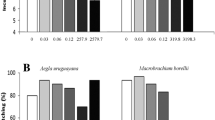
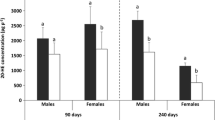
Abstract
Gammarus fossarum is an important test organism which is currently used as a bio-indicator as well as in ecotoxicological tests. Nevertheless, data on ecdysteroids in endocrine toxicity test are not yet available for these species, despite its crucial role in molting and reproduction. In the present paper, ecdysteroids concentrations were studied during the molt cycle (in females) and embryonic development in G. fossarum (Crustacea, Amphipoda) in order to propose an ecdysteroids toxicity test. Ecdysteroids levels in G. fossarum showed a single peak during premolt at stage Dl-D2. In embryos, ecdysteroids levels progressively increased over stages 3 and 4, with peak levels at stage 4. A Cadmium toxicity test was proposed to examine if the molting and embryogenesis disturbances previously observed after cadmium exposure (Geffard et al. 2010) could be attributed to changes in ecdysteroids titers. Exposure to the different cadmium concentrations (3; 9; 300; 900 µg/l) increased ecdysteroids secretion by Y-organs in vitro, but it had no significant effect on exposed embryos (in vivo). Based on previous findings, we are led to conclude that the molting impairments in cadmium-exposed females of G. fossarum is connected to the changes in ecdysteroids concentrations.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abigail P, Moreno R, Medesani DA, Rodriguez EM (2003) Inhibition of molting by cadmium in the crab Chasmagnathus granulate (Decapoda Brachyura). Aquat Toxicol 64:155–164
Baldaia L, Porcheron P, Coimbra J, Cassier P (1984) Ecdysteroids in the shrimp Palaemon serratus: relations with the molt cycle. Gen Comp Endocrinol 55:437–443
Blanchet MF, Porcheron P, Dray F (1976) Variations in the level of ecdysones during the intermolt of male Orchestia gammarellus Pallas (Crustacea, Amphipoda) by radioimmunoassay. C.R Seances Acad Sci D 283:651–654
Bodar CWM, Voogt PA, Zandee DI (1990) Ecdysteroids in Daphnia magna: their role in moulting and reproduction and their levels upon exposure to cadmium. Aquat Toxicol 17:339–350
Chang ES, Mykles D (2011) Regulation of crustacean molting: a review and our perspectives. Gen Comp Endocrinol 172:323–330
Chang ES, Hertz WA, Prestwich GD (1992) Reproductive endocrinology of the shrimp Sicyonia ingentis, steroids, peptide and terpenoid hormones. NOAA Tech Rep NMFS 106:1–6
Chávez V, Marqués G, Delbecque J, Kobayashi K, Hollingsworth M, Burr J, Natzle J, O’Connor M (2000) The drosophila disembodied gene controls late embryonic morphogenesis and codes for a cytochrome P450 enzyme that regulates embryonic ecdysone levels. Development 127:4115–4126
Correia AD, Sousa A, Costa MH, Moura I, Livingstone DR (2004) Quantification of metallothionein in whole body Gammarus locusta (crustacea: amphipoda) using differential pulse polarography. Toxicol Environ Chem 86(1):23–36
Cuzin-Roudy J, Strambi C, Strambi A, Delbecque JP (1989) Hemolymph ecdysteroids and molt cycle in males and females of Siriella armata M-Edw. (Crustacea: Mysidacea): possible control by the MI-ME X-organ of the eyestalk. Gen Comp Endocrinol 74:96–109
Engel DW, Brouwer M (1987) Metal regulation and molting in the blue crab, Callinectes sapidus: metallothionein function in metal metabolism. Biol Bull 173:339–351
Fingerman M (1987) The endocrine mechanisms of crustaceans. Crustac Biol 7:1–24
Geffard O, Xuereb B, Chaumot A, Geffard A, Biagianti S, Noel C, Abbaci K, Garric J, Charmantier G, Charmantier-Daures M (2010) Ovarian cycle and embryonic development in Gammarus fossarum: application for reproductive toxicity assessment. Environ Toxicol Chem 29:2249–2259
