A review of organotin regulatory strategies, pending actions, related costs and benefits. Science of the Total Environment, 258(1), 21–71.
China Statistical Yearbook. (1984). National Bureau of Statistics PRC: China Statistics Press. (in Chinese).
China Statistical Yearbook. (1995). National Bureau of Statistics PRC: China Statistics Press. (Chinese-English Edition).
China Statistical Yearbook. (2012). National Bureau of Statistics PRC: China Statistics Press. (Chinese-English Edition).
China Statistical Yearbook. (2013). National Bureau of Statistics PRC: China Statistics Press. (Chinese-English Edition).
Clarke, L. B. (1993). The fate of trace elements during coal combustion and gasification: An overview. Fuel, 72(6), 731–736.
Craig, P. J., & Rapsomanikis, S. (1985). Methylation of tin and lead in the environment: Oxidative methyl transfer as a model for environmental reactions. Environmental Science and Technology, 19(8), 726–730.
Dai, S., Chou, C.-L., Yue, M., Luo, K., & Ren, D. (2005a). Mineralogy and geochemistry of a Late Permian coal in the Dafang Coalfield, Guizhou, China: Influence from siliceous and iron-rich calcic hydrothermal fluids. International Journal of Coal Geology, 61(3), 241–258.
Dai, S., Li, D., Chou, C.-L., Zhao, L., Zhang, Y., Ren, D., et al. (2008). Mineralogy and geochemistry of boehmite-rich coals: New insights from the Haerwusu Surface Mine, Jungar Coalfield, Inner Mongolia, China. International Journal of Coal Geology, 74(3), 185–202.
Dai, S., Li, D., Ren, D., Tang, Y., Shao, L., & Song, H. (2004). Geochemistry of the late Permian No. 30 coal seam, Zhijin Coalfield of Southwest China: Influence of a siliceous low-temperature hydrothermal fluid. Applied Geochemistry, 19(8), 1315–1330.
Dai, S., Ren, D., Chou, C.-L., Finkelman, R. B., Seredin, V. V., & Zhou, Y. (2012). Geochemistry of trace elements in Chinese coals: A review of abundances, genetic types, impacts on human health, and industrial utilization. International Journal of Coal Geology, 94, 3–21.
Dai, S., Ren, D., Chou, C.-L., Li, S., & Jiang, Y. (2006a). Mineralogy and geochemistry of the No. 6 coal (Pennsylvanian) in the Junger Coalfield, Ordos Basin, China. International Journal of Coal Geology, 66(4), 253–270.
Dai, S., Ren, D., Li, D., Chou, C., & Luo, K. (2006b). Mineralogical anomalies and their influences on elemental geochemistry of the main workable coal beds from the Dafang Coalfield, Guizhou, China. Acta Geologica Sinica-English Edition, 80(4), 589.
Dai, S., Ren, D., Tang, Y., Yue, M., & Hao, L. (2005b). Concentration and distribution of elements in Late Permian coals from western Guizhou Province, China. International Journal of Coal Geology, 61(1), 119–137.
Dai, S., Zeng, R., & Sun, Y. (2006c). Enrichment of arsenic, antimony, mercury, and thallium in a Late Permian anthracite from Xingren, Guizhou, Southwest China. International Journal of Coal Geology, 66(3), 217–226.
Dai, S., Zhang, W., Seredin, V. V., Ward, C. R., Hower, J. C., Song, W., et al. (2013a). Factors controlling geochemical and mineralogical compositions of coals preserved within marine carbonate successions: A case study from the Heshan Coalfield, southern China. International Journal of Coal Geology, 109, 77–100.
Dai, S., Zhang, W., Ward, C. R., Seredin, V. V., Hower, J. C., Li, X., et al. (2013b). Mineralogical and geochemical anomalies of late Permian coals from the Fusui Coalfield, Guangxi Province, southern China: Influences of terrigenous materials and hydrothermal fluids. International Journal of Coal Geology, 105, 60–84.
