Abstract
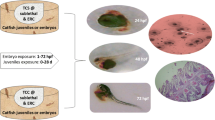
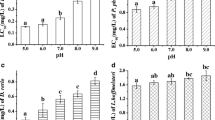
The presence of emerging pollutants in the environment is of major concern not only because of the potential negative impact in human health, but also due to the potential toxicity to non-target organisms. Within the personal and care products (PCPs), the disinfectant Triclosan (TCS) is one of the most concerning compounds. Once in the wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs), a small part of TCS can be biotransformed into a more persistent by-product: methyl-triclosan (M-TCS). Although several studies have focused on the occurrence of this compound in the water systems, the information on its toxicity to aquatic organisms is very limited. Here, we used embryo bioassays with two aquatic model animals to improve risk assessment of M-TCS; zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryo bioassays run up to 144 h post fertilization (hpf) and sea urchin (Paracentrotus lividus) up to 48 hpf, following established protocols. M-TCS and TCS exhibited similar toxicity to zebrafish with a NOEC of 160 µg/L. In contrast, M-TCS induced a delay in the development of the sea urchin larvae at all tested concentrations (1–1000 µg/L), whereas NOEC of TCS for P. lividus embryos was 40 µg/L. Overall, given the reported effects of M-TCS in the close range of environmentally relevant concentrations, and considering the low degradation rate and tendency to bioaccumulation (logKow: 5.2), further studies are warrant to better characterize the risk of this TCS metabolite to aquatic organisms.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agüera A, Fernández-Alba AR, Piedra L, Mézcua M, Gómez MJ (2003) Evaluation of triclosan and biphenylol in marine sediments and urban wastewaters by pressurized liquid extraction and solid phase extraction followed by gas chromatography mass spectrometry and liquid chromatography mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 480(2):193–205
Ajao C, Andersson MA, Teplova VV, Nagy S, Gahmberg CG, Andersson LC, Hautaniemi M, Kalasi K, Roivainen M, Salkinoja-Salonen M (2015) Mitochondrial toxicity of triclosan on mammalian cells. Toxicol Rep 2:624–637
Aranami K, Readman JW (2007) Photolytic degradation of triclosan in freshwater and seawater. Chemosphere 66(6):1052–1056
Balmer ME, Poiger T, Droz C, Romanin K, Bergqvist PA, Müller MD, Buser HR (2004) Occurrence of methyl triclosan, a transformation product of the bactericide triclosan, in fish from various lakes in Switzerland. Environ Sci Technol 38(2):390–395
Bätscher R (2006a) Methyl-triclosan: acute toxicity to Daphnia magna in a 48-h immobilization test. Environmental Chemistry & Pharmanalytics, RCC Ltd., Itlingen, Switzerland
Bätscher R (2006b) Methyl-triclosan: toxicity to Scenedesmus subspicatus in a 72-hour algal growth inhibition test. Environmental Chemistry & Pharmanalytics, RCC Ltd., Itlingen, Switzerland
Bedoux G, Roig B, Thomas O, Dupont V, Le Bot B (2012) Occurrence and toxicity of antimicrobial triclosan and by-products in the environment. Environ Sci Tech Pollut Res 19(4):1044–1065
Bellas J, Beiras R, Mariño-Balsa JC, Fernández N (2005) Toxicity of organic compounds to marine invertebrate embryos and larvae: a comparison between the sea urchin embryogenesis bioassay and alternative test species. Ecotoxicology 14(3):337–353
Boehmer W, Ruedel H, Wenzel A, Schroeter-Kermani C (2004) Retrospective monitoring of triclosan and methyl-triclosan in fish: results from the German environmental specimen bank. Organohalogen Compd 66:1516–1521
Brausch JM, Rand GM (2011) A review of personal care products in the aquatic environment: environmental concentrations and toxicity. Chemosphere 82(11):1518–1532
Castro LFC, Santos MM (2014) To bind or not to bind: the taxonomic scope of nuclear receptor mediated endocrine disruption in invertebrate phyla. Environ Sci Technol 48(10):5361–5363
Cherednichenko G, Zhang R, Bannister RA, Timofeyev V, Li N, Fritsch EB (2012) Triclosan impairs excitation–contraction coupling and Ca2+ dynamics in striated muscle. P Natl Acad Sci 109(35):14158–14163
Dann AB, Hontela A (2011) Triclosan: environmental exposure, toxicity and mechanisms of action. J Appl Toxicol 31(4):285
Farré M, Asperger D, Kantiani L, González S, Petrovic M, Barceló D (2008) Assessment of the acute toxicity of triclosan and methyl triclosan in wastewater based on the bioluminescence inhibition of Vibrio fischeri. Anal Bioanal Chem 390(8):1999–2007
Franz S, Altenburger R, Heilmeier H, Schmitt-Jansen M (2008) What contributes to the sensitivity of microalgae to triclosan? Aquat Toxicol 90(2):102–108
Gaume B, Bourgougnon N, Auzoux-Bordenave S, Roig B, Le Bot B, Bedoux G (2012) In vitro effects of triclosan and methyl-triclosan on the marine gastropod Haliotis tuberculata. Comp Biochem Phys C 156(2):87–94