Girard P, Maissiat R (1983) Variations du taux des ecdysteroides hemolymphatiques chez le male de Ligia oceanica (L.) (Cmstacea, Isopoda, Oniscoidea) en fonction du cycle de mue et des modifications structurales de l’organe Y. Can J Zool 61:534–538
Graf F, Delbecque JP (1987) Ecdysteroid titerduring the molt cycle of Orchestia cavimana (Crustacea, Amphipoda). Gen Comp Endocrinol 61:22–32
Hagedorn HH (1985) The role of ecdysteroids in reproduction. In: Kerkut GA, Gilbert LI (eds) Comprehensive insect physiology, biochemistry and pharmacology. Pergamon, Oxford, pp 205–262
Hoffmann J, Lagueux M (1985) Endocrine aspects of embryonic development in insects. In: Kerkut GA, Gilbert LI (eds) Comprehensive insect physiology, biochemistry, and pharmacology. Pergamon, Oxford
Hopkins P (1983) Patterns of serum ecdysteroids during induced and uninduced proecdysis in the fiddler crab, Uca pugilator. Gen Comp Endocrinol 52:350–356
Hyne R (2011) Review of the reproductive biology of amphipods and their endocrine regulation: identification of mechanistic pathways for reproductive toxicants. Environ Toxicol Chem 30:2647–2657
Jegla TC, Ruland C, Kegel G, Keller R (1983) The role of the Y-organ and cephalic gland in ecdysteroids production and the control of molting in the crayfish, Orconectes limosus. Comp Physiol 152:91–95
Kast-Hutcheson K, Rider CV, LeBlanc GA (2001) The fungicide propiconazole interferes with embryonic development of the crustacean Daphnia magna. Environ Toxicol 20:502–509
Kobayashi M, Uchida M, Kuriyama K (1989) Evaluation of 20-hydroxyecdysone level by buprofezin inNilaparvata lugens Stal nymphs. Pestic Biochem Physiol 34:9–16
Lafont R (2000) Understanding insect endocrine systems: molecular approaches. Entomol Exp Appl 97(2):123–136
Lafont R, Dauphin-Villemant C, Warren J, Rees HH (2005) Ecdysteroid chemistry and biochemistry. In: Gilbert LI, Iatrou K, Gill SS (eds) Comprehensive molecular insect science, vol 3. Elsevier Press, Oxford, UK, pp 125–196
Lagueux M, Hoffmann JA, Goltzené F, Kappler C, Tsoupras G, Hetru C, Luu B (1984) Ecdysteroids in ovaries and embryos of Locusta migratoria. In: Hoffmann JA, Porchet M (eds) Biosynthesis, metabolism and mode of action of invertebrate hormones. Springer, Berlin, pp 168–180
LeBlanc GA (2007) Crustacean endocrine toxicology: a review. Ecotoxicol 16:61–81
LeBlanc GA, Campbell PM, den Besten P, Brown RP, Chang E, Coats J, deFur PL, Dhaldialla T, Edwards J, Riddiford L, Simpson MG, Snell TW, Thorndyke M, Matsumura F (1999) The endocrinology of invertebrates. In: deFur PL, Crane M, Ingersoll C, Tattersfield L (eds) Endocrine disruption in invertebrates: endocrinology, testing, and assessment. SETAC Press, Pensacola, FL, pp 23–106
Maniere G, Rondot I, Bullesbach E, Gautron F, Vanhems E, Delbecque J (2004) Control of ovarian steroidogenesis by insulin-like peptides in the blowfly (Phormia regina). Endocrinology 181:147–156
Mondy N, Corio-Costet M-F (2000) Response to dietary phytopathogenic fungus (Botrytis cinerea) in grape berry moth (Lobesia botrana): the significance of fungus sterols. Insect Physiol 46:1557–1564
Mu X, Le Blanc G (2004) Synergistic interaction of endocrine disrupting chemicals: model development using an ecdysone receptor antagonist and a hormone synthesis inhibitor. Environ Toxicol Chem 23:1085–1091
Mu X, Leblanc GA (2002) Environmental antiecdysteroids alter embryo development in the crustacean Daphnia magna. J Exp Zool 292(3):287–292
OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development) (2012) Guidance document on standardised test guidelines for evaluating chemicals for endocrine disruption. ENV/JM/MONO (2012) 23 Environment, Health and Safety Publications Series on Testing and Assessment (150), vol 22. OECD, Paris
Okumura T, Han CH, Suzuki Y, Aida K, Hanyu I (1992) Changes in hemolymph vitellogenin and ecdysteroids levels during the reproductive and non reproductive cycles in the freshwater Prawn macrobrachium nipponense. Zool Sci 9:37–45
Rees HH, Isaac RE (1984) Biosynthesis of ovarian ecdysteroid phosphates and their metabolic fate during embryogenesis in Schistocerca gregaria. In: Hoffmann JA, Porchet M (eds) Biosynthesis, metabolism and mode of action of invertebrate hormones. Springer, Berlin, pp 181–195
Rodríguez EM, Medesani DA, Fingerman M (2007) Endocrine disruption in crustaceans due to pollutants: a review. Comp Biochem Physiol 146:661–671
Sangalang GB, Freeman HC (1974) Effects of sublethal Cadmium on maturation and testosterone and 11-ketotestosterone production in vivo in Brook Trout. Biol Reprod 11:429–435
Shurin JB, Dodson SI (1997) Sublethal toxic effects of cyanobacteria and nonylphenol on environmental sex determination and development in Daphnia. Environ Toxicol Chem 16:1269–1276
Soin T, Iga M, Swevers L, Rouge P, Janssen CR, Smagghe G (2009) Towards Coleoptera-specific high-throughput screening systems for compounds with ecdysone activity: development of EcR reporter assays using weevil (Anthonomus grandis) derived cell lines and in silico analysis of ligand binding to A. grandis EcR ligand-binding pocket. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 39:523–534
Spindler KD, Van Wormhoudt A, Sellos D, Spindler-Barth M (1987) Ecdysteroids levels during embryogenesis in the shrimp, Palaemon serratus (Crustacea Decapoda): quantitative and qualitative changes. Gen Comp Endocrinol 66:116–122
Stevenson J, Armstrong P, Chang J, O’Connor E (1979) Ecdysone titers during the molt cycle of the crayfish Orconectes sanborni. Gen Comp Endocrinol 39:20–25
Subramoniam T (2000) Crustacean ecdysteriods in reproduction and embryogenesis. Comp Biochem Physiol C 125:135–156
Thompson JJ, Houk RS (1987) A study of internal standardization in inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. Appl Spectrosc 41:801
Toullec J-Y (1999) Crustacean primary cell culture: a technical approach. Methods Cell Sci 21:193–198
Vight DA, Fingerman M (1985) Molt staging in the fiddler crab Uca pugilator. J Crustac Biol 5:386–396
Voogt PA, Den Besten PJ, Kusters GC, Messing MW (1987) Effects of cadmium and zinc on steroid metabolism and steroid level in the sea star Asterias rubens. Comp Biochem Physiol C 86:83–89
Williams D, Fisher M, Rees H (2000) Characterization of ecdysteroid 26-hydroxylase: an enzyme involved in molting hormone inactivation. Arch Biochem Biophys 376:389–398
Willig A, Keller R (1973) Molting hormone content, cuticle growth and gastrolith growth in the molt cycle of the crayfish Orconectes limosus. Comp Physiol 86:377–388
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Dr. JP. Delbecque (University of Bordeaux) for giving antibodies and Dr René Lafont for provid-ing very helpful comments on revision of this manuscript. We received financial support from Irstea LYON: Milieux aquatiques, Ecologie et pollutions. Equipe Ecotox Villeurbanne France.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abidi, S., Abbaci, K.T., Geffard, O. et al. Impact of cadmium on the ecdysteroids production in Gammarus fossarum . Ecotoxicology 25, 880–887 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-016-1645-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-016-1645-7