Dai, S., Zhou, Y., Ren, D., Wang, X., Li, D., & Zhao, L. (2007). Geochemistry and mineralogy of the Late Permian coals from the Songzo Coalfield, Chongqing, southwestern China. Science in China, Series D: Earth Sciences, 50(5), 678–688.
Davies, P. (2005). BP statistical review of world energy. BP technical report.
Dale, L., & Lavrencic, S. (1993). Trace elements in Australian export thermal coals. Australian Coal Journal, 39, 17–21.
Ding, R. (2009). Distribution and environmental influence of accompanying elements in coal of Dingji mine. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Durasova, N. (1967). Some problems of the geochemistry of tin. Geochemistry International, 4, 671–681.
Ebdon, L., & Wilkinson, J. R. (1987). Direct atomic spectrometric analysis by slurry atomisation. Part 3. Whole coal analysis by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2(3), 325–328.
Fang, T., Liu, G., Zhou, C., Sun, R., Chen, J., & Wu, D. (2013). Lead in Chinese coals: Distribution, modes of occurrence, and environmental effects. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 36(3), 1–19.
Feldman, R. G., White, R. F., & Eriator, I. I. (1993). Trimethyltin encephalopathy. Archives of Neurology, 50(12), 1320–1324.
Finkelman, R. B. (1980). Modes of occurrence of trace elements in coal. Reston: US Geological Survey.
Finkelman, R. (1993). Trace and minor elements in coal. In M. Engel & S. Macko (Eds.), Organic geochemistry: Topics in geobiology (Vol. 11, pp. 593–607). US: Springer.
Finkelman, R. B. (1999). Trace elements in coal. Biological Trace Element Research, 67(3), 197–204.
Finley, M. (2013). BP statistical review of world energy. BP technical report.
Fortemps, E., Amand, G., Bomboir, A., Lauwerys, R., & Laterre, E.-C. (1978). Trimethyltin poisoning report of two cases. International Archives of Occupational and Environmental Health, 41(1), 1–6.
Frandsen, F., Dam-Johansen, K., & Rasmussen, P. (1994). Trace elements from combustion and gasification of coal—An equilibrium approach. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 20(2), 115–138.
Gäbler, H.-E., & Suckow, A. (2003). Chronology of anthropogenic heavy-metal fluxes and Pb isotope ratios derived from radiometrically dated lake sediments in Northern Germany. Water, Air, and Soil pollution, 144(1–4), 243–262.
Gao, X., He, B., Ma, Y., & Yang, M. (2009). Preliminary investigation on correlation between depositional environment and content of trace elements in coal seam of Fuxin formation. Coal Technology, 28(9), 191–192. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Gao, X., & Yang, Z.-R. (2008). Research on trace elements of fuxin formation coal seam in Haizhou Open-Pit, Fuxin, Liaoning Province. Coal Technology, 9, 066. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Gibbs, P., & Bryan, G. (1996). Reproductive failure in the gastropod Nucella lapillus associated with imposex caused by tributyltin pollution: A review. In M. Champ & P. Seligman (Eds.), Organotin (pp. 259–280). Springer.
Gilmour, C. C., Tuttle, J. H., & Means, J. C. (1987). Anaerobic microbial methylation of inorganic tin in estuarine sediment slurries. Microbial Ecology, 14(3), 233–242.
Hoch, M. (2001). Organotin compounds in the environment—An overview. Applied Geochemistry, 16(7), 719–743.
Hong, S., Lee, K., Hou, S., Hur, S. D., Ren, J., Burn, L. J., et al. (2009). An 800-year record of atmospheric As, Mo, Sn, and Sb in Central Asia in high-altitude ice cores from Mt. Qomolangma (Everest), Himalayas. Environmental Science and Technology, 43(21), 8060–8065. doi:10.1021/es901685u.
Horn, M., & Adams, J. (1966). Computer-derived geochemical balances and element abundances. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 30(3), 279–297.