Heath RJ, Rock CO (2000) Microbiology: a triclosan-resistant bacterial enzyme. Nature 406(6792):145–146
Heidler J, Halden RU (2007) Mass balance assessment of triclosan removal during conventional sewage treatment. Chemosphere 66:362–369
Hwang J, Suh SS, Park SY, Ryu TK, Lee S, Lee TK (2014) Effects of triclosan on reproductive parameters and embryonic development of sea urchin, Strongylocentrotus nudus. Ecotox Environ Safe 100:148–152
Kapoor M, Reddy CC, Krishnasastry MV, Surolia N, Surolia A (2004) Slow-tight-binding inhibition of enoyl-acyl carrier protein reductase from Plasmodium falciparum by triclosan. Biochem J 381(3):719–724
Lammer E, Carr GJ, Wendler K, Rawlings JM, Belanger SE, Braunbeck T (2009) Is the fidh embryo toxicity test (FET) with zebrafish (Danio rerio) a potential alternative for the fish acute toxicity test? Comp Biochem Physiol C, Comp Pharmacol Toxicol 149:196–209
Lyndall J, Fuchsman P, Bock M, Barber T, Lauren D, Leigh K et al. (2010) Probabilistic risk evaluation for triclosan in surface water, sediments, and aquatic biota tissues. Integr Environ Assess Manag 6(3):419–440
Oliveira R, Domingues I, Grisolia CK, Soares AM (2009) Effects of triclosan on zebrafish early-life stages and adults. Environ Sci Tech Pollut Res 16(6):679–688
Orvos DR, Versteeg DJ, Inauen J, Capdevielle M, Rothenstein A, Cunningham V (2002) Aquatic toxicity of triclosan. Environ Toxicol Chem 21(7):1338–1349
Petrie B, Barden R, Kasprzyk-Hordern B (2015) A review on emerging contaminants in wastewaters and the environment: current knowledge, understudied areas and recommendations for future monitoring. Water Res 72:3–27
Pintado-Herrera MG, González-Mazo E, Lara-Martín PA (2014) Determining the distribution of triclosan and methyl triclosan in estuarine settings. Chemosphere 95:478–485
Ramaswamy BR, Shanmugam G, Velu G, Rengarajan B, Larsson DJ (2011) GC–MS analysis and ecotoxicological risk assessment of triclosan, carbamazepine and parabens in Indian rivers. J Hazard Mater 186(2):1586–1593
Reiss R, Mackay N, Habig C, Griffin J (2002) An ecological risk assessment for triclosan in lotic systems following discharge from wastewater treatment plants in the United States. Environ Toxicol Chem 21:2483–2492
Ribeiro S, Torres T, Martins R, Santos MM (2015) Toxicity screening of diclofenac, propranolol, sertraline and simvastatin using Danio rerio and Paracentrotus lividus embryo bioassays. Ecotox Environ Safe 114:67–74
Rodrigues P, Reis-Henriques MA, Campos J, Santos MM (2006) Urogenital papilla feminization in male Pomatoschistus minutus from two estuaries in northwestern Iberian Peninsula. Mar Environ Res 62(1):S258–S262
Rüdel H, Böhmer W, Müller M, Fliedner A, Ricking M, Teubner D, Schröter-Kermani C (2013) Retrospective study of triclosan and methyl-triclosan residues in fish and suspended particulate matter: results from the German environmental specimen bank. Chemosphere 91(11):1517–1524
Santos MM, Ruivo R, Lopes-Marques M, Torres T, Carmen B, Castro LFC, Neuparth T (2016) Statins: an undesirable class of aquatic contaminants? Aquat Toxicol 174:1–9
Schmidt S, Braun P, Crouse M, Dean A, DuPre E and Palenske N (2013) Triclosan effects on zebrafish heart rate. Proceedings of The National Conference On Undergraduate Research (NCUR) 2013 University of Wisconsin La Crosse, 604–610.
Soares J, Coimbra AM, Reis-Henriques MA, Monteiro NM, Vieira MN, Oliveira JMA et al. (2009) Disruption of zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryonic development after full life-cycle parental exposure to low levels of ethinylestradiol. Aquat Toxicol 95(4):330–338
Suller MTE, Russell AD (2000) Triclosan and antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. J Antimicrob Chemoth 46(1):11–18
Villa S, Vighi M, Finizio A (2014) Experimental and predicted acute toxicity of antibacterial compounds and their mixtures using the luminescent bacterium Vibrio fischeri. Chemosphere 108:239–244
Acknowledgements
This paper was developed under the project INNOVMAR—Innovation and Sustainability in the Management and Exploitation of Marine Resources (reference NORTE-01-0145-FEDER-000035), with- in Research Line ECOSERVICES—Assessing the environmental quality, vulnerability and risks for the sustainable management of NW coast natural resources and ecosystem services, supported by North Portugal Regional Operational Programme (NORTE 2020), under the PORTUGAL 2020 Partnership Agreement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All Authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Macedo, S., Torres, T. & Santos, M.M. Methyl-triclosan and triclosan impact embryonic development of Danio rerio and Paracentrotus lividus . Ecotoxicology 26, 482–489 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-017-1778-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-017-1778-3