Hu, J. (2007). Research on geochemistry of 22 environmental sensitive trace elements in Chinese coals. Hefei: Institute of Geochemistry Chinese Academy of Science. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Huang, J.-H., & Matzner, E. (2004). Biogeochemistry of organotin compounds and tin in a forested catchment in Germany. Science of the Total Environment, 332(1), 231–241.
Jiang, Y., Shifeng, D., Xibo, W., Zhao, L., Zhou, G., Lili, Z., et al. (2011). Geochemical characteristic study on high and low sulfur coal seam sections in Jining. Shandong. Coal Geology of China, 4, 002. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Jiang, G., Zhou, Q., & Bin, H. (2000). Speciation of organotin compounds, total tin, and major trace metal elements in poisoned human organs by gas chromatography-flame photometric detector and inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. Environmental Science and Technology, 34(13), 2697–2702.
Kang, Y., Liu, G., Chou, C.-L., Wong, M. H., Zheng, L., & Ding, R. (2011). Arsenic in Chinese coals: Distribution, modes of occurrence, and environmental effects. Science of the Total Environment, 412, 1–13.
Ketris, M., & Yudovich, Y. E. (2009). Estimations of Clarkes for Carbonaceous biolithes: World averages for trace element contents in black shales and coals. International Journal of Coal Geology, 78(2), 135–148.
Kim, J., Yang, M., Son, Y., Jang, H., Kim, D., Kim, J.-C., et al. (2014). Glial activation with concurrent up-regulation of inflammatory mediators in trimethyltin-induced neurotoxicity in mice. Acta Histochemica,. doi:10.1016/j.acthis.2014.09.003.
Kong, H., Zeng, R., Zhuang, X., & Xu, W. (2001). Study of trace elements of coal in Beipiao district, Liaoning Province. Geoscience, 15, 6.
Kuwae, M., Tsugeki, N. K., Agusa, T., Toyoda, K., Tani, Y., Ueda, S., et al. (2013). Sedimentary records of metal deposition in Japanese alpine lakes for the last 250 years: Recent enrichment of airborne Sb and In in East Asia. Science of the Total Environment, 442, 189–197.
Lachas, H., Richaud, R., Herod, A., Dugwell, D., Kandiyoti, R., & Jarvis, K. (1999). Determination of 17 trace elements in coal and ash reference materials by ICP-MS applied to milligram sample sizes. Analyst, 124(2), 177–184.
Lei, C., Landsberger, S., Basunia, S., & Tao, Y. (2004). Study of PM2.5 in Beijing suburban site by neutron activation analysis and source apportionment. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 261(1), 87–94. doi:10.1023/B:JRNC.0000030939.64724.9d.
Li, D., & Tang, Y. (2005). Geological genesis of coal geochemical anomalies of the Late Permian coals from the Qinglong coalfield in western Guizhou, China. Geology Review, 51(2), 163–168. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li, J., Zhuang, X., & Querol, X. (2011). Trace element affinities in two high-Ge coals from China. Fuel, 90(1), 240–247.
Liu, L. (2009). Preliminary study of geochemical behavior of the main minable coal of the Late Permian in Qianxi County. Guizhou: Guizhou University. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Mackenzie, F. T., Lantzy, R. J., & Paterson, V. (1979). Global trace metal cycles and predictions. Journal of the International Association for Mathematical Geology, 11(2), 99–142.
Meng, H., Ma, S., Zhang, S., & Fu, S. (2012). Study on distribution characteristics of trace elements in close range coal seams in Daizhuang coal mine. Journal of Henan Polytechnic University (Natural Science), 31(1), 44–47. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Meo, S. A., & Al-Khlaiwi, T. (2003). Health hazards of welding fumes. Saudi Medical Journal, 24(11), 1176–1182.
Pang, Q., Zhuang, X., Li, J., Fu, L., & Gangtemuer, X. (2012). Petrographical, chemical and geochemical characteristics of Jurassic Coal in Western Chaoshui Basin, Inner Mongolia. Geological Science and Technology Information, 1, 007. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Petridis, D., & Bakas, T. (1997). Tin–clay complexes: A mossbauer study. Clays and Clay Minerals, 45(1), 73–76.
Qi, H., Hu, R., & Zhang, Q. (2007). Concentration and distribution of trace elements in lignite from the Shengli Coalfield, Inner Mongolia, China: Implications on origin of the associated Wulantuga Germanium Deposit. International Journal of Coal Geology, 71(2), 129–152.
Querol, X., Alastuey, A., Lopez-Soler, A., Plana, F., Fernandez-Turiel, J., Zeng, R., et al. (1997). Geological controls on the mineral matter and trace elements of coals from the Fuxin basin, Liaoning Province, northeast China. International Journal of Coal Geology, 34(1), 89–109.
Querol, X., Alastuey, A., Zhuang, X., Hower, J., Lopez-Soler, A., Plana, F., et al. (2001). Petrology, mineralogy and geochemistry of the Permian and Triassic coals in the Leping area, Jiangxi Province, southeast China. International Journal of Coal Geology, 48(1), 23–45.
Querol, X., Fernández-Turiel, J., & Lopez-Soler, A. (1995). Trace elements in coal and their behaviour during combustion in a large power station. Fuel, 74(3), 331–343.
Rapsomanikis, S., & Weber, J. H. (1985). Environmental implications of methylation of tin(II) and methyltin(IV) ions in the presence of manganese dioxide. Environmental Science and Technology, 19(4), 352–356.
Ren, D., Zhang, J., Xu, D., Zhao, F., Li, L., & Xie, G. (1999). Distribution of associated elements in coals from Shenbei Coalfield. Journal of China University of Mining and Technology, 28(1), 01 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Richaud, R., Lachas, H., Healey, A., Reed, G., Haines, J., Jarvis, K., et al. (2000). Trace element analysis of gasification plant samples by icp–ms: Validation by comparison of results from two laboratories. Fuel, 79(9), 1077–1087.
Rollinson, H. R. (2014). Using geochemical data: Evaluation, presentation, interpretation. London: Routledge.
Rüdel, H. (2003). Case study: Bioavailability of tin and tin compounds. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 56(1), 180–189.
Sansoni, B., Brunner, W., Wolff, G., Ruppert, H., & Dittrich, R. (1988). Comparative instrumental multi-element analysis I: Comparison of ICP source mass spectrometry with ICP atomic emission spectrometry, ICP atomic fluorescence spectrometry and atomic absorption spectrometry for the analysis of natural waters from a granite region. Fresenius’ Zeitschrift für analytische Chemie, 331(2), 154–169.
Schleicher, N., Cen, K., & Norra, S. (2013). Daily variations of black carbon and element concentrations of atmospheric particles in the Beijing megacity—Part 1: General temporal course and source identification. Chemie Der Erde-Geochemistry, 73(1), 51–60. doi:10.1016/j.chemer.2012.11.006.
Smith, R. D., Campbell, J. A., & Nielson, K. K. (1979). Concentration dependence upon particle size of volatilized elements in fly ash. Environmental Science and Technology, 13(5), 553–558.
Sun, R., Liu, G., Zheng, L., & Chou, C.-L. (2010). Geochemistry of trace elements in coals from the Zhuji Mine, Huainan Coalfield, Anhui, China. International Journal of Coal Geology, 81(2), 81–96.
Sun, D., Miao, X., Chen, J., Tang, X., Ping, Y., & Peng, B. (2007). Clinical analysis on 52 cases of acute trimethyl tin poisoning. Chinese Journal of Industrial Medicine, 20(5), 289–292. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Swaine, D. J. (2000). Why trace elements are important. Fuel Processing Technology, 65, 21–33.
Swaine, D. J., & Goodarzi, F. (1995). Environmental aspects of trace elements in coal (Vol. 2). Berlin: Springer.
Tang, X., & Huang, W. (2004). Trace elements in Chinese coals. Beijing: The Commercial Press. (in Chinese).
Tang, Y., Yin, Z., Chang, C., Zhang, Y., Song, H., Wang, S., et al. (2005). Distribution of trace elements in the Kailuan coalfield. Journal of Chinese Coal Society, 30, 80–84. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Taylor, S. R., & McLennan, S. M. (1985). The continental crust: Its composition and evolution. Palo Alto, CA, United States: Blackwell Scientific Publications.
Wang, Q., Chen, X., He, G. L., Lin, S. B., Liu, Z., & Xu, D. Q. (2013). Study on Characteristics of Elements in PM2.5 during Haze-Fog Weather in Winter in Urban Beijing. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 33(6), 1441–1445. doi:10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2013)06-1441-05. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang, X., Dai, S., Ren, D., & Yang, J. (2011). Mineralogy and geochemistry of al-hydroxide/oxyhydroxide mineral-bearing coals of Late Paleozoic age from the Weibei coalfield, southeastern Ordos Basin, North China. Applied Geochemistry, 26(7), 1086–1096.
Wang, X., Li, D., Lu, Y.-F., & Zhang, Y. (2007). Geochemistry of late triassic coals from the Changhebian mine in Chongqing. China. Coal Geology and Exploration, 3, 001. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang, D., & Zhang, Y. (2012). Jurassic Tariq formation coal geochemical characteristics in Kuqa-Bay coalfield, Xinjiang. Coal Geology of China, 45, 10524–10530. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Xiao, D. (1989). Study of arsenic and its modes of occurrence in coals (pp. 36–48). Xi’an Branch of CCRI Anthology, (in Chinese).
Yan, R., Gauthier, D., & Flamant, G. (2001). Volatility and chemistry of trace elements in a coal combustor. Fuel, 80(15), 2217–2226.
Yang, J. (2006). Contents and occurrence modes of trace elements in the Late Permian coals from Puan Coalfield, Guizhou Province. Journel of Fuel Chemistry Technology, 34(2), 129. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang, J. (2008). The 6# coal of Heidaigou from Junger Coalfield in inner Mongolia: The action of trace elements separation in the Coal Facies. Journel of Fuel Chemistry Technology, 36, 646–652. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang, J., Deng, J., Li, L., Wang, X., & Liu, Z. (2008a). Organic residual hydrocarbon-inorganic mineral affinity of trace elements and their influence on coal-formed hydrocarbon. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 29(2), 235. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang, J., & Li, L. (2007). A preliminary study on the correlations among major elements, trace elements, and parameters of coal hydrocarbon-generation in low rank coal. Journel of Fuel Chemistry Technology, 35(1), 10. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang, L., Liu, C., & Li, H. (2008b). Geochemistry of trace elements and rare earth elements of coal in Chenjiashan coal mine. Coal Geology and Exploration, 2, 002. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang, J., Ren, D., & Zhao, L. (2005). Relationship between sporopollen and major trace elements in the low-rank coals. Coal Geology and Exploration, 33, 4. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yanofsky, N. N., Nierenberg, D., & Turco, J. H. (1991). Acute short-term memory loss from trimethyltin exposure. The Journal of emergency Medicine, 9(3), 137–139.
Yao, D. (2003). Abundance and distribution of trace elements in the coals and burnt products from Yunnan–Guizhou–Sichuan area. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yao, D., Zhi, X., Wang, X., & Zheng, B. (2004). Study on the effect of kaolin on the emission of trace elements during staged 2 combustion of coal. Acta Science Circumstantiae, 24, 210–214. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yudovich, Y. E., & Ketris, M. (2005). Arsenic in coal: A review. International Journal of Coal Geology, 61(3), 141–196.
Zeng, R., Zhao, J., & Zhuang, X. (1998). Quality of Late Permian coal and its controlling factors in Shuicheng mining district of Liupanshui area, Guizhou. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 14(4), 549–558. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zeng, R., Zhuang, X., Koukouzas, N., & Xu, W. (2005). Characterization of trace elements in sulphur-rich Late Permian coals in the Heshan coal field, Guangxi, South China. International Journal of Coal Geology, 61(1), 87–95.
Zeng, R., Zhuang, X., & Yang, S. (2000). Qualitative features of coal in centre of western Shandong coalbearing area. Coal Geology of China, 12, 6–15. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhao, J., & Huang, W. (2002). Abundance of trace elements in Chinese coals. Chinese Coal Geology, 14(B07), 5–13. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhao, J., Tang, X., & Huang, W. (2002). Abundance of trace elements in coal of China. Coal Geology of China, 14(7), 5–13. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zheng, L., Liu, G., & Chou, C.-L. (2007). The distribution, occurrence and environmental effect of mercury in Chinese coals. Science of the Total Environment, 384(1), 374–383.
Zhou, C., Liu, G., Yan, Z., Fang, T., & Wang, R. (2012). Transformation behavior of mineral composition and trace elements during coal gangue combustion. Fuel, 97, 644–650.
Zhou, J., Zhuang, X., Alastuey, A., Querol, X., & Li, J. (2010). Geochemistry and mineralogy of coal in the recently explored Zhundong large coal field in the Junggar basin, Xinjiang province, China. International Journal of Coal Geology, 82(1), 51–67.
Zhu, C., & Li, D. (2010). Occurrences of Trace Elements in the No. 2 Coal of the Changhebian Coal Mine, Chongqing, China. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 82, 17. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhuang, X., Gong, J., Wang, Z., Zeng, R., & Xu, R. (2001). Trace elements of the late Permian coal in the Shuicheng and Liupanshui coal fields, Guizhou. Geological Science and Technology Information, 20, 6. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhuang, X., Querol, X., Alastuey, A., Juan, R., Plana, F., Lopez-Soler, A., et al. (2006). Geochemistry and mineralogy of the Cretaceous Wulantuga high-germanium coal deposit in Shengli coal field, Inner Mongolia, Northeastern China. International Journal of Coal Geology, 66(1), 119–136.
Zhuang, X., Querol, X., Alastuey, A., Plana, F., Moreno, N., Andrés, J., et al. (2007). Mineralogy and geochemistry of the coals from the Chongqing and Southeast Hubei coal mining districts, South China. International Journal of Coal Geology, 71(2), 263–275.
Zhuang, X., Querol, X., Plana, F., Alastuey, A., Lopez-Soler, A., & Wang, H. (2003). Determination of elemental affinities by density fractionation of bulk coal samples from the Chongqing coal district, Southwestern China. International Journal of Coal Geology, 55(2), 103–115.
Zhuang, X., Querol, X., Zeng, R., Xu, W., Alastuey, A., Lopez-Soler, A., et al. (2000). Mineralogy and geochemistry of coal from the Liupanshui mining district, Guizhou, south China. International Journal of Coal Geology, 45(1), 21–37.
Zhuang, X., Su, S., Xiao, M., Li, J., Alastuey, A., & Querol, X. (2012). Mineralogy and geochemistry of the Late Permian coals in the Huayingshan coal-bearing area, Sichuan Province, China. International Journal of Coal Geology, 94, 271–282.
Zhuang, X., Xiang, C., Zeng, R., & Xu, W. (1999a). Comparative studies of trace elements in coals from three different types of basins. Acta Petrrologica et Mineralogica, 3, 007. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhuang, X., Yang, S., & Zeng, R. (1999b). Characteristics of trace elements in coals from several main coal districts in China. Geological Science and Technology Information, 18(3), 63–66. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhuang, X., Zeng, R., & Xu, W. (1998). Trace elements in 9 coal from Antaibao open pit mine, Pingshuo, Shanxi Province. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 23(6). (in Chinese with English abstract).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, 2014CB238900), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 41173032 and 41373110). We acknowledge editors and reviewers for polishing the language of the paper and for in-depth discussion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, Q., Liu, G., Sun, R. et al. Geochemistry of tin (Sn) in Chinese coals. Environ Geochem Health 38, 1–23 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-015-9686-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-015-9686-z